Background
Adrenocortical carcinoma is a rare malignancy. In children, it accounts for 0.6% of tumours and 0.2% of malignancies. It accounts for 5% of all adrenocortical tumours [1, 2, 3]. The purpose of this article is to present the case of a 10-year-old female patient with symptoms of hypercortisolaemia and androgenization, who was diagnosed with ACC.
Case presentation
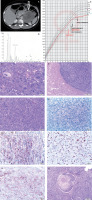
A 10-year-old girl, previously developing normally, was admitted to the Endocrinology Department because of symptoms of hypercortisolaemia and androgenization that had been present for about 5 months. Family history included ovarian cancer on the mother’s side. On admission, she was found to have excess body weight (BMI 23 kg/m2), hirsutism (10 points on the Ferriman-Gallwey scale), acne, buffalo hump, excessive body fat, depressed mood, and apathy. Signs of puberty on the Tanner scale: thelarche II, pubarche III, and axillarche II. Tests revealed abnormal circadian rhythm of cortisol, elevated serum androgen levels, decreased ACTH (Table I), impaired glucose tolerance in OGTT, and normal lipids. The result of the steroid profile in the 24-hour urine collection suggested an adrenocortical tumour producing excess cortisol and androgens (Table I, Fig. 1B). Computed tomography (CT) scan of the abdomen revealed a heterogeneous tumour of the left adrenal gland 96 × 73 × 86 mm. The density in the pre-contrast agent phase was 39 jH, in the venous phase 53 jH, and in the late phase 66 jH (Fig. 1A). A left adrenalectomy (laparotomy) was performed. Macroscopically, a tumour of the left adrenal gland was found, covered by a capsule damaged over 5 cm. Histopathological examination showed: foci of necrosis (Fig. 1E), presence of mitoses (including atypical mitoses) (Fig. 1D), cells with features of nuclear pleomorphism, features of angioinvasion (Fig. 1K) and infiltration of the tumour capsule. Immunohistochemical examination showed positive Melan-A in neoplastic cells (Fig. 1J), negative immunoexpression for chromogranin A (Fig. 1G), synaptophysin (Fig. 1H), and proliferative index Ki67 of about 20% (Fig. 1I). A diagnosis of adrenocortical carcinoma was made (Fig. 1F). The modified Weiss score was 7 points. The patient was qualified for complementary chemotherapy: doxorubicin, etoposide, and cisplatin (for 4 months). The course of the disease was complicated by 3 recurrences (at age of: 11.2; 11.7; 13.7 years). The first recurrence was local (size 45 × 47 × 25 mm), the second was in the mesenteric transverse colon and metastasized in the lower lobe of the right lung (size 7.5 mm), and the third was in the left lung (size 9 mm). Surgical treatment accompanied by chemotherapy (doxorubicin, etoposide, cisplatin, ifosfamide, fluorouracil) was used. At the first recurrence, radiation therapy was also used (5400 cGy to the tumour locus). At the second recurrence, mitotane was included in the treatment under serum level control (for 3 years). During mitotane treatment, the patient required hydrocortisone and levothyroxine substitution. The test result for TP53 gene mutation was negative. The follow-up period is 12 years, with no biochemical or radiological features of recurrence for 8 years. Final height was at the 3rd centile, the normal course of sexual maturation, and menarche at 13 years (Fig. 1C).
Table I
Results of laboratory tests, imaging scans, and treatment at diagnosis – recurrences and at present
[i] ACTH – adrenocorticotropic hormone; DHEAs – dehydroepiandrosterone sulphate; 11-OHAN – 11-hydroxy-androsterone; DHA dehydroepiandrosterone; 5-AND –5 androstendiol; 16a-OHDHA – 16 alfa-hydroxy-DHA; 5-PT – pregnantriol; THS – tetrahydro-11 deoxycortisol; THDOC- tetrahydro-11-deoxycorticosterone; THE – tetrahydro-cortisone; THF – tetrahydro-cortisol; E – free cortisone; F –free cortisol; F/E – free cortisol/free cortisone
Figure 1
A) Computed tomography of the abdominal cavity demonstrating a tumour in the left adrenal cortex (size 96 × 73 × 86 mm).B) Chromatogram of the urinary steroid profile (24 h) at diagnosis suggested an adrenocortical tumour producing excessive delta 5 androgen and cortisol metabolites of the steroid profile in the 24-hour urine collection. C) Patient's percentile grid with marked moments of surgery and recurrences. Final height at the 3rd c. D) Tumour composed of polymorphic cells which have abundant cytoplasm and large nucleus with features of anisokaryosis. Many mitotic figures are present. E) Cells with marked pleomorphism. Atypical mitotic figure is seen in central part. F) Neoplastic necrosis within the tumour area. G) Chromogranin negative stain. H) Synaptophysin positive stain in cytoplasm of neoplastic cells. I) Ki 67 positive stain in more than 20% of neoplastic cells.7. Ki 67 positive stain in more than 20% of neoplastic cells. J) Melan-A positive stain in cytoplasm of neoplastic cells. K) Thrombus composed of fibrin and neoplastic cells inside the lumen of vessel. Neoplastic cells adhere to the vessel wall.
Discussion
We present a case of adrenocortical carcinoma in a 10-year-old female patient, her 12-year follow-up in the Department of Endocrinology from 2010 to 2022, and a review of the literature on the above-mentioned diagnosis.
According to the International Paediatric Adrenocortical Tumour Registry (IPACTR), the median age at diagnosis of ACT is 3.2 years. Less than 15% of patients are older than 13 years at the time of diagnosis. The incidence of ACT is higher among girls than boys, with the overall female/male ratio being 1.6 : 1. However, the ratio ranged from 1.7 : 1 in the 0–3 years group to 6.2 : 1 in adolescents (≥ 13 years) [3].
Symptoms of androgen excess are the most common clinical manifestation of ACC in children, present in 60-80% of cases. They can occur alone or accompanied by clinical manifestations of overproduction of other adrenal cortical hormones, including glucocorticoids (as in the present case), aldosterone, or oestrogens. Overproduction of glucocorticoids alone occurs in 5–8% of patients, is relatively rare in young children, and is more common in adolescents. Primary hyperaldosteronism (Conn syndrome) and pure feminization occur very rarely, i.e. in less than 1% of patients [3].
The diagnosis of ACT is based on laboratory tests, which include serum levels of cortisol daily (i.e. 8:00 a.m. and 00:00 a.m.), ACTH, DHEAs, testosterone, androstenedione, 17-hydroxyprogesterone (17OHP), oestradiol (E2), aldosterone, renin, and steroid profile in daily urine collection. These tests should be performed both when ACT is suspected and as monitoring for possible recurrence. Dexamethasone inhibition tests are also performed. When ACT is found, to exclude pheochromocytoma, testing of serum catecholamines and catecholamines, and their metabolites in the 24-hour urine collection, should be performed. In the present case, laboratory results indicated mixed ACT secreting excess androgens and cortisol (Table I). On the CT scan our patient’s tumour had features of potential malignancy: diameter greater than 5 cm, irregular shape, high densitometry and contrast enhancement, and delayed contrast washout [2, 4].
The diagnosis of ACC is made based on histological examination of surgically obtained tissue. The modified Weiss score is the most commonly used in paediatric practice, which includes criteria such as the presence of 25% or fewer cells with bright cytoplasm, mitotic index > 5/50 HPF, atypical mitoses, necrosis, and infiltration of the tumour capsule. Malignancy is indicated by a score of 3 or more points (the first 2 criteria are scored at 2 points each). In the presented case, the score on the aforementioned scale was the maximum, i.e. 7 points. This score indicated a malignant tumour. An immunohistochemical examination is also important. The Ki-67 expression above 10% indicates a malignant lesion and has the greatest prognostic significance of all stains. Chromogranin A expression in neoplastic cells is of greatest use in differentiating between tumours of cortical and medullary origin; it shows a positive response in 100% of adrenal paraganglioma (pheochromocytoma). Markers typical of adrenocortical tumours are inhibin, Melan-A, and calretinin (they may show a positive reaction also in a small group of pheochromocytoma tumours) [5, 6]. The result of the immunohistochemical examination in our patient indicated a malignant lesion in the adrenal cortex: positive Melan-A neoplastic cells, negative for chromogranin A and synaptophysin, and Ki67 proliferative index of about 20%. The stage of the tumour is most often determined by the ENSAT (European Network for the Study of Adrenal Tumours) classification; our patient had stage IV disease, a tumour with distant metastases.
The most common locations for metastasis of adrenocortical cancer are liver (73%), lungs (69%), and lymph nodes (27%). Therefore, at the time of diagnosis and during follow-up, chest imaging should be performed in addition to abdominal imaging.
The basis of treatment and the most important factor in improving the prognosis is radical surgical treatment. The most common complementary treatment in children is chemotherapy consisting of a combination of cisplatin and doxorubicin with or without etoposide, administered with mitotane. Mitotane is an insecticide derivative that causes necrosis of the adrenal cortex. A response to mitotane is achieved in 15–60% of treated adult patients; in children such data are not known. According to data from the Mayo Clinic, USA between 1950 and 2017, of 41 patients under the age of 21 years, 20 were treated with mitotane: 15 died of the disease, one achieved complete remission, and the results of 4 patients are unknown [7]. Zancanella analysed a group of 11 children aged from 2 to 11 years, of whom 10 had confirmed TP53 gene mutation; complete remission was achieved in 2 patients [8].
Mitotane treatment can cause several side effects (usually with toxic levels of the drug in the blood, i.e. > 20 mg/l), as can be observed in the case of our patient. These include a state of functional adrenal insufficiency which requires steroid hormone substitution. Hypothyroidism can also result, requiring treatment with levothyroxine preparation. Another important disadvantage of mitotane treatment is that it significantly alters the metabolism of steroid hormones, and tests of serum androgens and their metabolites in urinary steroid profile cannot be used as markers of tumour recurrence. This can be seen in the case of the third recurrence in our patient (Table I). Of the patient’s other side effects, gastrointestinal disorders and paraesthesia were also observed (Fig. 1C).
In the present case, there are many adverse prognostic factors in addition to those previously mentioned: radiological, histopathological and immunohistochemical, age at diagnosis > 4 years, tumour producing excess glucocorticoids and stage IV disease. A germline mutation of the TP53 gene is also an important factor for a worse prognosis. Most patients with Li-Fraumeni syndrome (about 80%), a rare autosomal dominantly inherited cancer predisposition syndrome, have it. This mutation is found in 50-60% of young children with ACT [3]. The result of the aforementioned test in our patient was negative.
According to IPACTR data, the survival rate at 2 years and 5 months of follow-up was 61.8%, and the 5-year estimated survival time was 54.7% [8]. According to data presented in the SEER (Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results) program established by the National Cancer Institute in the US, the overall 5-year survival rate for patients less than 4 years old was 91.1%. This rate decreases significantly for the group of patients aged 5–19 years and is 29.8% [3, 7, 9].
Based on the presented case, we can see how important it is for patients with ACC to perform frequent follow-up examinations. This allows for faster diagnosis of disease recurrence, the inclusion of appropriate treatment, and improvement of prognosis.

 POLSKI
POLSKI






