Introduction
Childhood obesity is a growing public health problem worldwide, associated with adverse effects in the form of metabolic syndrome (MetS). MetS includes visceral obesity, elevated fasting glucose, triglycerides (TG), and blood pressure levels, and reduced high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL). In previous years, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) was a disease closely associated with MetS [1, 2]. Given the growing number of studies linking the occurrence of metabolic abnormalities in patients with NAFLD, an expert group proposed to redefine NAFLD as metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD). The MAFLD criteria in children are based on an invasive or non-invasive diagnosis of fatty liver in combination with visceral obesity or high fasting blood glucose/type 2 diabetes or the presence of at least two metabolic risk factors in lean patients [3].
NAFLD/MAFLD is the most frequently observed chronic liver disease in children. Most of the published studies concern the prevalence of NAFLD in children and adolescents. One study reported a steady increase in the incidence of fatty liver from 19.34 million in 1990 to 29.49 million in 2017 among children and adolescents [4]. So far, several studies evaluating the incidence of MAFLD among children have been published, which show a rising incidence of this disease among adolescents [5, 6]. It is also worth noting that fatty liver can lead to more severe non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and cirrhosis with all its consequences, e.g. increased risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and end-stage liver disease [3]. Given the prevalence and life-threatening consequences of MAFLD, it is important to search for non-invasive biomarkers of the disease and its severity. Considering the change in definition, it is also worth mentioning that the group of paediatric patients with NAFLD and MAFLD are not identical. According to Xing et al., almost 20% of children diagnosed with NAFLD do not have MAFLD [7]. Therefore, the results obtained previously should be treated with caution, and children diagnosed with MAFLD according to the latest criteria should be included in newly published reports.
The progression of MAFLD from simple steatosis to NASH and fibrosis is connected with liver damage resulting from lipotoxicity, oxidative stress, redox imbalance, inflammation and apoptosis [8]. During apoptosis of liver cells, keratin-18 (CK18), the major intermediate fibrillar protein in hepatocytes, is cleaved by activated caspases [9]. Apoptotic cleavage of CK18 exposes two epitopes, M30 (a marker of apoptosis) and M65 (a marker of overall cell death), which can be measured in serum and indicate the intensity of the process [10]. Agiopoietin-2 (Ang2) is a growth factor mediated through Tie-1 and Tie-2 tyrosine kinase receptor signalling pathways. The biological activity of Ang2 is complex and depends on several factors. The physiological functions of Ang2 are related to embryonic development, vascular homeostatic reactions and permeability [11]. In the disease state, Ang2 has been implicated as a promotor of cell death, vascular regression or inflammation [11, 12]. Circulating levels of M30 and Ang2 have been evaluated as good biomarkers for severity of NAFLD, mainly in adult patients [13–17].
Aim
The aim of this study was to assess serum concentrations of M30 and Ang2 in obese children and adolescents and to determine the association of these parameters with paediatric MAFLD.
Material and methods
The prospective study included 76 consecutive overweight (defined as a body mass index (BMI) at or above the 85th percentile and below the 95th percentile)/obese (defined as a BMI at or above the 95th percentile) paediatric patients diagnosed in our department due to suspected liver disease based on physical examination (hepatomegaly), or elevated alanine aminotransferase (ALT) activity or liver hyperechogenicity in abdominal ultrasonography (USG). The control group included 57 children without any somatic organ pathology and a normal BMI matched for sex and age. The control group presented with normal activity of liver enzymes and normal liver on USG. BMI was calculated by dividing weight in kilograms by the square of height in meters (kg/m2). The percentile values of BMI were taken from a study by Kułaga et al. [18]. The waist-to-hip ratio (WHR) was measured as waist circumference (WC) divided by hip circumference (HC). There is a lack of universal calculators of WC percentile values in relation to age and sex in children and adolescents. Based on a recently published article [19], all children in the study group had WC ≥ 90th percentile. A body fat analyser (Tanita, Tokyo, Japan) was used to determine body composition by bioelectrical impedance. The following data were obtained: body fat percentage (fat %), fat mass, fat-free mass (FFM), muscle mass and total body water mass (TBW) and percentage (TBW%). The diagnosis of MAFLD was established according to the previously mentioned criteria [3]. The exclusion criteria from the study group were: a history of any concomitant chronic disease, acute infection and taking medications that affect lipid or carbohydrate metabolism or alcohol consumption. Viral hepatitis, selected metabolic liver diseases (Wilson’s disease, α1-antitrypsin deficiency), cystic fibrosis, celiac disease, autoimmune hepatitis and toxic conditions were excluded in all participants.
All patients in our study had a blood sample taken at the time of admission after a 10-hour fast. All sera were immediately frozen and stored at –80°C until use. Routine biochemical measurements, including total blood count, ALT, aspartate aminotransferase (AST), γ-glutamyltransferase (GGT), bilirubin, total cholesterol, HDL-C and low-density lipoprotein (LDL-C) cholesterol, TG, uric acid, glucose and insulin were conducted using standard methods. Homeostasis model assessment score [HOMA-IR = (fasting insulin (mIU/l) × fasting glucose (mmol/l))/22.5)] was calculated to estimate insulin resistance. Serum Ang2 and M30 levels were quantitatively measured using ELISA kits (ELISA Kit for Angiopoietin 2, Cloude-Clone Corp., Katy, the United State of America; M30 Apoptosense ELISA kits Peviva, Bromma, Sweden). All assays were conducted according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The liver steatosis was diagnosed in abdominal ultrasonography. The degree of hepatic steatosis was assessed using a four-grade scale (0–3) according to Saverymuttu et al. [20]. Carotid ultrasonography examinations were performed to evaluate carotid intima-media thickness (IMT).
The protocol was approved by the Bioethics Committee of the Medical University of Bialystok prior to patient recruitment, and the study is in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki (approval number: APK.002.70.2023). Informed consent was obtained from all the patients’ parents and patients aged ≥ 16 years old.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using IBM SPSS Statistics version 27.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY). The quantitative data were shown as median and quartiles (Q1–Q3). The qualitative variables were presented as absolute frequency and percentage. The significance of the difference between subgroups was evaluated with the non-parametric Mann–Whitney U-test for quantitative data and the χ2 test for categorical variables. Spearman’s correlation test was used to analyse the correlations between variables. Receiver operating characteristics (ROC) analysis was performed to calculate the power of selected parameters to detect MAFLD in obese children. Areas under the curve (AUCs) were compared using statistical tests against the value of 0.5, representing the diagonal line of no information in the ROC plot. All statistical hypotheses were considered as statistically significant for p < 0.05.
Results
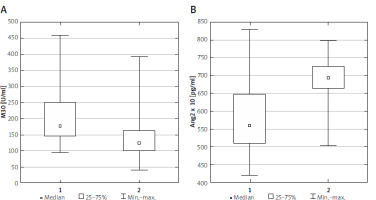
Patients from the study group presented significantly different concentrations of M30 and Ang2 compared to the control group (p < 0.001, p < 0.001, Figure 1). General details in the analysed groups are listed in Supplementary Table SI. In the next stage of the study, overweight/obese children with liver steatosis in ultrasound were assigned to the MAFLD group, and children without liver steatosis in ultrasound were assigned to the non-MAFLD subgroup. Liver steatosis was diagnosed in abdominal ultrasound in 45 obese patients (59.2%). Among all participants with MAFLD, 25 children had mild liver steatosis in ultrasound (stage 1) and 20 children developed more advanced liver steatosis (stages 2 and 3) according to the Saverymuttu scale. Children with MAFLD had elevated levels of ALT, AST, GGT, uric acid and M30 in comparison to non-MAFLD children. The only anthropometric parameter significantly different between the two groups was WHR. The clinical and laboratory characteristics of children included in the study are summarized in Table I.
Table I
Characteristics of the study group divided according to the MAFLD diagnosis
[i] ALT – alanine aminotransferase, AST – aspartate aminotransferase, GGT – γ-glutamyltransferase, HDL-C – high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, LDL-C – low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, TG – triglycerides, HOMA-IR – homeostasis model assessment score, Ang2 – agiopoietin-2, M30 – cytokeratin-18 fragments, IMT – carotid intima-media thickness, BMI – body mass index, WHR – waist-to-hip ratio, fat % – body fat percentage, FFM – fat-free mass, TBW – total body water mass, TBW% – percentage total body water mass.
Figure 1
Serum M30 (A) and Ang2 (B) concentrations in study (1) and control (2) groups. Statistical analysis by Mann-Whitney U test. The minimum, maximum and median values of M30 and Ang2 are shown
In the next stage of the study, we assessed the differences in individual parameters, including apoptosis markers, depending on the degree of hepatic steatosis in USG. We did not observe any significant differences between the two groups (Supplementary Table SII).
The correlations between studied markers and Ang2, M30 and stage of liver steatosis in ultrasound are presented in Table II. Interestingly, M30 positively correlated with some biochemical indicators (ALT, AST, GGP, uric acid, Ang2) and stage of liver steatosis. Ang2 positively correlated only with GGP, total bilirubin and M30.
Table II
Correlations of Ang2, M30 and stage of liver steatosis with studied markers
[i] ALT – alanine aminotransferase, AST – aspartate aminotransferase, GGT – γ-glutamyltransferase, HDL-C – high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, LDL-C – low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, TG – triglycerides, HOMA-IR – homeostasis model assessment score, Ang2 – agiopoietin-2, M30 – cytokeratin-18 fragments.
The ROC analysis presented in Table III and Figure 2 was performed to determine which potential markers of apoptosis had the best predictive value for distinguishing overweight/obese children with MAFLD from those without MAFLD. A statistically significant result was obtained for M30 (p < 0.001; AUC = 0.7742 with 76.9% sensitivity and 69.6% specificity at the cut-off level 173.74 U/ml). Ang2 was not useful for predicting MAFLD in overweight/obese children (p > 0.05).
Figure 2
ROC curve for ability of Ang2 (grey line) and M30 (black line) to detect children with MAFLD
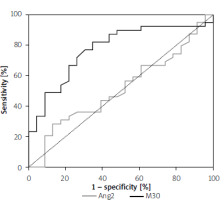
Table III
Analysis of the diagnostic efficiency of selected markers that significantly differentiated overweight/obese patients with and without MAFLD
| Parameter | AUC | SE | 95% CI (AUC) | P-value | Cut-off | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ang2 | 0.5139 | 0.0764 | (0.364–0.664) | NS | 5551 pg/ml | 56.4% | 47.8% |
| M30 | 0.7742 | 0.0618 | (0.653–0.895) | < 0.001 | 173.74 U/ml | 76.9% | 69.6% |
Discussion
The pathogenesis of hepatic lipid accumulation is complex and multifactorial. One of the factors that may affect the development and progression of NAFLD/MAFLD is apoptosis, which may be based on several mechanisms [21]. This may be due to increased de novo lipogenesis affecting the occurrence of inflammation and subsequent apoptosis of liver cells [22]. Recently, it has been proven that endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy also participate in the regulation of hepatocyte apoptosis processes, playing a role in the development and progression of NAFLD [23]. Apoptosis is triggered by cysteine proteases of the caspase family. Caspase-3 cleaved intracellular CK-18 at two sites and the released fragments can be measured in serum [24]. We observed that children and adolescents with MAFLD had significantly higher concentrations of M30 compared to their overweight/obese peers. In addition, M30 also correlated with established liver damage markers such as ALT, AST and GGT. Another marker of apoptosis, Ang2, was also analysed in our study. However, its concentration compared to M30 was not significantly different between the MAFLD and non-MAFLD groups, further confirmed by the ROC analysis.
The accumulation of lipids in hepatocytes leads to cell death and is associated with disease progression to NASH. The diagnosis of NASH refers to hepatocyte balloon degeneration with or without fibrosis in histological examination and may affect up to 50% of children with NAFLD [25]. So far, only a few studies on M30 level in paediatric patients with NAFLD have been published [26–29]. In reports involving healthy children as controls, similarly to us, M30 concentrations were higher in children with NAFLD [26, 27]. Also, increased levels of M30 have been reported in children with steatohepatitis and fibrosis [26, 29, 30]. In another study, the concentration of M30 was found to correlate with the degree of liver fibrosis [27]. In addition, the probability of NASH increased with higher M30 levels [30]. Apoptosis markers were also significantly elevated in children/adolescents with other causes of liver damage, such as alcohol intoxication [31]. In another study involving children and adults with NAFLD, Vuppalanchi et al. observed an association between serum M30 levels and histological changes in the liver after a 96-week intervention. However, changes in serum M30 and ALT in predicting liver histology improvement in NAFLD had similar prognostic value [28]. Based on the mentioned studies, it can be assumed that the process of apoptosis is associated not only with the onset of hepatic steatosis, but also with its progression. More research is needed to evaluate the usefulness of M30 in diagnosing and monitoring NAFLD/MAFLD in children.
To date, few reports have been published on M30 levels in adult NAFLD patients. The aim of most studies was to evaluate the usefulness of M30 in the non-invasive diagnosis of NASH [13–17]. Significantly higher concentrations of M30 were observed in patients with biopsy-proven NASH compared to non-alcoholic fatty liver (NAFL) patients [13–15, 17]. Moreover, some studies have demonstrated the utility of M30 as a non-invasive marker of liver fibrosis [14, 32, 33]. It is worth noting that systems for assessing the probability of liver fibrosis and/or NASH have been developed, such as MACK-3 [33] or the FIC-22 sore [32]. The parameters included in these scoring systems include serum M30 levels. Further research is needed to confirm their usefulness in everyday clinical practice. Expanding knowledge about the importance of the apoptosis process in the occurrence and progression of fatty liver disease may contribute to the development of an effective treatment for MAFLD. Attempts to use anti-apoptotic drugs in the treatment of NASH and liver fibrosis are made at the stage of clinical trials [34]. To the best of our knowledge, studies using caspase-3 inhibition in NAFLD/MAFLD have not been performed to date.
In our analysis, we did not observe significant differences in Ang2 values between overweight/obese MAFLD and non-MAFLD children. Manco et al. noted increased serum Ang2 levels in paediatric patients with NAFLD in parallel with disease activity [29]. This observation is not consistent with our study. The differences in the obtained outcome may result from various values of anthropometric parameters of study participants (in the cited study, patients with normal and abnormal BMI were compared). Studies in mice showed a beneficial effect of Ang2 inhibition on the reduction of hepatocyte ballooning and fibrosis in liver biopsy [35]. What is more, Ang2 gene expression in visceral adipose tissue correlated with lobular inflammation in adult NAFLD patients. However, in the same study, serum Ang2 levels did not show similar relationships [36]. To understand the role of Ang2 in the development of MAFLD in children, it is necessary not only to assess the concentration of Ang2 in the serum, but also to evaluate Ang2 gene expression in liver, visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue.
The strength of our study is that we analysed the associations between apoptosis markers and multiple clinical and biochemical parameters in children with MAFLD. It is also worth mentioning that previous work on apoptosis markers involved NAFLD children and adolescents, and no studies have been published on MAFLD patients in both children and adults. However, our work has several potential limitations. First, the number of patients was too small to draw definite conclusions. Second, our patients did not meet criteria to perform a liver biopsy [37]; therefore we could not assess the correlation of M30 and Ang2 with histological grades of steatosis, inflammation and fibrosis. However, given the patchy nature of NASH lesions compared to other chronic liver diseases, liver biopsy in patients in our study is prone to sampling errors. In addition, liver biopsy is associated with significant intra- and inter-observer variabilities [38].
Conclusions
Our results suggest that the mechanism of apoptosis may play an important role in the development of MAFLD in children. This is underlined by adding a correlation of ALT, AST or GGT values with serum M30 levels There is a need for further studies in children to determine whether the M30 concentration may be an indicator of MAFLD progression and whether inhibition of apoptosis may become one of the therapeutic options for this disease.










