Introduction
The incidence of non-melanoma skin carcinoma shows a rising trend. The most frequently occurring malignant eyelid carcinoma is the basal cell carcinoma (BCC) [1]. Non-melanoma skin carcinoma (NMSC), including the tumours in the eyelid region, are the most common tumours afflicting the Caucasian population. Based on the evidence obtained in multiple published studies, there is a provable correlation between the gender, the age, and the incidence of this disease [2, 3]. The malignant tumour diagnosis may only be definitively confirmed based on the histopathological examination of a collected tissue sample. In most cases, the primary treatment of eyelid carcinoma is surgical resection. Advanced lesions require extensive surgical interventions as well as the application of other available therapeutic modalities. Over the last years, there has been an increasing interest in the development of biomarkers with the aim of improving the prevention and ensuring early detection of cancer with personalised therapy management [4].
There are multiple risk factors that contribute to the development of new NMSC. NMSC risk factors include the age, male gender, pale skin, frequent exposure to the sun, severe actinic damage, previous radiotherapy in the medical history, tumour size above 1 cm, width of the lesion margin, family history with other types of skin cancer, low DNA repair capacity, detected tumour necrosis factor (TNF), microsatellite polymorphism, polymorphism of the PTCH gene, as well as polymorphism of glutathione S-transferase and P450 cytochrome [5].
Prognostic biomarkers facilitate the identification of high-risk tumours for the purpose of targeted screening and targeted primary and secondary prevention for early detection and treatment [6]. One of the mechanisms engaged in the tumour growth is that the cell escapes the cell death – apoptosis. The mechanism of apoptosis is also facilitated by other proapoptotic genes (BAD, BAX, BID, and p53) and apoptotic inhibitors (Bcl-2, BCL-X). Non-Bcl-2 family proteins emerge as new regulators of apoptosis and are currently subjected to pharmacological research. A cell proliferation degree correlates with the tumour growth rate. A higher degree of proliferation is associated with a lower degree of differentiation, more aggressive biological behaviour, and a worse prognosis of the malignant disease [7]. The proliferation activity is most frequently identified based on immunohistochemical tests, using the antibody against the Ki-67 antigen. The Ki-67 antigen is a non-histone protein [8]. The apoptotic index (AI) is regarded as an important, yet still unexplained, prognostic factor of biological behaviour of tumours. AI is calculated as the number of apoptotic cells and apoptotic bodies, expressed as the percentage of the total number of tumour cells counted in each case in a histology sample [9].
Aim
This paper is based on the persisting need for understanding new prognostic parameters of malignant eyelid cancer that determine a personalised approach to the individual patients. We evaluated the association of the Bcl-2 protein and Ki-67 antigen expression and the apoptotic index with biological behaviour of non-melanoma eyelid tumours.
Material and methods
This study is a combined analysis of retrospective and prospective study with patients presenting with malignant lesions in the eyelid region. The cohort consisted of the patients treated in the UVEA Eye Clinic in the period from 2018 to 2023 and the patients treated in the Department of Ophthalmology of the Central Military Hospital in Ružomberok in the period from 2008 to 2021 who presented with histologically confirmed malignant cancer in the eyelid region, without applying any age limitation. Patients suspected to have a tumour were referred for surgical resection including the histological examination of the excised sample. Those patients were monitored for the epidemiological parameters, such as the gender and age, location of their malignant tumour, tumour size, and the application of any other therapy. The selected surgical approach depended on the tumour location and size and was performed following the recommended procedures. This paper presents the evaluation of the resection margin size and of the R0/R1/R2 resection types in terms of the risk of recurrence of malignant cancer.
One of the key objectives of this paper was the tumour evaluation from the histopathological and immunological point of view. Samples were divided into two groups based on the histological classification – aggressive and non-aggressive tumours. The subject of the evaluation included selected prognostic markers related to aggressive or non-aggressive tumours as well as the recurrence and metastases. The Bcl-2 expression was calculated as the total percentage of positive tumour cells in the carcinoma. The value of the Ki-67 index was calculated as the average percentage of proliferating tumour cells in the carcinoma. The apoptotic index was evaluated through the semi-quantitative evaluation of apoptosis.
Statistical analysis
With regard to the determined hypotheses and the nature of the related data, the data were statistically analysed by applying the χ2 test for data distribution, the Cramer’s V test, the Phi Coefficient test, the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test for normality, the Shapiro-Wilk test for normality, and the Mann-Whitney U-test for 2 independent sets. All of those tests were used for the individual hypotheses based on the nature of the particular data included in the given hypothesis. Statistical analysis was carried out in the SPSS 22 environment.
Results
The data set included 70 cases of NMSC of the eyelid. Out of those, in 25 cases it was diagnosed in the UVEA Eye Clinic in Martin in the period from 2018 to 2023, representing 35.7%, while in 45 cases the NMSC was diagnosed in the Department of Ophthalmology of the Central Military Hospital in Ružomberok in the period from 2008 to 2021, representing 64.3%. Sixty-eight patients had a histologically confirmed BCC (97.1%). Two patients had a spinocellular carcinoma (SCC) (2.9%). BCC type of NMSC occurs at a frequency of higher statistical significance than the frequency of the SCC (p < 0.001).
The patients who underwent surgical excision were aged 14–95 years, with a median of 68 years. There was no statistically significant difference in the number of patients with NMSC with regard to the age categories of below 65 years and 65+ years of age (p = 0.140). A 14-year-old patient had a BCC in the region of the medial canthus on the right side, sized 3 × 3 × 2 mm. It was the nodular type (trichoepithelioma-like) of BCC. The resection was carried out with thin margins of less than 2 mm. The histological sample exhibited the Bcl-2 protein expression and positivity, Ber-EP4 positivity and CD10 positivity. No correlation with genetically determined syndromes has been confirmed in this patient.
The NMSC incidence slightly prevailed in the female population. The cohort consisted of 29 (43.9%) men and 37 (56.1%) women. There was no statistically significant difference between the number of men and the number of women enrolled as patients with NMSC (p = 0.325).
The largest subgroup of the cohort consisted of the patients with the nodular tumour type – 41.4% of the cohort. By contrast, the smallest subgroup consisted of the patients with the nodular-infiltrative or SCC (2.9%) (Table 1). The tumour was located on the right side in 54.5%, while in 45.5% the location was on the left side. NMSC was most frequently located in the lower eyelid region, representing 41.5% of the cohort. The smallest subgroup included the patients with a tumour located near the lateral canthus – 1.5% of the cohort.
Table 1
Histological types of NMSC in our cohort study
The frequency of the tumour located in the region of the medial canthus is statistically more significant (p = 0.003). No statistically significant difference was observed between the frequency of the tumour located in the region of the medial canthus and the frequency of the tumour located in the regions of the upper or the lower eyelids (p = 0.157). There was no statistically significant correlation between the presence of recurrence and the tumour location in patients with NMSC (p = 0.165). The aggressive tumours as well as the non-aggressive tumours were most frequently located on the lower eyelid of patients. An interesting fact is that all the patients with a carcinoma located in the lateral region had the non-aggressive type of tumour.
Tumour size larger than 5 mm was in 32.9%. There was a slight positive statistically significant correlation between the presence of the aggressive tumour and a tumour size of more than 5 mm; therefore, aggressive tumours are more frequently larger than 5 mm, while non-aggressive tumours are more frequently sized 5 mm or smaller (ϕ = 0.238). The cohort consisted of 47 patients with the resection margins larger than 2 (67.1%) mm. There was no statistically significant correlation between the presence of recurrence and the resection margins smaller than 2 mm (ϕ = 0.076).
A relatively extensive surgical excision with the use of skin flaps was carried out in 2 cases. The R1 resection was performed in 8 (0.13%) cases. Out of those, in 2 cases it was sufficient to perform a subsequent re-excision with free margins. In 3 cases, adjuvant HDR brachytherapy was applied at a dose of 12 × 500 cGy; in 3 cases, the re-excision was combined with HDR brachytherapy.
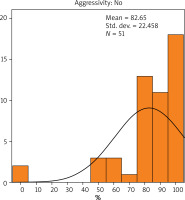
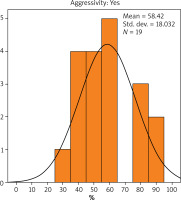
The results showed that the average value of Bcl-2 expression in patients with non-aggressive cancer was 82.65% (Figure 1), while in patients with aggressive cancer it was 58.42% (Figure 2). There was a statistically significant difference in the value of Bcl-2 expression due to the difference in the cancer aggressiveness. The value of Bcl-2 expression in patients with non-aggressive cancer was statistically significantly higher than that observed in patients with aggressive cancer (p < 0.001). The Bcl-2 expression was calculated as the total percentage of positive cancerous cells in the carcinoma.
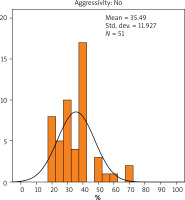
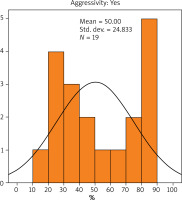
The Ki-67 index was calculated as the average percentage of proliferating cancerous cells in the carcinoma. The results indicated that the average value of Ki-67 expression in patients with non-aggressive cancer was 35.49% (Figure 3), while in patients with aggressive cancer it was 50% (Figure 4). There was no statistically significant difference in the value of Ki-67 expression with regard to the presence or absence of aggressive cancer (p = 0.068).
The AI was determined based on the semiquantitative evaluation of apoptosis (Figure 5). No statistically significant difference in the apoptotic index was observed with regard to the presence of either aggressive or non-aggressive cancer (p = 0.535). However, Grade I apoptotic index values were identified in the largest number of samples that were histologically confirmed as non-aggressive cancer. By contrast, in the group of patients with aggressive cancer, the number of Grade I values, and the number of Grade II values were identical, while none of the patients with aggressive cancer was confirmed to have Grade III AI.
Figure 5
Details on 3 mitoses (white arrows) and 3 apoptotic tumour cells (black rings) in nodular BCC
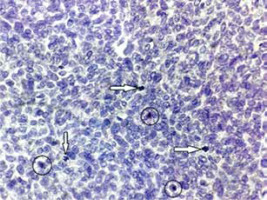
Grade I (Gr. I) – the average number of apoptotic tumour cells ranging from 1 to 10 per 10 HPFs (high power fields); i.e. 10 times the microscope objective with a 40× magnification.
Grade II (Gr. II) – the average number of apoptotic tumour cells ranging from 11 to 20 per 10 HPFs (high power fields); i.e. 10 times the microscope objective with a 40× magnification.
Grade III (Gr. III) – the average number of apoptotic tumour cells of ≥ 21 per 10 HPFs (high power fields); i.e. 10 times the microscope objective with a 40× magnification.
In 2 cases, the orbit was exenterated due to invasive BCC with the infiltration of the surrounding structures (0.03%). In 1 case, the patient was administered biological therapy. Recurrence was observed during the analysed period in 4 cases – after 2 years on average. As to the expression of prognostic markers, no statistically significant difference was observed.
Discussion
Investigation into a correlation between the growth rate of a malignant tumour of the eyelid and the risk of tumour recurrence after surgical resection might bring some interesting information. Understanding that correlation might bring more light to the dilemma whether the long-growing NMSCs acquire a more aggressive phenotype or their biological behaviour remains stationary. According to the published studies, it may be assumed that there is a correlation between a higher incidence of NMSC and a higher risk of recurrence in individual patients. According to the paper published by Bumpous et al., for patients with multiple BCCs, there was a statistically higher probability of developing BCC and recurrence compared to the patients with a solitary tumour [10].
Age is a proven risk factor for NMSC, with the peak in the 7th decade of life [11]. According to the data in the National Oncology Register of the Slovak Republic, the age structure of Slovak patients indicates a rising trend with ageing. The highest incidence was observed in the age group of 70–74 years [12]. In our study median was 68 years. There was no statistically significant difference with regard to the age categories (p = 0.140).
Several studies have confirmed a correlation between the gender, age and NMSC incidence. The incidence is slightly higher in the male population – men represent 61% of cases. The correlation between the patient gender and the risk of BCC recurrence is still controversial [5, 13]. Our cohort consisted of 29 (43.9%) men.
The tumour location is an important risk factor for the development of NMSC. In more than 50% of cases, BCC is located on the lower eyelid; in 30%, it is in the region of the medial canthus; in 15% on the upper eyelid; and in 5% in the region of the lateral canthus. This was the same in our cohort. BCC with the orbital invasion is mainly present in the region of the medial canthus (in 60% of cases, on average) compared to the lower eyelid (30%), the upper eyelid (6%) and the lateral canthus (14%) [14, 15]. Therefore, there is a significantly higher risk of intraorbital and perineural infiltration in BCC located in the regions of the medial and lateral canthi. Where a lesion afflicts the medial canthus in advanced basal cell carcinoma, there might be a significantly higher need for a mutilating procedure, such as the orbital exenteration [16]. In our study, there was no statistically significant correlation between the presence of recurrence and the tumour location in patients with NMSC (p = 0.165).
Data on recurrence after a surgical resection of NMSC vary, depending on the applied surgical technique. The most frequent cause of recurrence is a thin resection margin, in particular less than 0.3–1 cm from clinically visible margins [17]. The risk of developing non-melanoma eyelid cancer increases if the cancer is also present on/in other body parts. The 5-year cumulative risk of new BCC in patients with at least one previous BCC is 41–45% compared to the 5% risk for the Caucasian population without BCC [18, 19].
The Bcl-2 protein family determines whether a cell dies or survives by controlling mitochondrial apoptosis during the cell division process [20, 21]. Sivrikoz et al. applied the immunohistochemical staining of Bcl-2 in BCC tissues and found out that the reduced levels of Bcl-2 correlated with the aggressive tumour subtypes. Apparently, Bcl-2 protein suppresses cellular death and protects the cells against induced apoptosis [22]. In the study by Puizina-Ivić et al., the authors performed an immunohistochemical analysis of the expression of Bcl-2 protein in histopathological variants of malignant tumours in basal cell carcinoma (BCC) and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), as well as in a precancerous lesion of actinic keratosis (AK) and in benign seborrheic keratosis (SK). The Bcl-2 expression in BCCs with a lower risk exhibited the immunoreactivity of the tumour stroma with more intensive staining between the peripheral palisade cells. The morphoeic variant exhibited reduced Bcl-2 expression. None of the SCC tumour samples was Bcl-2 positive [23]. The value of Bcl-2 expression in our study with non-aggressive cancer was statistically significantly higher than that observed in patients with aggressive cancer (p < 0.001).
A cell proliferation degree correlates with the rate of tumour growth. Proliferation activity is normally determined immunohistochemically with the use of the antibody against the Ki-67 antigen. The proliferation activity of cancer cells in BCC exhibits an average Ki-67 index of 20–40.6%. Expression of the Ki-67 antigen exhibits significant qualitative and quantitative differences between the individual histological types of BCC [24]. Multiple studies indicated a correlation between the aggressive behaviour of BCC and a higher degree of cell proliferation – the Ki-67 proliferation index. Some of the studies provide controversial conclusions [25]. Healy et al. and Yerebakan et al. observed a higher Ki-67 expression in the primary BCC which eventually recurred. Lower Ki-67 expression was confirmed in BCC without any recurrence [8, 24]. On the other hand, Janisson-Dargaud et al. did not confirm any significant differences in the Ki-67 antigen expression in the primary BCC, without any subsequent recurrence, compared to non-recurrent BCC [25]. In our study, there was no statistically significant difference in the value of Ki-67 in aggressive and non-aggressive tumours (p = 0.068).
The apoptotic index (AI) is calculated as the number of apoptotic cells and apoptotic bodies, expressed as the percentage of the total number of tumour cells counted in each case in a histology sample. AI may be regarded as an important prognostic factor of biological behaviour of cancer. However, it is still an unexplained prognostic factor of aggressive histological types of BCC and its recurrence. In their study, Staibano et al. evaluated 60 cases of basal cell skin cancer. In 30 cases, it was the non-aggressive type of basal cell carcinoma (BCC1), while in 30 cases, it was the aggressive type (BCC2). In the tested preparations, BCC1 exhibited a lower AI than that observed in BCC2 (BCC1: AI: 2.03–10.45% (median: 5.98%); BCC2: AI: 21.91–43.82% (median: 39.82%)). It may be assumed that a low apoptotic index in basal cell carcinoma might indicate a good prognosis of a malignant tumour. In our study, we noticed no statistically significant difference in the apoptotic index about the presence of aggressive or non-aggressive cancer (p = 0.535). But none of the patients with aggressive cancer was confirmed to have AI = Grade III [9].
The primary therapeutic modality for non-melanoma periocular tumours is surgical resection [4]. The tumour shape, the distance from the margin, and the tumour diameter are the decisive factors when deciding on the best surgical technique. If the skin lesion covers up to 1/3 of the width of the palpebral fissure, the most appropriate technique is the excision and primary closure. If the skin lesion covers more than 1/3, a different surgical technique should be applied [26]. The incidence of BCC recurrence after the Mohs micrographic surgery (MMS) is lower than that after the surgical excision (SE). However, MMS is longer and therefore more expensive than SE [27].
Radiotherapy offers two options of administration – the application of external radiotherapy and brachytherapy in NMSC. Radiotherapy plays an important role in the therapy of BCC, spinocellular carcinoma (SCC), and sebaceous carcinoma (SGC). Brachytherapy, when compared to surgical resection, has a theoretical advantage as it facilitates the use of a high dose to cover larger skin areas (macroscopic disease, microscopic disease, safety edge) without the necessity of irreversible damage to the surrounding tissues [28]. HDR brachytherapy was applied in 6 cases in our cohort with good effect.
Based on the available literature, it was observed that in the case of primary, well-surrounded BCC smaller than 2 cm in the low-risk cohort, a safety reserve of 3 mm in the resection margins brings satisfactory outcomes. In the high-risk cohort with lesions larger than 2 cm, it is recommended to leave a margin of 4–6 cm to achieve the R0 resection. In some patients, the orbit is exenterated after the previous therapeutic modalities fail. Since the recurrence after the exenteration may amount to 50–75%, it is crucial not to underestimate the early management of such lesions [26]. Tumour size of more than 5 mm corelates with aggressive type of carcinoma (ϕ = 0.238) according to our results.
Data on recurrence after the surgical resection of NMSC vary, depending on the applied surgical technique. In the available literature published over the last 10 years, the incidence of recurrence without the use of the Mohs micrographic surgery or the perioperative histopathological examination of frozen sections ranged from 1.8% to 39% [16]. The incidence of recurrence after the primary surgery was 1–5% per year. Smaller resection margins – less than 0.3–1 cm from the clinically visible margins, represent a risk factor for BCC recurrence [17]. In our cohort, margins < 2 mm were sufficient, without any connection to recurrence rate (p = 0.076). The risk of the development of NMSC increases by 41–45% with NMSC in the patient’s medical history. The histological classification and the subtype of cancer have been clearly established as prognostic factors for invasive and malignant behaviour [29].
Vismodegib is a specific small-molecule inhibitor of the Hedgehog signalling pathway [30]. The approved oral dose of Vismodegib is 150 mg/day. It is currently approved for the treatment of advanced lesions as well as metastatic or recurrent BCC [31–33]. We used biological therapy once. Other therapeutic procedures in the treatment were marginal.