Introduction
DNA repair is a biological process by which cells routinely identify and correct genetic damage. This regular maintenance of genome integrity is crucial for the survival of all organisms. Environmental factors and metabolic activities can cause deleterious lesions, like doublestrand breaks, which adversely affect genome stability and must be repaired rapidly (Tiwari and Wilson, 2019; Alhmoud et al., 2020). Various DNA repair pathways, such as homologous recombination (HR), nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ), mismatch repair (MMS), base excision repair (BER), and nucleotide excision repair (NER), are known to correct DNA damage (Chatterjee and Walker, 2017; Alhmoud et al., 2020). The activation of the repair pathway depends on the nature of the DNA damage. For example, double-strand breaks (DSBs) are repaired by two DNA repair pathways, NHEJ and HR. While NHEJ is a rapid, error-prone pathway that does not require long homologous sequences, HR is a slow, homology-based, error-free DNA repair mechanism (Shen and Li, 2022; Lam, 2022).
The phase of the cell cycle, the presence of sister chromatids, and the mode of resection determine which DSB repair pathway must be chosen, whether HR or NHEJ (Frigerio et al., 2023). In mitotic cells, the HR pathway is activated during the S and G2 phases, during which the sister chromatids are available to provide the region of homology. At the DSBs, the broken DNA is resected to form 3’ single-stranded (ss) DNA overhangs, which are recognized by either the HR-specific protein Replication Protein A (RPA) or the CTC1-STN1-TEN1 (CST) complex. Additionally, RAD51-mediated strand exchange is exhibited in the CST-coated ssDNA at high ionic strength (Lei et al., 2021). In contrast, NHEJ is activated during the G0 and G1 phases of the cell cycle, where the sister chromatids are not available and DSB resection activity is downregulated (Lamarche et al., 2010).
HR is a well-characterized DNA repair pathway in mammals (Krejci et al., 2012). The HR pathway involves several steps: detection of DSB, activation of protein kinases, activation of cell cycle checkpoints, recruitment of proteins involved in the HR pathway to the break site, and, finally, DSB repair (Lamarche et al., 2010). HR serves dual functions in two different types of cells: it facilitates DNA repair in somatic cells and develops genetic variability during meiosis in germline cells. In plants, many genes related to the HR pathway have been studied and characterized using various T-DNA insertion mutants. The HR pathway genes such as RAD54, RAD51, ATM, XRCC, and BRCA2A have been well-characterized in Arabidopsis thaliana (Garcia et al., 2000; Osakabe et al., 2006; Durrant et al., 2007; Wang et al., 2010; Da Ines et al., 2013).
BRCA2 is a prominent member of the HR pathway (De Picciotto et al., 2016). In mammals, BRCA2 is highly expressed in the S-phase, and improper functions of the BRCA2 gene can result in replication errors in somatic cells that may later transform into cancer (Roy et al., 2012). In humans, HsBRCA2 is a potent oncogene (Roy et al., 2012) and is involved in releasing RAD51 protein into the ssDNA (exposed during DSB or at the site of stalled replications), coated with RPA protein (Holloman, 2011). Given that mutations in HsBRCA2 result in a high risk of cancer, this gene has been well-characterized in humans (Venkitaraman, 2019). In Arabidopsis, the BRCA2 gene exists as two homologs: AtBRCA2A and AtBRCA2B (Pfeffer et al., 2017). A previous study on double homozygous insertion mutants of AtBRCA2A showed a 30% reduction in spontaneous somatic homologous recombination (SHR) frequency compared to wild plants (Wang et al., 2010). Both AtBRCA2 genes are required for meiotic as well as somatic HRs (Siaud et al., 2004; Seeliger et al., 2012). Both sister loci seem to play a redundant role in somatic recombination (Seeliger et al., 2012). In this study, we report the influence of the BRCA2B gene in maintaining spontaneous SHR rates and regulating the expression of other HR pathway genes in A. thaliana plants.
Materials and methods
Plant materials
The A. thaliana Columbia (Col-0) ecotype and the BRCA2B mutant (SALK_124404) seeds were purchased from the Arabidopsis Biological Resource Center and provided by R. Baskar (Indian Institute of Technology – Madras, India). The mutation detector line R2L1, in Col-0 background (Li et al., 2004), was obtained from Francois Belzile (University of Laval, Canada). The detector BRCA2B-gus mutant was generated by crossing homozygous plants from the R2L1 and SALK_124404 lines. This was followed by the selfing of the F1 progeny to obtain homozygotes for both loci.
Arabidopsis growth conditions
A. thaliana seeds were surface-sterilized, germinated, and grown as previously described (Joseph et al., 2019). Two-week-old plants were carefully transferred to standard vermicompost, purchased from the Central Plantation Crop Research Institute, Kasaragod, India.
Confirmation of the T-DNA insertion mutant of AtBRCA2B gene
The BRCA2B mutant line, SALK_124404, is a homozygous mutant in which the T-DNA was inserted into the 13th intron (supplementary Fig. 1A). The mutant was reconfirmed by PCR (supplementary Fig. 1C) using T-DNA-specific primers (supplementary Fig. 1A and Fig. 1B) (O’Malley et al., 2015) and by sequencing the amplicon using the Sanger sequencing method, executed by Xcelris, India (Crossley et al., 2020) (supplementary Fig. 1D).
Making of the GUS detector, BRCA2B-gus mutant line
The GUS detector, BRCA2B-gus mutant line, was generated by crossing the plants from line R2L1 with BRCA2B mutant plants. The GUS gene in R2L1 is a noncoding gene into which two identical introns are inserted in reverse orientation (supplementary Fig. 2A). Recombination events are monitored by GUS expression due to the HR that occurs between the introns. The double homozygous BRCA2B-gus mutant line has two T-DNAs (supplementary Fig. 2B). To identify such events, sequential steps of screening and confirmation were followed in each generation (supplementary Fig. 3A). Crossing R2L1 with BRCA2B mutants developed heterozygous F1 progenies. Selfing of F1 progenies resulted in F2 progenies. All F2 plants were germinated on kanamycin-containing growth media. Kanamycin-resistant F2 plants were screened for the homozygosity of BRCA2B loci using PCR with BP/RP (supplementary Fig. 4A) and LP/RP (supplementary Fig. 4B) primer pairs. Identified F2 plants homozygous for the mutant BRCA2B loci were screened using PCR with GUS primers to check whether they have the second T-DNA harboring the GUS recombinant construct (supplementary Fig. 4C). To identify the F2 plant homozygous for gus loci, we performed semi-quantitative real-time PCR of the DNA with NPTII* primers (supplementary Fig. 4D). Homozygotes for both T-DNAs would have four copies of NPTII, and those that are hemizygous for the gus loci would have three copies of NPTII (supplementary Fig. 3B). The identified double homozygous mutant was re-confirmed by segregation analysis of its F3 generation using PCR with GUS and T-DNA-specific primers (supplementary Fig. 5A–5C).
Phenotype analysis
Phenotype analysis was conducted in three experimental replicates, each with 15–20 plants. The root length was measured manually. Fresh weight was assessed using a weighing balance (Shimadzu, Japan). The lengths of seeds, siliques, and rosettes were measured digitally using a stereo microscope (Motic, Spain). The number of seeds per silique was counted manually. Chlorophyll extraction was performed using DMSO, and the optical density was measured at 645 and 663 nm in a UV spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific, USA) against a DMSO blank (Hiscox and Israelstam, 1979). Chlorophyll content was calculated based on Arnon’s equation (Pérez-Patricio et al., 2018).
Extraction and quantification of RNA/DNA, and cDNA synthesis
RNA was isolated from 4-week-old plants using Tri reagent (Origin, Diagnostics & Research, India) (Shi and Bressan, 2006). DNA was extracted using the CTAB method (Doyle and Doyle, 1987) from 4-week-old plants. Both nucleic acids were quantified using the Nanodrop 2000c Spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific, USA). cDNA was synthesized using the Moloney murine leukemia virus reverse transcriptase (M-MLV-RT) kit (Invitrogen, USA) from 1 μg of the isolated RNA samples, following the manufacturer’s protocol.
Primer designing
The T-DNA-specific primers used to screen the AtBRCA2B loci (supplementary Fig. 1B) were as recommended by the Salk Institute Genome Analysis Laboratory. The remaining primers (supplementary Table 1) were designed using the PrimerQuest tool from IDT (https://www.idtdna.com/pages/tools/primerquest). All primers were synthesized by Sigma-Aldrich India Pvt Ltd.
PCR screening and sequence confirmation
The PCR reaction mixture contained 100 ng of genomic DNA, 1 μl (10 pmol/μl) each of forward and reverse primers, 2.5 μl of Taq polymerase (1U)-containing master mix, and nuclease-free water. All PCR components were from Origin Diagnostics & Research, India, and the experiments were run on an Eppendorf Mastercycler-PCR Thermal Cycler. PCR conditions were as follows: initial denaturation for 2 min at 94°C, denaturation for 1 min at 94°C, annealing (temperature based on the primer used), extension for 1 min at 72°C, and cooling for 5 min at 4°C. Confirmation was achieved by sequencing the amplicon using the Sanger sequencing method from Xcelris, India (Crossley et al., 2020).
Somatic recombination assay
Recombination assays were conducted using homozygous plants from the GUS detector mutant and the BRCA2B mutation detector lines. Somatic mutations were detected in 4-week-old plants by the occurrence of blue spots, obtained after GUS histochemical staining as previously described (Jefferson, 1989; Shah et al., 2015). The experiments were repeated three times, with more than 100 plants in each trial. Images of plants with blue sectors were captured using a stereo microscope (Motic, Spain).
Real-time PCR
For expression analysis, UBC9 was used as the reference gene, and PCR conditions were described previously (Joseph et al., 2019). Semiquantitative real-time PCR (Haurogné et al., 2007) was used for the zygosity confirmation of the double homozygous BRCA2B-gus detector mutant. For this, 100 ng of total DNA was subjected to real-time PCR using NPTII * primers (supplementary Fig. 4D).
All reactions were performed using the Essential DNA Green Master (Roche Diagnostics India Pvt Ltd) master mix, and the experiments were run on the Roche LightCycler® 480 II system. The reaction mixture for expression analysis comprised 1 μl cDNA/DNA, 10 μl master mix, 1 μl (10 pmol/μl) of each forward and reverse primer, and nuclease-free water.
Statistical analysis
The phenotypic characters, spontaneous SHR rates, and real-time expression of repair genes were statistically analyzed using the Student’s t-test (Kalpić et al., 2011) with Microsoft Excel 2016. The significance of the data was determined at P < 0.01 for phenotypic characters and P < 0.05 for spontaneous SHR and real-time expression.
Results
BRCA2B mutation results in altered morphology of Arabidopsis
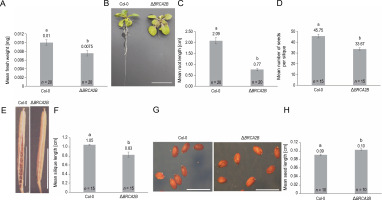
Mutation in the AtBRCA2B gene induced distinct changes in plant morphology compared to wild plants (Fig. 1). The mutant plants exhibited significantly reduced fresh weight (1.3-fold) (Fig. 1A), root length (2.7-fold) (Fig. 1B, Fig. 1C), average number of seeds per silique (1.4-fold) (Fig. 1D), and silique length (1.3-fold) (Fig. 1E, Fig. 1F) in comparison to wild plants. In contrast, seed length in mutants was 1.1-fold longer than in control plants (Fig. 1G, Fig. 1H). Neither chlorophyll content nor rosette diameter showed any significant variation (supplementary Fig. 6A, Fig. 6B).
Fig. 1
Comparison of morphological characteristics of wild type (Col-0) and the Arabidopsis mutant ΔBRCA2B (A) fresh weight, (B) 2-week-old plants displaying the root lengths (scale bar – 1 cm), (C) mean root lengths of 2-week-old plants, (D) a mean number of seeds, (E) a silique of the wild type and mutant plant (scale bar – 0.5 cm), (F) mean length of the siliques, (G) mature seeds of the wild type and mutant plants (scale bar – 0.01 cm), (H) mean length of the seeds; error bars represent the ± standard error; a,b indicate that the mean values are significantly different at P < 0.01 as determined by the Student’s t-test; n – number of plants observed in each experiment
Confirmation of the GUS detector, BRCA2B-gus mutant line
To understand the influence of the AtBRCA2B gene on spontaneous SHR in plants, we developed a double homozygous mutant line ( BRCA2B-gus) by crossing the BRCA2B mutant line SALK_124404 with the mutation detector Arabidopsis line R2L1 (Li et al., 2004). The R2L1 line serves as an in planta intrachromosomal recombination assy system, where the SHR rate can be monitored using the mutated GUS gene, visualized as blue sectors on the plant after histochemical staining with 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl glucuronide (X-gluc) (Li et al., 2004). Twenty-five kanamycin-resistant F2 plants were screened for homozygosity of BRCA2B loci using PCR with T-DNA screening primer pairs. Three F2 plants (numbers 5, 15, and 18) were identified as homozygous for the mutant BRCA2B loci because they yielded the expected amplicon with BP/RP primers and did not amplify with the LP/RP primers (supplementary Fig. 1A, Fig. 4A, Fig. 4B). Plants that amplified with both primer pairs were hemizygous for this locus. Plants 5, 15, and 18 also produced the expected amplicons when screened using GUS primers, indicating that they harbor the second T-DNA containing the GUS recombinant construct (supplementary Fig. 4C). F2 plants homozygous for gus loci were screened using semiquantitative real-time PCR of DNA with NPTII * primers. Homozygosity was confirmed by the variation in CP value proportional to the number of NPTII gene copies. Of the three F2 plants, plant number 15 had a lower CP value (supplementary Fig. 4D), indicating higher copies of the NPTII gene. Loci segregation was re-confirmed in the F3 generation; all F3 plants displayed results expected of a homozygote double mutant (supplementary Fig. 5A–5C).
BRCA2B mutants display a hypo-recombination phenotype
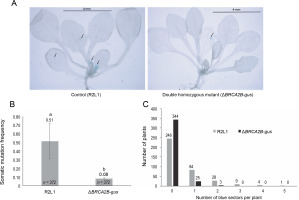
Similar to the R2L1 lines, the double homozygous mutant BRCA2B-gus also exhibited blue sectors upon GUS histochemical staining (Fig. 2A). A significant reduction in the SHR frequency (6.3 fold) was observed in the BRCA2B-gus mutants compared to the control R2L1 plants (Fig. 2B). Furthermore, the analysis of blue sector distribution within individual plants revealed a higher number of blue sectors per plant in the control R2L1 plants (Fig. 2C). A maximum of only two blue sectors per plant were observed in BRCA2B-gus mutants, compared to five in the R2L1 control plants. Approximately 92% of the BRCA2B-gus mutants did not exhibit any spontaneous SHR in the GUS recombination region, in contrast to 66% of the control R2L1 plants. Consequently, our results suggest that BRCA2B is essential for inducing spontaneous SHRs in plants.
Fig. 2
Somatic homologous recombination (SHR) analysis (A) Image of control (R2L1) and ΔBRCA2B-gus double homozygous mutant plant after GUS-histochemical staining (scale bar-4 mm); black arrows indicate blue sectors developed on the plants (B) graphical representation of somatic mutation frequency in control (detector line) and double homozygous mutant plant; error bars represent the ± standard error and a,b represent statistically significant differences in SHR rate at P < 0.05 as determined by Student’s t-test; n – total number of plants observed (C) graphical representation of the number of blue sectors in individual plant
BRCA2B mutation downregulates the expression of other genes in the HR pathway
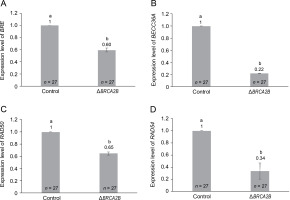
To further examine the influence of BRCA2B on the HR pathway, we explored the expression of four additional genes – BRE, BRCC36A, RAD50, and RAD54 – within the HR pathway (Fig. 3). Among these, BRE, BRCC36A, and RAD50 operate upstream of BRCA2B in the HR repair pathway, while RAD54 functions downstream (D’Amours and Jackson, 2002; Mazin et al., 2010; Biswas et al., 2018). All four HR genes, namely BRE, BRCC36A, RAD50, and RAD54, demonstrated a significantly diminished expression, with respective fold changes of 0.60, 0.22, 0.65, and 0.34, in the BRCA2B mutants (Fig. 3A–3D). This suggests that the presence or absence of BRCA2B is required for regulating other HR proteins. Further, the overall reduction in the SHR rates in BRCA2B-gus mutant plants might be attributable not solely to the absence of the BRCA2B protein but also to the decreased availability of BRE, BRCC36A, RAD50, and RAD54 proteins.
Fig. 3
Comparison of relative expression levels of genes involved in homologous recombination pathway, in the wild type and BRCA2B mutant Arabidopsis plants (A–D) represent comparative expression levels of genes BRE, BRCC36A, RAD50, and RAD54, respectively; error bars represent ± standard error; symbols a and b indicate that the expression values are significantly different as determined by the Student’s t-test at P < 0.05; the data represent the mean of the three independent trials; n – total number of plants
Discussion
BRCA2 plays a pivotal role in the HR pathway, prominently functioning in double-strand break repair (Roy et al., 2012). HsBRCA2, recognized as a tumor suppressor gene and widely regarded as an oncogene, has mutations associated with the onset of breast and ovarian cancers in humans (Paul and Paul, 2014). Germline mutations in the human HsBRCA2 gene are correlated with a heightened risk of developing breast cancer (Pietschmann et al., 2005). In mice, mutations in BRCA2 lead to early embryonic lethality, and surviving mice manifest sterility in adulthood (Jensen et al., 2013). Although the DNA repair pathway is highly conserved across higher eukaryotes, mutations in BRCA2 genes are nonlethal in plants (Seeliger et al., 2012). The model plant A. thaliana carries two homologs of the BRCA2 gene, BRCA2A (1151 aa) and BRCA2B (1155 aa), which share a 94.5% identity. The HsBRCA2 gene encodes a substantially larger protein comprising 3418 amino acids and shares a 21% identity with the AtBRCA2A/B proteins. In Arabidopsis, AtBRCA2A and AtBRCA2B are situated on chromosomes IV and V, respectively, and diverge only in their second BRC repeat (Trapp et al., 2011). In this study, we report the influence of the AtBRCA2B gene on Arabidopsis phenotype, spontaneous SHR frequency, and other genes within the HR pathway.
We examined the BRCA2B mutant line SALK_124404, which exhibited a notable decrease in plant fresh weight, root length, silique length, and seed quantity. However, the seeds of BRCA2B mutants were longer than those in wild-type plants. Abe et al. (2009) and Wang et al. (2010) previously reported that other BRCA2B mutant lines, namely atbrca2b-1 (a Ds mutant, Nossen background), and SALK_037617 (T-DNA insertion mutant, Columbia background), were fertile but did not provide additional phenotypic details. Both studies indicated that the atbrca2a/b double mutants displayed severe growth abnormalities, such as hypersensitivity to genotoxic stresses, altered cell cycle progression, and sterility under various DNA damaging stresses. Previous reports also revealed that the atbrca2a/b double mutants (Dumont et al., 2011) and RNAi-silenced mutants for the AtBRCA2A/B genes (Siaud et al., 2004) were sterile and exhibited malformed male and female gametophyte development (Seeliger et al., 2012).
While AtBRCA2A and AtBRCA2B participate in the HR pathway and are hypothesized to fulfill redundant roles, we aimed to investigate whether AtBRCA2B alone contributed to maintaining spontaneous SHR rates. To this end, we created a double homozygous mutant, combining the BRCA2B line SALK_124404 with the previously documented GUS mutation detector line R2L1 (Li et al., 2004; Shah et al., 2015). SHR was markedly reduced – by 6.3-fold – in these detector mutants. Wang et al. (2010) have previously reported SHR reductions of about 2.5 and 1.1 in BRCA2A and BRCA2B lines, respectively. Nonetheless, the rates due to BRCA2B mutants (1.1-fold) were not significantly lower compared to ours (6.3-fold). This discrepancy may arise because Wang et al. (2010) utilized a different GUS mutant line, and the chromosomal position effect on the GUS recombination substrate might influence its sensitivity (Ülker et al., 2012). Nonetheless, akin to AtBRCA2A (Wang et al., 2010), our results indicate that AtBRCA2B is requisite for maintaining spontaneous SHR rates. Comparable reporter lines have been used to screen somatic mutation rates in prior studies by mating with Arabidopsis mutants for other DNA repair genes like AtRAD54 (Osakabe et al., 2006), AtRAD51D, AtRAD51B, and AtXRCC (Da Ines et al., 2013), which also exhibited reduced SHR compared to control plants.
BRCA2, a pivotal gene in the HR pathway, has been extensively studied in animal models to deeply probe its functional dynamics. It plays a role in loading the RAD51 protein onto the ssDNA (Davies et al., 2001). RAD51 and DMC1, the two recombinases of the HR pathway, operate in somatic and meiotic cells, respectively. BRCA2 acts as a positive regulator for both of these recombinases (Kumar et al., 2019). In humans, BRCA2 interacts with RAD51 via its BRC repeat and also exerts an antagonistic function over FIGL1 (a protein with antirecombinase activity), which subsequently governs RAD51 and DMC1 (Kumar et al., 2019). A mutation in BRCA2 is known to activate alternative pathways, such as NHEJ (alt-NHEJ) and single-strand annealing (SSA), and it also possesses an antagonistic effect on Pol and RAD52-mediated RPA displacement from ssDNA, thereby constraining the alt-NHEJ and SSA repair (Han et al., 2017). In a prior study, Wang et al. (2010) reported that AtBRCA2A also significantly regulated the transcription of defense-related genes.
Given the regulatory function of AtBRCA2A and our findings on SHR rates, we sought to explore whether the absence of AtBRCA2B impacted the expression of other HR genes. The expression of four genes – BRE, BRCC36A, RAD50, and RAD54 – was reduced (by 50% or more) in the Atbrca2b mutants. Prior research demonstrated that BRE aids in the localization of the BRCA1 complex to the DSB site during SHR (Feng et al., 2009). Interestingly, in mouse embryonic cells, while BRCA2 mutations prove lethal, BRE gene over-expression can sustain these cells’ viability by facilitating the deubiquitylation of CDC25A phosphatase (Biswas et al., 2018). BRCC36 is a component of the BRCC holoenzyme complex, comprising proteins BRCA1, BRCA2, RAD51, and BRCC36. Working in tandem with BRE, BRCA1, and BARD1, BRCC36 facilitates E3 ligase activity and acts as a regulator of BRCA1 activation during ionizing radiation (IR) exposure, thus downregulation of BRCC36 expression compromises DNA repair (Chen et al., 2006). A. thaliana contains two BRCC36 homologs: AtBRCC36A and AtBRCC36B (Block-Schmidt et al., 2011). RAD54, known as a chromatin remodeling factor (Heyer et al., 2006), belongs to the SWI2/SNF2 family of helicases, regulating RAD51 (Solinger et al., 2002). Moreover, RAD54 stabilizes nucleofilament formation and strand invasion by RAD51, promotes nucleosome remodeling, and enhances homology search during HR. In DMC1 mutated plants, meiotic recombination necessitates RAD54 for RAD51-mediated DSB repair (Sanchez-Rebato et al., 2021). RAD50, part of the MREll complex, influences the predisposition to cancer due to its complex interactions with various oncogenes such as ATM, BRCA1, and CHK2 (Heikkinen et al., 2003). The expression of RAD50 and RAD51 is elevated in tissues comprising actively dividing cells (Gallego et al., 2001; Doutriaux et al., 1998). Thus, all four genes we selected are requisite for maintaining genome integrity, and our study illuminates the influence of the BRCA2B mutation on their expression.
In conclusion, our examination of the phenotype, spontaneous SHR rates, and expression analysis of HR genes using mutant BRCA2B plants reveals that AtBRCA2B is an essential homolog of BRCA2A, crucial for maintaining spontaneous HR in Arabidopsis plants. Considering that a homozygous BRCA2 condition is lethal in the mammalian system and given the high conservation of the DNA repair system in higher eukaryotes, plant system-based experiments have provided deeper insights into the functions of this pivotal gene. It could be possible that, similar to plants, BRCA2 – which is an oncogene – may also influence the expression of other DNA repair genes in animals. A similar strategy could be employed to study other mammalian homologs, where double knock-outs are lethal in animals.










