Summary
In this study, we aimed to determine the predictive parameters of in-hospital mortality and septic embolism in patients with infective endocarditis (IE). The most important finding in this study was that vegetation size, high D-dimer and low albumin increased the risk of in-hospital mortality and septic embolism in IE. Additionally, the presence of vegetation on the aortic and/or mitral valve indicates a high risk of in-hospital mortality/septic embolism in IE.
Introduction
Infective endocarditis (IE) is the infection of the cardiac endothelium and heart valves. IE can develop due to bacterial, viral or fungal pathogens [1]. The main risk factors are intravenous drug use, structural heart diseases, immunosuppression, presence of a pacemaker, hemodialysis, catheter-related bacteremia, prolonged surgery and a prosthetic valve [1, 2]. The incidence of IE ranged from 3 to 10 cases per 100,000 people but has recently increased due to the widespread use of cardiac device therapies and prosthetic heart valves [2, 3]. Despite modern medical and surgical treatment methods, morbidity and mortality are still high, and it leads to severe complications. The mortality rate in treated patients is approximately 20–25% and can be as high as 70% in some high-risk patients [2]. Advanced age, heart failure, prosthetic valve endocarditis, treatment-resistant fever, renal failure, and septic embolism are poor prognosis indicators that increase mortality [3, 4].
The primary causes of death in patients with IE are heart failure and embolism complications. Septic embolism as a complication of IE has been reported in 20–50% of patients. Vegetation size, location, mobility, and infection with Staphylococcus spp. are associated with septic embolism [2, 3, 5]. The brain is the most common site of embolic complications, accounting for approximately 50% of cases, followed by the spleen, lungs, kidneys, and extremities [3–5]. The EURObservational Research Programme analysis by the European Society of Cardiology indicated that a vegetation cut-off value beyond 10 mm predicts 30-day death in IE [6]. Furthermore, a history of heart failure, creatinine levels exceeding 2 mg/dl, the presence of coronary artery disease, the occurrence of hemorrhagic stroke, the existence of cardiogenic shock, and the absence of surgical intervention in left-sided infective endocarditis have been identified as predictors of death [6]. Research conducted in Turkey identified acute renal failure, dialysis, and cerebrovascular events as independent risk factors for IE [7, 8].
Evaluation of septic embolism predictors, which are essential in terms of mortality and morbidity, is vital for determining modifiable factors and treatment modalities to improve outcomes in IE.
Aim
We aimed to determine the predictive parameters of in-hospital mortality and septic embolism in patients with IE.
Material and methods
This study was designed as a multicenter, retrospective cohort study. The study included patients diagnosed with IE between January 2017 and June 2023 from three university hospitals in Turkey. Patients were divided into groups 1 (septic embolism or mortality +) and 2 (septic embolism or mortality –). Patients with a history of malignancy, severe liver or kidney failure, and those without optimal echocardiographic image recording were excluded from the study.
Laboratory and imaging findings of the patients were examined from the hospital record system. The modified Duke criteria defined IE as two major findings or one major and three minor or five minor findings. IE was diagnosed according to modified Duke criteria [1].
Statistical analysis
The IBM SPSS Statistics 25.0 program was used for statistical analysis. In comparing two groups regarding numerical variables, the independent sample t-test was used if the distribution was normal, and the Mann-Whitney U test was used if the distribution was abnormal. Categorical variables were shown as number (n) and ratio (%). The relationship between categorical variables was analyzed using Pearson’s χ2 and Fisher’s exact test. Normally distributed continuous variables were reported as mean ± standard deviation, while non-normally distributed variables were reported as median (interquartile range – IQR). Vegetation size, albumin, D-dimer, cut-off value, specificity, sensitivity, area under the curve (AUC) and 95% confidence interval (95% CI) were evaluated by receiver operating characteristics (ROC) analysis. The cut-off value was determined according to the Youden index. Univariable and multivariable regression analyses were conducted to identify parameters substantially associated with in-hospital mortality and septic embolism in IE. OR and 95% CI values were recorded. In addition, parameters obtained as independent predictors as a result of multivariate analysis were shown with a forest plot. Parameters predicting in-hospital mortality and septic embolism separately were evaluated with Spearman correlation analysis. Rho and p-values were recorded. The significance level for all hypotheses was set at < 0.05. The relationship between predictor parameters and in-hospital mortality/septic embolism was also examined using Spearman correlation analysis.
Results
Sixty-four patients diagnosed with IE were included in the study. Mean age and female gender ratios were not significantly different between group 1 (n = 21 patients) and group 2 (n = 43 patients) (p = 0.209 and p = 0.158, respectively). The rates of hypertension, chronic hemodialysis, history of coronary artery disease, intravenous drug use and presence of a central venous catheter were not significantly different between groups 1 and 2 (Table I). In contrast, the rates of chronic renal failure, diabetes mellitus and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease were higher in the group with septic embolism or mortality than in the group without septic embolism or mortality (p = 0.013, p = 0.023, p = 0.032, respectively) (Table I). Considering the echocardiography findings, vegetation size was larger in group 1 (20.5 ±6.0) than in group 2 (14.9 ±5.7) (p = 0.001) (Table I). Among the hematological and biochemical parameters, creatinine value (p = 0.008), D-dimer (p = 0.002), C-reactive protein (CRP) value (p < 0.001) and median sedimentation value (p = 0.001) were significantly higher in group 1 than in group 2 (Table II).
Table I
Comparison of demographic and clinical characteristics, physical examination results and imaging results of patients
| Parameter | Septic embolism or mortality (+) (n = 21) | Septic embolism or mortality (–) (n = 43) | Total (n = 64) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age [years] | 57.2 ±15.3 | 51.2 ±15.3 | 53.1 ±17.9 | 0.20 |
| Female, n (%) | 5 (23.8) | 18 (41.9) | 23 (35.9) | 0.15 |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 10 (47.6) | 13 (30.2) | 23 (35.9) | 0.17 |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 12 (57.1) | 11 (25.6) | 23 (35.9) | 0.013 |
| CKD, n (%) | 12 (57.1) | 12 (27.9) | 24 (37.5) | 0.023 |
| Chronic hemodialysis patients, n (%) | 3 (14.3) | 1 (2.3) | 4 (6.3) | 0.09* |
| Intravenous drug use, n (%) | 1 (4.8) | 1 (2.3) | 2 (3.1) | 0.55* |
| Central venous catheter, n (%) | 0 | 1 (2.3) | 1 (1.6) | 0.67* |
| CAD, n (%) | 4 (19.0) | 6 (14.0) | 10 (15.6) | 0.59 |
| Heart failure, n (%) | 7 (33.3) | 9 (20.9) | 16 (25.0) | 0.28 |
| CHD, n (%) | 3 (14.3) | 4 (9.3) | 7 (10.9) | 0.54 |
| Pacemaker, n (%) | 1 (4.8) | 0 | 1 (1.6) | 0.32* |
| Heart prosthetic valve, n (%) | 2 (9.5) | 3 (7.0) | 5 (7.8) | 0.72 |
| Rheumatic heart valve, n (%) | 2 (9.5) | 4 (9.3) | 6 (9.4) | 0.97 |
| Bicuspid aortic valve, n (%) | 1 (4.8) | 0 | 1 (1.6) | 0.32* |
| Atrial fibrillation, n (%) | 2 (9.5) | 3 (7.0) | 5 (7.8) | 0.72 |
| COPD, n (%) | 3 (14.3) | 0 | 3 (4.7) | 0.032* |
| Splenic abscess, n (%) | 1 (4.8) | 0 | 1 (1.6) | 0.32* |
| Splinter hemorrhage, n (%) | 3 (14.3) | 1 (2.3) | 4 (6.3) | 0.09* |
| Janeway lesion, n (%) | 1 (4.8) | 0 | 1 (1.6) | 0.32* |
| Osler’s nodule, n (%) | 1 (4.8) | 0 | 1 (1.6) | 0.32* |
| Glomerulonephritis, n (%) | 2 (9.5) | 0 | 2 (3.1) | 0.10* |
| Vegetation size [mm] | 20.5 ±6.0 | 14.9 ±5.7 | 16.8 ±6.3 | 0.001 |
| Aortic valve vegetation, n (%) | 11 (52.4) | 11 (25.6) | 22 (34.4) | 0.034 |
| Mitral valve vegetation, n (%) | 17 (81.0) | 23 (53.5) | 40 (62.5) | 0.033 |
| Tricuspid valve vegetation, n (%) | 3 (14.3) | 9 (20.9) | 12 (18.8) | 0.52 |
| Prosthetic valve vegetation, n (%) | 1 (4.8) | 1 (2.3) | 2 (3.1) | 0.55* |
Table II
Comparison of laboratory results of patients
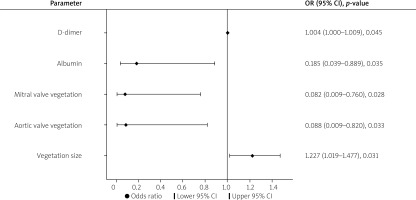
In the multivariable regression analysis, vegetation size (OR = 1.227; 95% CI: 1.019–1.477, p = 0.031), aortic valve vegetation (OR = 0.088; 95% CI: 0.009–-0.820, p = 0.033), mitral valve vegetation (OR = 0.082; 95% CI: 0.009–0.760, p = 0.028), albumin (OR = 0.185; 95% CI: 0.039–0.889, p = 0.035) and D-dimer (OR = 1.004; 95% CI: 1.000–1.009, p = 0.045) were found to be independent predictors (Table III).
Table III
Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analysis to determine predictors of in-hospital mortality and septic embolisms
A vegetation size > 17.50 mm predicted in-hospital mortality and septic emboli in IE, with 67% sensitivity and 69% specificity (ROC area under curve: 0.735, 95% CI: 0.600–0.871, p = 0.003). Albumin < 2.25 g/dl predicted in-hospital mortality and septic emboli in IE, with 90% sensitivity and 17% specificity (ROC area under curve: 0.327, 95% CI: 0.187–0.467, p = 0.030). D-dimer > 761.7 μg/l was a predictor of in-hospital mortality and septic emboli in IE, with 81% sensitivity and 67% specificity (ROC area under curve: 0.750, 95% CI: 0.607–0.893, p = 0.002) (Table IV, Figure 1).
Table IV
ROC analysis results of the association of vegetation size, albumin and D-dimer with in-hospital mortality and septic embolisms
| Parameter | Cut-off | AUC | 95% CI | P-value | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vegetation size | 17.50 | 0.735 | (0.600–0.871) | 0.003 | 67% | 69% |
| Albumin | 2.25 | 0.327 | (0.187–0.467) | 0.030 | 90% | 17% |
| D-dimer | 761.7 | 0.750 | (0.607–0.893) | 0.002 | 81% | 67% |
Figure 1
ROC analysis results of the association of vegetation size, albumin and D-dimer with in-hospital mortality and septic embolisms

Vegetation size was moderately correlated with in-hospital mortality and septic embolism (rho = 0.461, p < 0.001; rho = 0.319, p = 0.010, respectively) in IE. D-dimer was moderately correlated (rho = 0.550, p < 0.001) with septic embolism in IE. Albumin was negatively correlated (rho = –0.249, p = 0.047) with in-hospital mortality in IE (Table V, Figure 2).
Table V
Evaluation of the relationship of parameters with in-hospital mortality and septic embolisms separately by Spearman’s correlation analysis
Discussion
Evaluating the predictors of in-hospital mortality and septic embolism, one of the significant complications of IE, which has a high risk of mortality and morbidity despite treatment, is important for determining modifiable factors and treatment models to improve outcomes in IE. The most important finding in this study was that vegetation size, high D-dimer and low albumin increased the risk of in-hospital mortality and septic embolism in IE. Additionally, the presence of vegetation on the aortic and/or mitral valve indicates a high risk of in-hospital mortality/septic embolism in IE.
A study involving 37 patients diagnosed with infective endocarditis aimed to identify clinical and laboratory markers linked to in-hospital death, revealing an in-hospital mortality rate of 32.4% [9]. Creatinine and CRP values were significantly higher in the mortality group than in the other group [9]. Early diagnosis of septic emboli in IE is crucial to prevent the morbidity and mortality associated with this condition. In a retrospective study that aimed to investigate the relationship between systemic coagulation inflammation index and septic embolism, which included 167 IE patients, the rate of septic embolism was 25.7% [10]. In our study, the in-hospital mortality/septic embolism rate in patients with IE was 32.8%.
Since echocardiography plays an important role in measuring vegetation size and thus estimating embolism risk, careful measurement of maximum vegetation size at the time of diagnosis and during follow-up is recommended as part of risk stratification using both transthoracic and transesophageal echocardiography [1]. Our study confirmed vegetation detection with transesophageal echocardiography in patients with suspected vegetation on transthoracic echocardiography. Estimating embolization risks is essential for decision making in IE. Echocardiography is vital in identifying potentially embolizing structures in the heart, but predicting the time point of embolization remains difficult. Several factors are associated with an increased risk of embolism, particularly the size of the vegetation and its location on the mitral valve [11, 12]. Several studies have reported that the size and mobility of vegetations are the most important independent predictors of new embolic events [13, 14]. The risk of neurologic complications is exceptionally high in patients with very large vegetations (> 30 mm in length) [15]. Additional factors must be considered, and an embolic risk calculator may be helpful [16]. Embolic events in IE have critical prognostic implications and have been associated with increased length of stay in intensive care units and mortality. In a meta-analysis examining the relationship between vegetation size greater than 10 mm and embolism events, it was found that patients with vegetation size greater than 10 mm had higher embolic event (OR = 2.28; 95% CI: 1.71–3.05; p < 0.001) and mortality rates (OR = 1.63; 95% CI: 1.13–2.35; p = 0.009) compared to those with vegetation size smaller than 10 mm [17]. As a result of our study, we found that vegetation size > 17.50 mm was a predictor of in-hospital mortality and septic embolism in IE.
D-dimer indicates both fibrin turnover in vegetation and autoimmune inflammatory response in patients with IE. Seventy-nine patients with IE were included in a study investigating the relationship between D-dimer level and in-hospital mortality and complications in patients with IE [18]. In-hospital mortality occurred at a rate of 39%. D-dimer levels were significantly higher in the group with in-hospital mortality compared to the group without (median 3048.0 (IQR = 4911.0) vs. 556.0 (IQR = 1100.2) ng/ml, p < 0.001). When the D-dimer value was 795 ng/ml or higher, the sensitivity and specificity for in-hospital mortality were 83.5% and 66.7%, respectively [18]. In our study, the mean D-dimer level was higher in the group of IE patients who developed in-hospital mortality/septic embolism compared to the patient group without mortality/septic embolism. Also, in multivariable regression analysis, D-dimer level was found to be an independent predictor. In addition, similar to the results of the study mentioned above, we found that D-dimer > 761.7 was a predictor of in-hospital mortality and septic embolism in IE, with 81% sensitivity and 67% specificity. These findings support the view that a high D-dimer level is a predictor of in-hospital mortality or embolism in patients with IE.
Albumin is an essential acute-phase protein with anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antiplatelet functions. Increased inflammatory status, such as IE, may decrease albumin synthesis and increase catabolism, associated with poor prognosis. Low albumin levels are associated with increased mortality, especially in critically ill patients with IE [19–21]. In a study that aimed to evaluate preoperative serum albumin as a biomarker to predict early mortality after IE surgery, 20 of 276 IE patients (7.2%) died in hospital or within 30 days of surgery. Hypoalbuminemia (albumin level < 3.5 g/dl) was present in 109 (39.5%) patients [20]. In conclusion, preoperative serum albumin was found to be inversely associated with early mortality after IE surgery [20]. Our research demonstrated that albumin can predict septic embolism and mortality in descriptive statistical analyses, logistic regression, and ROC analyses. Nevertheless, the relatively low AUC value implies that it may be a less specific predictor than D-dimer and vegetation size. Including albumin in a score or index parameter may be more significant than its use alone. A retrospective study including 196 patients with IE investigated whether there was a relationship between CRP/albumin values and prognosis [21]. Serum CRP/albumin values were associated with prognosis in IE patients. According to Cox regression analysis, the admission serum CRP/albumin ratio remained an independent predictor of mortality (p < 0.05) [21].
Limitations. The study’s main limitations are the small number of centers and patients included. The rarity of IE has led to this situation. Other limitations of our study include the retrospective nature of the study and the lack of analysis of the patients’ long-term prognosis.
Conclusions
Vegetation size, high D-dimer, and low serum albumin levels are predictive parameters of in-hospital mortality and septic embolism in patients with IE. Identifying the predictive parameters of in-hospital mortality/septic embolism is important in terms of determining modifiable factors and a treatment model and initiating treatment at an early stage.