Introduction
The primary exocrine function of the liver is the secretion of bile. Hepatocytes are responsible for 60% of bile production. Epithelial cells of the bile ducts (cholangiocytes), constituting 3-5% of the liver cell population, secrete the remaining 40% of the bile volume. Abnormalities in bile production involving hepatocytes and cholangiocytes and obstructions in bile flow lead to the development of cholestasis. Cholestasis may accompany high activity of parenchymal liver disease or advanced fibrosis. On the other hand, cholestatic diseases may contribute to an increase in the activity of liver enzymes through secondary damage to hepatocytes. Cholestasis in the course of infections is more common in children than in adults. In neonates and infants, the risk of jaundice due to severe infection is 20-60%. Much less frequently, cholestasis is a complication of viral infection, fungal infection or protozoan invasion [1, 2]. The liver’s first response to inflammation is the activation of Browicz-Kupffer cells, which constitute 70% of the entire macrophage population. In addition to bacterial endotoxins, bacteria and viruses, they also remove inflammatory mediators from the intestines or other organs, limiting the spread of inflammation. Their activation also leads to the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as tumour necrosis factor α (TNF-α), interleukin (IL)-1, IL-6, IL-12, nitric oxide, and free radicals. The inflammatory response affects the expression and function of key hepatobiliary transporters [3].
The excretion of bile acids is dependent on a well-functioning hepatobiliary system. Microbial products such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and endotoxin directly stimulate hepatocytes and Kupffer cells to secrete cytokines that inhibit the expression of bile duct transporter genes, especially sodium-taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide (NTCP) and bile salt export pump (BSEP). The main protein involved in this process is the BSEP transporter. BSEP has ATPase activity and is expressed almost exclusively in the liver [4]. It consists of 1321 amino acids with a molecular weight of ~160 kDa. The ATP binding cassette subfamily B member 11 (ABCB11) gene encoding the BSEP protein is located on chromosome 2q24-31 and consists of 27 coding and 1 non-coding exon [5]. A decrease in its activity may contribute to the development of cholestasis. Some mutations in the ABCB11 gene responsible for BSEP transport protein deficiency are closely associated with a specific form of cholestasis.
Single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) have been documented to affect BSEP activity [6]. To date, 86 polymorphisms in BSEP have been described in Caucasian, Korean and African-American populations. Genetic mutations in BSEP can result in altered BSEP function and subsequent liver disease. These mutations cause a range of mild to severe progressive forms of intrahepatic cholestasis. In addition, pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6 and TNF-α reduce BSEP protein expression thereby disrupting bile acid homeostasis [7, 8]. To date, documented SNPs that reduce BSEP expression and affect the development of secondary cholestasis, e.g. drug-induced liver injury (DILI), include c.1331T>C (p.V444A) in exon 13 and c.2029A>G (p.M677V) in exon 17, which have a frequency of more than 0.5% [9]. The c.1331 T > C (p.V444A) polymorphism (rs2287622) is a point transition of thymine from position 1331 to cytosine. Serum bile acid concentrations in carriers of the 1331CC genotype have been shown to be higher than those in carriers of the 1331TT genotype, while the 1331C allele is more common in patients with DILI and intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (ICP) than the 1331T allele [10, 11]. Individuals with low or very low BSEP levels have a higher frequency of the C allele than those with normal BSEP levels [8]. There are clinical studies showing that in patients with intrahepatic cholestasis or idiopathic cholestasis during pregnancy, the V444A polymorphism is responsible for the inhibition of bile acid transport out of hepatocytes. Others suggest that the BSEP V444A polymorphism may be associated with the development of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection, progression of liver fibrosis and long-term response to treatment, as well as with drug-induced liver damage [12, 13]. The aim of our study was to analyse the rs11568364 and rs2287622 polymorphisms of the ABCB11 gene as potential biomarkers of hepatological complications in EBV-infected children.
Material and methods
The study included 68 children, comprising 36 girls and 32 boys aged between one and 18 years, hospitalised between 01.12.2018 and 31.12.2020 in the Department of Paediatrics, Infectious Diseases and Hepatology with serologically and molecularly confirmed EBV infection. The study group consisted of 54 children with hepatological complications (Table 1). Two subgroups were identified: with increased alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and γ-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGTP) activity, to which 33 patients were classified (Group IA); and a 21-person subgroup of patients with increased ALT activity and normal GGTP (Group IB). The control group consisted of 14 EBV-infected children with normal ALT and GGTP activity (Group II). The comparison group consisted of 13 healthy children in whom EBV genetic material was excluded by molecular testing (Group III) (Tables 2 and 3).
Table 1
Reference values of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and γ-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGTP) activity
Table 2
Baseline characteristics of EBV-infected patients with hepatological complications (IA, IB) and the control group (II)
| Parameter | IA n = 33 | IB n = 21 | II n = 14 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | ||
| Sex | Girls | 22 (76) | 10 (48) | 5 (36) |
| Boys | 11 (33) | 11 (52) | 9 (64) | |
| Age (years) | < 5 | 2 (6) | 0 (0) | 3 (21) |
| 5-10 | 10 (30) | 7 (33) | 5 (36) | |
| > 10 | 21 (64) | 14 (67) | 6 (43) | |
| BMI (kg/m2)* | Underweight | 2 (6) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Normal weight | 23 (70) | 21 (100) | 13 (93) | |
| Overweight | 7 (21) | 0 (0) | 1 (7) | |
| Obesity | 1 (3) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | |
Table 3
Median values (Q1-Q3) for the parameters studied in group IA (n = 33), group IB (n = 21) and group II (n = 14)
[i] Median values (Q1-Q3) for the parameters studied in group IA (n = 33), group IB (n = 21) and group II (n = 14); IA – group with increased ALT and GGTP activity, IB – group with increased ALT and normal GGTP activity, II – control group with normal ALT and GGTP activity; WBC – white blood cell, ALT – alanine aminotransferase, GGTP – γ-glutamyl transpeptidase, CRP – C-reactive protein
This study was approved by the scientific and ethical committees of Nicolaus Copernicus University in Torun and Ludwik Rydygier Collegium Medicum in Bydgoszcz. Informed consent letters for diagnostic tests on admission to the hospital were obtained from the children’s parents.
Antibodies against EBV were detected with the LIAISON EBV IgM assay (DiaSorin) using chemiluminescence immunoassay (CLIA) technology. The test was performed on a LIAISON XL analyser. Isolation of EBV DNA genetic material was performed using the Maxwell RSC Viral Total Nucleic Acid Purification Kit. A real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method was employed to quantify EBV DNA viral load using TaqMan probes according to the manufacturer’s protocol, using a pair of primers with the following sequences: for EBV 5’-GGGCTCTGGAGGCACCTA-3’and for RevEBV 5’-CCACCCCA GTCCCGTC-3’. A 99 base pair (bp) fragment of the non-coding region of the EBV genome (nucleotides 13640-13739) was amplified by primers using a 16 bp molecular probe: 5’-TCGAGGCAGGCTTACA-3’. Sensitivity levels of 16 copies/ml were applied. ALT and GGTP activities were determined according to the manufacturer’s protocols using a standard enzyme-colourimetric assay (COBAS INTEGRA 400/800, Roche).
Identification of single nucleotide poly-morphisms in bile salt export pump ABCB11
In order to perform genotyping analyses, first of all, genomic DNA was isolated from peripheral whole-blood samples collected in 0.5 M EDTA tubes using the commercial QIAamp DNA Blood Mini Kit. The DNA extraction process was performed according to the manufacturer’s instructions. After isolation, the samples were stored at –20°C until further analysis. The amount and purity of extracted DNA were assessed by measuring absorbance in a NanoDrop ND 2000 spectrophotometer. DNA concentration was calculated using the relationship: absorbance equal to 1 at a wavelength of 260 nm corresponds to 50 ng/μl DNA. The assessment of the purity of the isolates was based on the absorbance coefficients A260/A280 and A260/A230. The essence of this study is the genotyping of single nucleotide variation in the ABCB11 gene. For this purpose, real-time PCR using TaqMan probes was used. In this study, two polymorphisms of the ABCB11 gene were analysed – rs11568364 and rs2287622 – using commercially available predesigned TaqMan SNP Assays Kits (Thermo Fisher) containing appropriate sets of primers and probes for the target marker. The used probes complementary to individual alleles for a given marker were labelled with two FAM or VIC dyes. Real-time PCR was performed in 96-well PCR plates using the CFX Connect instrument (Bio-Rad) with the following standard reaction conditions: 95°C for 10 min, 95°C for 15 s, followed by 35 cycles of 60°C for 1 min. The composition of the reaction mixture included isolated genomic DNA (50-100 ng), TaqMan primers and probes, reaction buffer with DNA polymerase (LightCycler 480 Probes Master; Roche Diagnostics) and PCR grade water. 9 μl of the reaction mixture and 1 μl of genomic DNA were pipetted into each well. For each prepared reaction mixture, a negative control was performed in which the DNA was replaced with 1 μl of PCR grade water. Knowing the labelling of dyes for the detection of individual alleles of the analysed genetic marker, its genotype was read for each sample by fluorescence detection.
Statistical analysis
The values of the study parameters were measured as categorical variables. Categorical variables were described using counts and percentages (%). Differences in the distributions of categorical variables between analysed patients groups were assessed using Pearson’s chi-square test or Fisher’s exact test in the case of small group sizes. For comparisons of quantitative variables, the non-parametric Mann-Whitney U test for two independent groups was used. Odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were also calculated for association tests between the ABCB11 polymorphisms and the binary clinical variables. All statistical analyses were performed with SPSS software version 28 for Windows. For all tests, two-tailed p-values were used and the results were considered statistically significant when the p-value was less than 0.05.
Results
Based on the genotyping performed, the allele and genotype distributions were determined for the two ABCB11 gene markers with reference numbers rs11568364: c.2029A>G (p.M677V) and rs2287622: c.1331T>C (p.V444A) in the study and control groups. For the marker rs11568364, a heterozygous AG genotype was obtained in only one patient with hepatitis and biliary pole lesion. In the remaining 67 children analysed, the homozygous AA variant was observed. Therefore, this polymorphism was not included in further analyses. For the rs2287622 marker, the heterozygous TC variant was most common in the study group (IA and IB), in contrast to the control group (II), in which the CC genotype was most common. The homozygous TT genotype was not observed in the control group (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1
Genotype distribution for marker rs2287622. IA – group with increased ALT and GGTP activity, IB – group with increased ALT and normal GGTP activity, II – control group with normal ALT and GGTP activity
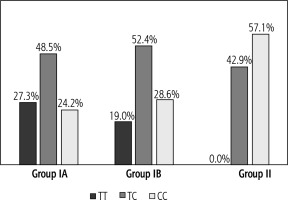
The significance of the rs2287622 marker for the development of hepatologic complications was determined by the allele frequency and genotypes of this marker in the different groups of patients analysed (Table 4).
Table 4
Distribution of genotypes and alleles for the 1331T > C polymorphism of the ABCB11 gene
Patients with the TT genotype were significantly more likely (p = 0.042) to present hepatitis with biliary pole damage compared to patients with the TC or CC genotype. The CC genotype reduced this risk by about 4-fold (OR = 0.24, 95% CI: 0.06-0.90) compared to patients with at least one T allele. For patients with hepatitis without a concomitant biliary pole lesion (group IB), there were no statistically significant differences between genotypes compared to the control group (II). Statistically significant differences in allele distribution were obtained for both group IA and IB patients. The observed level of statistical significance in these groups was p = 0.007 and p = 0.042, respectively. Patients in group IA showed the highest frequency of the T allele of the marker rs2287622 compared to children in groups IB and II (51.5% vs. 45.2% vs. 21.4%, respectively). It was calculated that having the T allele of rs2287622 increases the risk of hepatitis by 3-fold (OR = 3.029, 95% CI: 1.020-8.99) and the possibility of hepatitis with cholestasis by nearly 4-fold (OR = 3.89, 95% CI: 1.40-10.84) in EBV-infected patients.
Discussion
Primary bile acids are synthesised in hepatocytes. These include cholic acid (CA) and chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA). As a result of their metabolism in the intestines, secondary acids are formed: deoxycholic acid (DCA) and lithocholic acid (LCA). The individual bile acids differ in their physicochemical characteristics and biological properties, the most important of which is hydrophilicity. Of the major bile acids, CA is the most hydrophilic and LCA the least hydrophilic. The second important characteristic of bile acids is their toxicity. The severity of this feature is inversely related to hydrophilicity, with LCA being the most toxic and CA showing the least toxicity [14]. The pathomechanism of the cytotoxicity of the most hydrophobic bile acids is not yet fully understood. Several theories exist. One is that they destabilise cell membranes through their detergent action on its lipid components and thereby promote the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which in turn oxidatively modify lipids, proteins and nucleic acids, ultimately causing apoptosis of hepatocytes. Additionally, they can activate Kupffer cells to produce ROS, which can further contribute to liver cell damage [15].
The reciprocal proportions of these bile acids influence the maintenance of homeostasis in the lumen of the gastrointestinal tract, influencing the proper functioning of hepatocytes. The accumulation of hydrophobic bile acids such as CDCA and DCA has long been considered the main cause of liver damage in cholestasis. This parenchymal cell damage, which occurs at the onset of cholestasis, induces inflammatory responses and stimulates the secretion of growth factors, cytokines, chemokines.
ABCB11, classified as an ABC transporter, is a liverspecific group of transport proteins responsible for the export of conjugated bile acids from the hepatocyte to the bile ducts. Uptake of bile salts across the sinusoidal membrane occurs predominantly in a sodium-dependent manner and is mediated by the sodium-taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide (NTCP) and to a minor extent by the sodium-independent organic anion transporting polypeptides (OATPs). BSEP gene expression is mainly regulated by the farnesoid X receptor (FXR). Expression and activation of FXR in the cell are key to transcription and activation of the ABCB11 gene. FXR, encoded by NR1H4, binds to the retinoic X receptor (RXR) and as a heterodimer binds to the appropriate response element FXR (FXRE) in the promoter of the ABCB11 gene encoding BSEP. Loss of farnesoid X receptor expression is associated with loss of BSEP protein expression, resulting in a phenotype typical of progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. The patients with inherited mutations in the ABCB11 gene resulting in the absence of functional BSEP in the canalicular membrane develop early in life severe liver disease and are at a high risk of developing liver malignancies. Homozygous loss-of-function mutations of the ABCB11 gene result in the development of progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis 2 (PFIC2) and benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis 2 (BRIC2) [16]. The ABCB11 polymorphism has also been found to be associated with other inherited and acquired forms of cholestasis, such as mild recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis and drug-induced cholestasis. Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (ICP) and oral contraceptive-induced cholestasis (CIC) are two acquired forms of cholestasis that affect previously healthy young women. They are reversible in nature, suggesting that female sex hormones play a key role in these forms of cholestasis. There are a number of reports supporting an association between ABCB11 polymorphisms and ICP. In our study, girls constituted a statistically significantly higher proportion in the group with biliary pole lesions than in the EBV-infected group without hepatological complications. A study by Piątek et al. in a group of 96 women with ICP showed a higher frequency of the homozygous 1331CC genotype. These data are consistent with the results of Meier et al. and indicate that all female patients with ICP and CIC were homozygous carriers of the C allele at position 1331 [11, 17]. They observed the lowest bile acid concentrations in patients with the 1331TT genotype and the highest in those with the 1331CC genotype. The authors stated that dysfunction of the bile acid transporter BSEP resulting from the presence of the 1331CC ABCB11 genotype may lead to the development of cholestasis during oral contraception. The BSEP V44A polymorphism (1331T > C, rs2287622) has been identified as a risk factor for DILI in Caucasians [18]. Ulzurrun et al. investigated the impact of the 1331T>C ABCB11 polymorphism on the development of DILI. The homozygous CC genotype was found to be significantly associated with absent hepatocytes and DILI consequences in support of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory (NSAID) definitions [19]. The effect of the rs2287622 polymorphism on the development of DILI in the Chinese version was not confirmed in the study by Chen et al. [20]. Based on this, it can be assumed that the advice regarding the influence of BSEP polymorphisms on the development of DILI should also take into account the ethnicity of the members. Some risk may be specific to the ethnic group and drug.
The possibility of using the BSEP V44A polymorphism (1331T > C, rs2287622) as a non-invasive marker of the development of liver cirrhosis in the course of hepatitis C was demonstrated by Iwata et al. Age, gender, alcohol use, age at infection and co-infection with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) influence the progression to cirrhosis, but cannot accurately predict the individual risk of developing cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Iwata et al. observed in their study a significant association between the presence of cirrhosis and 1331CC ABCB11 genotype [21]. This correlation was not confirmed for patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). In the group of patients with chronic hepatitis C, no significant increase in bile acid concentration was observed for the 1331CC ABCB 11 genotype. Increased bile acid levels were observed in patients with hepatitis C virus (HCV) induced cirrhosis compared with non-cirrhotic patients. This indicates that the increased concentration of bile acids depends not only on genetic predisposition, but also on the inflammatory process in the liver. Analysis by Iwata et al. showed an association of the 1331CC ABCB11 genotype with progression of fibrogenesis during chronic hepatitis C infection.
Little information has been available regarding the functional relevance of genetic polymorphisms in ABCB11, despite increasing evidence supporting a crucial role of this transporter in the hepatic efflux of bile acids and its inhibition as a likely cause for drug-induced liver injury. To date, no studies have been conducted in the Polish paediatric population on the association between BSEP polymorphisms, EBV infection and the risk of developing hepatological complications. Similar analyses have also not been described in the available English-language literature. Our study showed that the presence of the T allele for the marker rs2287622 increases the risk of hepatitis by 3-fold and the possibility of hepatitis with cholestasis by nearly 4-fold in EBV-infected patients. In addition, the predominance of the homozygous 1331TT genotype was confirmed in the group of patients with hepatitis and biliary pole damage in the course of EBV infection. The data obtained may suggest that the single nucleotide polymorphism of the marker rs2287622 leading to a homozygous mutation disrupts the function of the ABCB11 gene, leading to impaired membrane transporter function, and thus contributes to an increased incidence of hepatological complications in EBV-infected patients.
The possibility of using SNPs as non-invasive markers of hepatological complications in the course of viral diseases requires further research. Understanding the molecular mechanisms of impaired BSEP function and knowledge about the pathomechanism of enterohepatic circulation are necessary to optimize therapeutic options in the group of patients at risk of developing hepatological complications in the course of infectious diseases. It will enable the optimisation of patient groups in whom the rapid application of ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) will improve prognosis, shorten the length of hospitalisation and influence the regulation of the hepatic-intestinal circulation. Indeed, UDCA, being a natural bile acid with no cytotoxic effects, has been shown to play an important role in preventing oxidative damage through direct antioxidant activity. The amide forms of UDCA inhibit the intestinal absorption of endogenous bile acids and increase bile acid secretion without altering bile acid synthesis. This leads to a reduction in the concentration of endogenous, hydrophobic bile acids in the blood, liver and extrahepatic tissues, thereby maintaining homeostasis of the hepatic-intestinal circulation [14, 22].
A limitation of the study is the small size of the study group. Confirmation of the results obtained will require further studies on a larger number of patients.
Conclusions
The present analysis suggests the possibility of using the rs2287622 polymorphism of the ABCB11 gene as a predictor of hepatological complications among EBV-infected children. The presence of the T allele for the rs2287622 marker increases the likelihood of hepatitis by 3-fold and the possibility of hepatitis with cholestasis by nearly 4-fold in EBV-infected patients.






