Introduction
In the field of immunology, our understanding of T-lymphocyte subpopulations and their functions has undergone significant advances in recent years [1]. These findings challenge the traditional categorization of lymphocyte function and call for a reevaluation of the characteristics attributed to different T-lymphocyte subsets. These new developments have been made possible by innovative reagents and techniques, which have allowed researchers to gain insights into thymic differentiation status and the phenotypes of both premalignant and malignant lymphocytic infiltrates [2]. Furthermore, the identification of previously unrecognized cells within lymphomas and the distinction between circulating and skin lymphocytes have provided valuable information. These discoveries not only expand our knowledge of T-lymphocyte biology, but also have potential therapeutic applications [3]. The study of T-lymphocyte subpopulations is a rapidly evolving field in immunology, challenging the conventional division of lymphocyte function [4]. Using advanced reagents and techniques, scientists have been able to gain a deeper understanding of T-lymphocyte subpopulations and their roles in immune responses.
Helper (Th) or memory (Tm) lymphocytes?
The classical division treats the two subpopulations as distinct. However, the introduction of single cell analysis techniques and the associated discovery of new lymphocyte surface markers disrupts this division. Increasingly, the newly discovered subpopulations of helper lymphocytes also show the function performed by the hitherto separate memory lymphocytes [5-7].
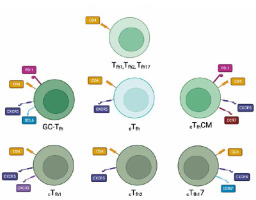
Helper lymphocytes, also known as CD4+ T cells, play a crucial role in regulating immune responses and maintaining immune homeostasis. Recent research in the field of immunology has uncovered several new variants of helper lymphocytes (Fig. 1), expanding our understanding of their diverse functions and potential therapeutic applications [8]. One of the emerging variants of helper lymphocytes is Tfh1, which stands for T follicular helper 1 cells. Tfh1 cells (Table 1) are a subset of helper lymphocytes that are characterized by their ability to provide help and support to B cells in the germinal centers of lymphoid structures and promote effective adaptive immune responses [9]. Another variant that has gained attention is Tfh2, which refers to T follicular helper 2 cells [10]. Tfh2 cells (Table 1) are involved in promoting humoral immunity and have been implicated in various diseases, including autoimmune disorders and allergic reactions [11]. In addition to Tfh1 and Tfh2 cells, another variant that has emerged is Tfh17 [10]. Tfh17 cells (Table 1) represent a specialized subset of helper lymphocytes that produce the cytokine interleukin (IL)-17 and are involved in promoting immune responses against extracellular pathogens and maintaining tissue barrier functions [12]. These Tfh subsets can be found in the germinal centers of lymphoid tissues, where they assist B cells in antibody production. However, they are not restricted to these sites. Studies have shown that Tfh1, Tfh2, and Tfh17 cells can also be detected in the peripheral blood, indicating their presence in circulation. This is essential for their role in systemic immune responses and their ability to migrate to different sites as needed [13-16]. Furthermore, the discovery of germinal center T follicular helper cells has shed light on a distinct population of helper lymphocytes that provide critical support to B cells in the germinal centers during the process of antibody production and affinity maturation [17]. These cells, known as GC-Tfh cells (Table 1), play a crucial role in shaping the humoral immune response and have been implicated in both protective and pathological immune responses [11]. Another noteworthy variant of helper lymphocytes is cTfh, which stands for circulating T follicular helper cells. cTfh cells (Table 1) are a subset of helper lymphocytes that circulate in the bloodstream and can migrate to secondary lymphoid organs, such as lymph nodes and the spleen, where they interact with B cells and contribute to the generation of antibody responses [18]. Specific subsets of circulating Tfh cells have also been identified, including cTfhCM, cTfh1, cTfh2, and cTfh17 [19] (Table 1). cTfhCM stands for circulating T follicular helper central memory cells, which are a subset of cTfh cells that possess memory-like properties and can provide long-lasting immune protection upon re-exposure to a specific antigen [20]. cTfh1 cells are a circulating subset of T follicular helper cells that primarily produce the cytokine interferon γ and have been associated with enhancing cellular immune responses and promoting antiviral immunity [17]. cTfh2 cells are another subset of circulating T follicular helper cells that produce the cytokine IL-4 and have been implicated in promoting humoral immune responses and supporting the generation of antibody production [18]. These subsets of cTfh cells have been found to play important roles in various diseases and immune responses [19]. Recent studies have highlighted the involvement of Tfh subsets in autoimmune disorders and allergic reactions. For example, Tfh17 cells have been shown to play a role in autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis, where they contribute to the activation of auto-reactive B cells and the production of pathogenic autoantibodies [21]. Additionally, Tfh subsets have also been implicated in certain types of cancer [9]. In the context of cancer, Tfh subsets have been found to infiltrate tumor tissues and play a dual role in either promoting or inhibiting anti-tumor immune responses, depending on the specific context [10]. Overall, the discovery of these new variants of helper lymphocytes has significantly expanded our understanding of their roles in immune responses and disease pathogenesis [22].
Table 1
Summary of Tfh lymphocytes and their surface markers
| Name of the population | Surface markers | |
|---|---|---|
| Tfh1 | CXCR5–, CD4+ | CXCR3+CCR6- [29] |
| Tfh2 | CXCR3+CCR6- [29] | |
| Tfh17 | CXCR3+CCR6+ [29] | |
| GC-Tfh | CD4+ CXCR5high PD-1high BCL6high | |
| cTfh | CD4+ CD45RA–CXCR5+ | |
| cTfhCM | CD4+ CXCR5+ CCR7high PD-1low CD4+ CXCR5+ CCR7low PD-1high | |
| cTfh1 | CD4+ CD45RA–CXCR5+ CXCR3+ CCR6– | |
| cTfh2 | CD4+ CD45RA–CXCR5+ CXCR3– CCR6- | |
| cTfh17 | CD4+ CD45RA–CXCR5+ CXCR3– CCR6+ | |
Cytotoxic lymphocytes (CTL)
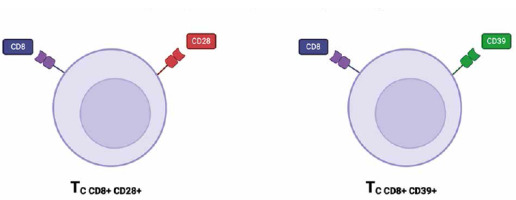
Cytotoxic T lymphocytes play a vital role in the immune response against pathogens and cancer cells by recognizing and eliminating target cells [23]. In recent years, new subsets of cytotoxic T lymphocytes have been identified and characterized, including CD8+CD39+ and CD8+CD28+ T cells (Fig. 2) [24]. These subsets have garnered interest due to their unique functional properties and potential for therapeutic applications in cancer immunotherapy [25]. The CD8+CD39+ T-cell subset was found in various locations within the body, with significant presence in tumor microenvironments, especially within tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs). These cells have been observed in lymph node metastases from melanoma patients, where they are associated with the regulation of immune responses within the tumor context. In addition to tumor patients, CD8+CD39+ T cells have been found in the peripheral blood of healthy patients [26-28]. These cytotoxic T cells subset has been found to express high levels of the ectonucleotidase CD39, which hydrolyzes ATP to AMP and ADP [29]. CD73 converts it into immunosuppressive adenosine. Adenosine interacts with adenosine receptors on immune cells, leading to the suppression of T cell activation, proliferation, and cytokine production. CD73 expression on CD8+ T cells can enhance the immunosuppressive effects initiated by CD39, contributing to the inhibition of effective anti-tumor immune responses. In the tumor microenvironment (TME), high levels of CD73 are often associated with worse prognoses due to the increased production of adenosine, which dampens the cytotoxic functions of CD8+ T cells and supports tumor progression [29-31]. This immunosuppressive property allows CD8+CD39+ T cells to dampen immune responses and contribute to immune tolerance [24]. On the other hand, CD8+CD28+ T cells are characterized by the expression of the co-stimulatory molecule CD28 [23]. CD28 provides a critical signal for T cell activation and enhances the cytotoxicity of CD8+ T cells [24]. CD8+CD28+ T cells are primarily found in the peripheral blood and lymphoid tissues, playing a crucial role in the immune system by providing costimulatory signals necessary for T cell activation and survival [32]. The presence of CD8+CD28+ T cells has been associated with a more potent anti-tumor immune response and improved clinical outcomes in cancer patients receiving immunotherapy [33]. Several studies have highlighted the functional capabilities of CD8+CD39+ and CD8+CD28+ T cells in different disease contexts. For instance, CD8+CD39+ T cells have been implicated in the regulation of autoimmune diseases by suppressing excessive immune activation [23]. Additionally, CD8+CD28+ T cells have shown efficacy in tumor cell killing and have been associated with favorable outcomes in cancer patients [33]. In the context of HIV infection, CD8+CD28+ T cells play a crucial role in the immune response against the virus. These cells are involved in the early stages of infection, providing essential costimulatory signals for T cell activation and proliferation. CD28 is a key molecule that enhances T cell receptor (TCR) signaling, leading to increased cytokine production, cell survival, and proliferation [34, 35]. CD8+CD28+ T cells play a significant role in the pathogenesis and progression of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). These cells contribute to the autoimmune response, inflammation, and joint damage characteristic of RA. Their presence in synovial fluid indicates active participation in the local inflammatory response, with sustained cytokine production driving chronic inflammation. Modulating the activity of these T cells could help control RA, making them potential therapeutic targets [36, 37]. However, when discussing CD8+CD28+ lymphocytes, one cannot fail to mention CD8+CD28– immunosenescent T cells. Immunosenescent CD28– T cells play significant roles in the TME due to their unique characteristics and impact on tumor immunity [38]. These cells, which lack the costimulatory molecule CD28, are commonly found in various cancers and are associated with poor prognosis [39]. These cells contribute to the immunosuppressive environment of tumors by secreting inhibitory cytokines such as IL-10 and TGF-β, which suppress the activity of effector T cells [40]. Their presence in the TME can hinder effective immune responses against tumor cells. The presence of immunosenescent CD28- T cells poses a challenge for immunotherapy. These cells are less responsive to treatments such as checkpoint inhibitors, which aim to reinvigorate exhausted T cells. This reduced responsiveness necessitates alternative strategies to either target these cells for removal or restore their function [38-41]. Further research on these subsets of cytotoxic T lymphocytes is needed to fully understand their mechanisms of action and optimize their use in therapeutic approaches.
In describing the CD28 molecule and its role, terminally differentiated effector memory T cells (TEMRA) are worth mentioning. TEMRA are a subset of CD8+ T cells characterized by their unique phenotype and functional attributes, often associated with the expression of CD28 [42]. TEMRA cells typically exhibit markers of terminal differentiation, including CD45RA and the loss of CD27 and CD28. However, subsets of TEMRA cells can still express CD28, indicating some degree of functional variability within this population [43]. These cells are commonly found in the peripheral blood as well as within the tumor microenvironment, where they can adopt different phenotypes depending on their location and the signals they receive [42]. TEMRA cells are highly cytotoxic, possessing a potent ability to produce effector molecules such as perforin and granzyme B. This cytotoxic capacity allows them to effectively target and kill infected or malignant cells [44]. The loss of CD28, however, can impair their proliferative response and reduce their capacity to mount sustained immune responses, which is particularly relevant in chronic infections and cancer [42]. Within tumors, TEMRA cells often display an exhausted phenotype, characterized by the expression of inhibitory receptors such as PD-1. This exhaustion limits their effectiveness in anti-tumor responses [43]. Additionally, the presence of CD28– TEMRA cells in tumors is associated with poor prognosis, as these cells can contribute to an immunosuppressive environment that supports tumor growth and progression. Understanding the dual roles of CD28+ and CD28– TEMRA cells in cancer can provide insights into their contributions to immune evasion and tumor progression. Targeting the pathways that regulate the differentiation and function of TEMRA cells could enhance the effectiveness of immunotherapies, particularly in cancers where these cells are prevalent and functionally impaired [42-44].
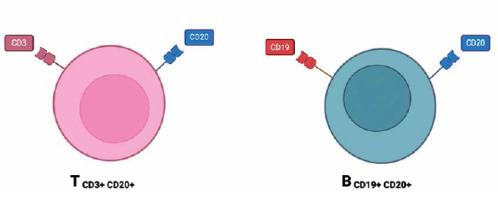
CD20+ T lymphocytes
CD20 is a cell surface antigen found on B cells and plays a crucial role in the regulation of B cell development and differentiation [22, 45]. CD20+ T cells, a newly discovered subset of T cells expressing the CD20 antigen (Fig. 3), have gained significant interest in recent research [46]. These CD20+ T cells have been found to possess unique characteristics and effector functions that make them promising candidates for immunotherapeutic interventions in various diseases including cancer, autoimmune disorders, and infectious diseases [47]. The presence of CD20+ T cells was initially thought to be an anomaly, as CD20 was primarily considered a B cell-specific marker. However, recent studies have demonstrated that a small subset of human T cells expresses low levels of CD20 or a cross-reacting antigen [7]. Further investigations using different CD20 monoclonal antibodies, such as Leu16, B1, and 1F5, have confirmed the presence of CD20 on T cells [46]. CD20+ T lymphocytes have been identified in many human tissues, i.e. peripheral blood, spleen, bone marrow, thymus, cerebral spinal fluid and tonsils [48-50]. The functional significance of CD20 expression on T cells is a topic of ongoing research. Recent studies have revealed that CD20+ T cells possess cytotoxic effector programs and can mediate direct killing of tumor cells. These findings suggest that CD20+ T cells play a role in anti-tumor immunity and have the potential to be used as therapeutic targets in cancer immunotherapy. Furthermore, omics technologies have provided further insight into the clinical relevance of CD20+ T cells in cancer. Single-cell RNA sequencing analyses of intra-tumoral immune cells have identified CD4+ T cells expressing cytotoxic molecules, including CD20, in a broad range of cancer types [7]. These cytotoxic CD4+ T cells have been found to exhibit MHC-II-restricted direct cytotoxicity against patient tumor cells, and their presence has been associated with a favorable prognosis or clinical response to anti-PD-L1 therapy or therapeutic vaccination [48]. Moreover, the therapeutic importance of CD20+ T cells extends beyond cancer immunotherapy. CD20+ T cells have also shown potential in the treatment of autoimmune disorders and infectious diseases. For example, in autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis, CD20+ T cells have been implicated in sustaining a local microenvironment that promotes disease progression. In infectious diseases, CD20+ T cells may have a role in modulating the immune response and potentially contributing to pathogen clearance [7]. In conclusion, the discovery of CD20+ T cells challenges the traditional view of CD20 as a B cell-specific marker. These findings highlight the need for further research to elucidate the functional significance of CD20 expression on T cells and explore its potential as a therapeutic target in anti- tumor immunity, autoimmune disorders, and infectious diseases [46].
Conclusions
This review article highlights significant advances in the understanding of T-lymphocyte subpopulations and their functions, shedding new light on the complexity of the immune system and potential therapeutic implications. Discoveries of new variants of helper lymphocytes, such as Tfh1, Tfh2, Tfh17, GC-Tfh, and cTfh cells and their different subtypes, together with the characterization of newly identified subpopulations of cytotoxic T cells, open new pathways for understanding the mechanisms of the immune response and the development of diseases.
Also, the demonstration of specific functions and surface markers of these T-lymphocyte subpopulations points to the possibility of more targeted interventions in various pathological conditions, including cancer, autoimmune diseases, and infections.
In conclusion, these breakthroughs in the immunology of T-lymphocyte subpopulations not only expand our knowledge of the complex ecosystem of the immune system, but also open new perspectives for the development of new therapeutic strategies. Further research is needed to fully understand the clinical potential of these discoveries and their application in medical practice, which may lead to the development of new, more effective targeted therapies.