In children, skeletal growth and development are governed primarily by the calcium-phosphate homeostasis. About 99% of systemic calcium and 80% of phosphorus are used to form hydroxyapatite, the basic component of bone support. In addition, a small amount of calcium in ionized form regulates the permeability of plasma membranes, acts a cofactor of enzymatic reactions and transmits stimuli. Phosphate, in turn, is an intracellular anion that participates in protein phosphorylation. It enables the storage and gradual conversion of energy by the formation and breakage of high-energy bonds (ATP, cAMP).
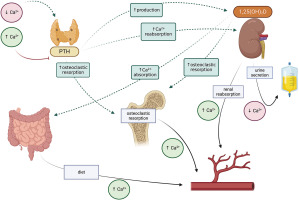
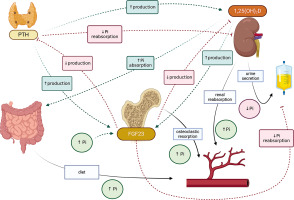
The effector organs for calcium and phosphorus are the gastrointestinal tract, bone and kidney. Calcium-phosphate homeostasis is maintained by the parathyroid hormone (PTH), calcitriol – 1,25(OH)2D, phosphatonins such as fibroblast growth factor (FGF-23), and to a small extent, calcitonin [1–3]. The mutual reactions between effector organs and factors regulating calcium metabolism are shown in Figure 1, and the regulation of phosphate metabolism is given in Figure 2.
Parathyroid hormone is secreted by the parathyroid glands in response to hypocalcemia. It stimulates calcium reabsorption in the renal tubules, increases bone resorption, and inhibits phosphate reabsorption. It also activates the conversion of 25-hydroxyvitamin D to calcitriol (1,25 dihydroxyvitamin D) in the tubules.
Fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF-23) is produced by osteocytes and, to a lesser extent, by osteoblasts; it inhibits phosphate reabsorption in the renal tubules by influencing sodium-dependent phosphorus cotransporters (NPTs). FGF-23 further decreases the expression of 1α-hydroxylase and increases that of 24-hydroxylase, thus reducing the concentration of 1,25(OH)2D in circulation (Figure 2) [2, 3].
Calcitriol, also known as dihydrocholecalciferol, the most active form of vitamin D3, regulates calcium and phosphate metabolism. In the gastrointestinal tract, it increases the calcium and phosphate absorption, releases them from the bones, and increases their reabsorption in the kidneys; it also inhibits PTH synthesis and increases the production of FGF-23. In addition to calcium and phosphorus homeostasis, it is known to affect bone cell metabolism.
It also participates in osteoclastogenesis, by affecting the RANK/RANKL/osteoprotegerin system, stimulates bone resorption and osteoclast activity. In the osteoblasts themselves, it increases the expression of alkaline phosphatase, osteocalcin and osteopontin and regulates cell proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis. It is formed in the kidneys by 1α-hydroxylation of 25(OH)D (calcidiol). Also, the 25-hydroxy-vitamin D form is routinely used as an indicator of systemic vitamin D level [3, 4]. Vitamin D levels below 20 ng/ml (50 mmol/l) indicate deficiency, while 30–50 ng/ml is optimal (75–125 mmol/l) [4–6]. In populations prone to deficiency, such as the Polish population, it is recommended to include prophylactic doses of vitamin D, ranging from 400 IU/day from the first days of life to 2,000 IU in people with obesity, as well as therapeutic doses in the case of deficiency [4].
In recent years, vitamin D3 has been found to play a pleiotropic role, because it also modulates innate and acquired immunity, growth and maturation processes at the cellular level, and supports hormone activity. It is also an important factor in cardiovascular, autoimmune, neuropsychiatric and infectious diseases, and in problems with the endocrine system. Global risk factors for vitamin D deficiency include lack of sun exposure, limited availability from natural food sources, dark skin pigmentation, chronic inflammatory bowel disease and malabsorption, obesity and old age [4, 6].
In childhood, a calcium-phosphate balance is needed to ensure proper growth and development of the skeleton, and a positive balance in periods of intensive growth. Any deficiency can lead to skeletal mineralization disorders. Abnormality can be attributed to genetic factors such as hypophosphataemic rickets (XLH), congenital bone fragility, osteogenesis imperfecta (OI), as well as idiopathic factors, such as idiopathic juvenile osteoporosis (IJO), and iatrogenic factors, (such as deficiency rickets and osteoporosis).
Premature babies may develop metabolic bone disease of prematurity (MBDP), defined as insufficient mineralization of the skeleton resulting from poor accumulation of calcium and phosphates in the prenatal and postnatal period [7]. The greatest accumulation of calcium (100–120 mg/kg of b.w./day) and phosphates (50–65 mg/kg of b.w./day) during pregnancy occurs in the third trimester. Therefore, giving birth before week 28 significantly increases the risk of MBDP. Other predisposing factors include very low (below 1,500 g) and extremely low birth weight (below 1,000 g), long-term parenteral nutrition (i.e. over 4 weeks), reduced intake and absorption of calcium (intestinal immaturity), mechanical stimulation and respiratory failure and infections, as well as the use of drugs such as caffeine, glucocorticoids and diuretics. Symptoms usually appear at between 4 and 8 weeks of age, and may be preceded by hypophosphataemia appearing after 7 to 14 days of life.
To screen for MBDP, it is recommended that the concentration of calcium, phosphorus and alkaline phosphatase be assessed. The child should also be tested for TRP (tubular reabsorption of phosphate) from week 4 after birth: the normal range is 78–91%, with low TRP indicating calcium deficiency and high TRP indicating phosphate deficiency. These tests can be accompanied by an assessment of 25(OH)D concentration, PTH assay and X-ray.
Treatment is based on replenishing deficiencies. When normal test results are achieved, the child should be monitored every 4 weeks until 6 months of age. It is estimated that MBDP affects 23–60% of children born with a body weight below 1,500 g, and the most serious clinical symptoms are fractures of the ribs and long bones, occurring in 10% [7–10].
Rickets is another disorder of calcium and phosphate metabolism. The most common form of deficient rickets (nutritional), with hypophosphataemic rickets and vitamin D-resistant rickets being less frequently diagnosed. All types of rickets are diagnosed based on biochemical tests, X-rays and genetic testing, in addition to clinical symptoms. It is a systemic disorder with most symptoms being associated with the skeletal system: delayed overgrowth of the parietal bone, thickening of the osteochondral joints of the ribs (rosary rickets), widening of the metaphyses of long bones (rickets bracelets), valgus or varus knees and short stature, delayed psychomotor development and gait disorders. In addition to calcium and vitamin D deficiency, known since Roman times, rickets is characterised by low concentrations of phosphorus and 25(OH)D, a low or normal concentration of calcium in serum, and high levels of PTH, 1,25(OH)2D and alkaline phosphatase. The condition can be confirmed by an X-ray of the wrist [3, 11, 12].
Hypophosphataemic rickets (XLH, X-linked hypophosphatemia) is the most common form of genetically determined rickets, resulting from a mutation of the gene for PHEX, expressed in osteocytes and odontoblasts. The mutation leads to an increase in FGF-23, which decreases the expression of sodium-dependent cotransporters; this in turn increases urinary phosphorus excretion and inhibits the activity of calcidiol and PTH.
Hypophosphataemia leads to bone deformities (rickets), gait disorders (duck-like, rocking), short stature, cronisinostosis, pseudofractures, chronic fatigue and hearing loss at a later age. This form is also characterised by periodontal abscesses. Classic treatment involves multiple (6 times) administration of phosphates per day. In 2018, the FDA approved burosumab, a human recombinant IgG1 monoclonal antibody directed against FGF-23, as a treatment for XLH. The drug is administered in children subcutaneously, every 2 weeks, at a dose of 0.8–1.2 mg/kg b.w. In 2017, the drug became available for patients with phosphataemic rickets in Europe (registry identifier NCT03193476), but not in Poland [11–15].
A primary cause of developmental age osteoporosis (OP) is calcium and vitamin D deficiency. In children and adolescents, OP is diagnosed based on densitometry and the presence of clinically-significant bone and/or vertebral fractures. According to the ISCD (International Society for Clinical Densitometry, 2013) osteoporosis can be diagnosed based on a Z-score equal to or below –2.0 in the TBLH program (total body less head) or in the spine option (L1–L4) and the following:
at least 2 fractures of long bones up to the age of 10 years, or
at least 3 fractures of long bones up to the age of 19 years, or
vertebral fracture without injury (loss of 20% of vertebral height according to the Genata criterion; it can be compressive, wedge-shaped or biconcave, i.e. fish-like).
The Z-score relates the DXA densitometry (dual-X-ray absorptiometry) score to that of a group from the same sex and age. In children and adolescents, secondary OP is most often diagnosed in the course of chronic diseases and/or their treatment, such as cancer, endocrine disorders, inflammatory bowel disease and malabsorption, autoimmune and neurological diseases, and long-term immobilization (i.e. over 6 months), including cerebral palsy.
Glucocorticoids have particularly adverse effects on the calcium and phosphate metabolism in bones, as well as bone cells and endocrine glands. This is known as GIOP, glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis.
Basic therapy, apart from treating the underlying disease, consists of calcium and vitamin D3 supplementation and physical activity adapted to the abilities of the patient. In OP with a serious course, i.e. with vertebral fractures, which occur in 33% of children with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia and in 50% with Duchenne muscular dystrophy, bisphosphonate treatment is indicated [16–20].
Primary osteoporosis is idiopathic juvenile osteoporosis (IJO) that meets the Dent criteria. It is most often described in the course of osteogenesis imperfecta [16, 18, 21]. Osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) is a rare (1/15,000–20,000 births) bone dysplasia. It is clinically and genetically heterogeneous, an characterised by increased bone fragility, multiple fractures and subsequent deformities of the skeletal system, as well as bone shortening, short stature and osteoporosis. In most cases (75–90%), it is caused by mutations in the COL1A1 and COL1A2 genes for type I collagen. Sillenc proposes a fourfold classification comprising type I – mild, type II – lethal, type III – progressive-deforming, and type IV – intermediate. Skeletal lesions are accompanied by extraosseous symptoms including blue sclera, dentinogenesis imperfecta, osteoarticular pain, muscle weakness, hearing loss and respiratory complications. OI can be diagnosed prenatally and treatment started as early as the neonatal period, with the optimal treatment currently regarded as bisphosphonate application (BF) [19, 22–26].
However, bisphosphonate therapy is associated with hypocalcaemia resulting from inhibition of bone resorption. Although low calcium levels are generally asymptomatic, mild, and transient, it is important to monitor calcium levels during treatment, and provide calcium and vitamin D supplementation up to a few days after the end of the treatment cycle [19, 23, 25, 26].
This brief review indicates the complex aetiology, mild to serious course and possible clinical consequences of selected disorders of calcium and phosphate metabolism, and highlights that their effects can be observed beyond the skeletal system. Our findings emphasise that it is important to monitor the patient throughout the course of disease, and that therapeutic options should be adapted to its aetiology.

 ENGLISH
ENGLISH