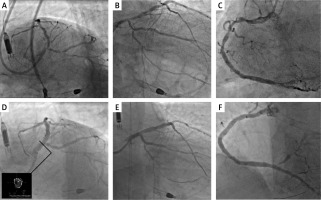
A 75-year-old male patient with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and type 2 diabetes mellitus without a previous history of cardiac disease presented to the hospital with a non-ST-elevated myocardial infarction (NSTEMI). Echocardiography revealed extensive contractile disorders (severe generalized hypokinesia, with slightly better anterior wall function) with significant impairment of left ventricle ejection fraction (LVEF) (20%) and moderate mitral regurgitation. Coronary angiography revealed diffuse disease of the right coronary artery (RCA) and a highly calcified high-grade stenosis in the distal left main (LM) artery and the left anterior descending (LAD) and circumflex (Cx) arteries (Figures 1 A–C). The patient was evaluated by the local heart team and the surgical approach was ruled out due to high perioperative risk. Therefore percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) with mechanical support of the left ventricle (Impella CP, Abiomed, Denver, USA) was performed. Due to the initial symptoms of heart failure, pretreatment with a 24-hour intravenous infusion of levosimendan (0.1 μg/kg/min – cumulative dose 12.5 mg) was performed. Two days later, the PCI through the right radial (7F) approach with additional Impella CP support (maximum flow 3.9 l/min) via the right femoral was performed. Initially, multiple high-pressure inflations were performed in the RCA using a non-compliant balloon (NCB) catheter. Subsequently, two overlapping drug-eluting stents (DES) of 2.5 × 30 mm and 3.5 × 48 mm were implanted under intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) guidance. Afterward, the LAD lesion was identified as uncrossable with a 1.5 × 20 mm balloon catheter. Consequently, a microcatheter was utilized to substitute the guidewire with Viper Wire (Cardiovascular Systems, Saint Paul, USA). Subsequently, multiple low-speed (80,000 rpm) and high-speed (120,000 rpm) orbital atherectomy runs were performed. After successful predilatation with NCB in the medial part of the LAD, a 2.5 × 38 mm DES was implanted. Then, the two-stent double-kissing culotte technique was employed to treat a bifurcation (LM/LAD/Cx). A 3.5 × 26 mm DES was implanted in the LM/LAD, and a 2.75 × 26 mm DES was implanted in the LM/Cx, with an additional final POT in the LM after IVUS assessment (Figures 1 D–F). The Impella CP was removed immediately after the procedure and the vascular access point was closed with Manta (Teleflex, Plymouth, USA) devices. Ten days following the procedure, the patient was discharged with a recommendation for dedicated heart failure pharmacotherapy (sacubitril/valsartan, dapagliflozin, and eplerenone). Furthermore, a wearable cardioverter defibrillator (WCD) vest was used to reduce the probability of sudden cardiac death (SCD). A 3-month follow-up was uneventful – a significant improvement in LVEF was observed (up to 40%); therefore the patient was no longer considered for implantation of an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD).
Figure 1
A – Coronary angiography of the left coronary system – spider view. B – Coronary angiography of the left coronary system – right-caudal view. C – Coronary angiography of the right coronary artery. D – Final results PCI LM/LAD/Cx + final IVUS-LM. E – Final results LM/LAD/Cx. F – Final result of PCI RCA
It is well established that there is a considerable risk of SCD during the convalescent period following PCI in patients with severely compromised LVEF. In the context of the availability of novel pharmacotherapy agents for heart failure, guidelines highlight the potential benefit of waiting periods, yet the residual risk of SCD is not addressed adequately. Utility and indication for WCD remain an equivocal topic [1]. The present case confirms that a combination of multidirectional advanced therapeutic actions, high-risk PCI with levosimendan and Impella CP support [2], with subsequent postprocedural dedicated pharmacotherapy [3] supported with the use of a WCD [4], may represent an efficacious therapeutic approach and significantly modify the prognosis of patients with severe ischemic cardiomyopathy.








