Summary
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a chronic and inflammatory disease. SYNTAX and Gensini scoring systems are used to evaluate CAD extent and severity. We aimed to investigate the relationship between uric acid-high-density lipoprotein ratio (UHR) and the extent and severity of CAD and its correlation with SYNTAX and Gensini scoring systems. As a result of the study, the UHR value was found to be significantly higher in patients with critical coronary stenosis and was found to be correlated with SYNTAX and Gensini scores. UHR can be used before invasive evaluation to predict the presence, severity, and extent of CAD.
Introduction
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is common worldwide and is a significant cause of morbidity and mortality [1, 2]. CAD is a chronic and inflammatory disease that is mainly caused by atherosclerosis [3]. SYNTAX (The SYNergy between percutaneous coronary intervention with TAXus and cardiac surgery) and Gensini scoring systems have been developed for determining the extent and severity of CAD. Validation of both scoring systems has been demonstrated in previous studies [4–6].
High-density lipoprotein (HDL) carries excess cholesterol from peripheral tissues to the liver and is distinguished from other lipoproteins by this feature [7]. HDL has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Although it is known that low HDL levels increase cardiovascular risk, the positive effects of high HDL levels on the risk of myocardial infarction have not been demonstrated [8]. For this reason, the use of HDL alone as a cardiovascular risk factor becomes doubtful, and strengthening this value with additional parameters is on the agenda.
Uric acid (UA) is the end product of purine metabolism [9]. Previous studies have shown that UA level is associated with cardiovascular diseases [10, 11]. Additionally, studies have shown that UA level predicts the distribution and severity of CAD [12]. It is thought that endothelial dysfunction, activation of the renin angiotensin aldosterone system and increased oxidative stress as a result of increased xanthine oxidase activity may cause this situation [13]. With these effects, hyperuricemia promotes the development of atherosclerosis and plaque.
Based on this information, it is known that UA to HDL ratio (UHR) increases in inflammatory conditions, and previous studies have shown that it increases in metabolic syndrome, thyroiditis and diabetes [14, 15]. In addition, a relationship between UHR level and incidental CAD has been shown [16].
Aim
We aimed to investigate the relationship between UHR and the extent and severity of CAD and its correlation with the SYNTAX and Gensini scoring systems.
Material and methods
Study subjects
This study is a retrospective observational cohort study. From May 2022 to October 2023, a total of 894 patients, over 18 years old, who underwent coronary angiography for highly suspected CAD were included in the study. 612 participants with ≥ 70% stenosis in at least one epicardial coronary artery were designated as the patient group, and 282 participants without critical coronary stenosis were designated as the control group. Exclusion criteria were: other cardiac diseases (heart valve diseases, myocardial diseases), drug uses for hyperlipidemia and hyperuricemia, chronic kidney disease, decompensated heart failure and left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) < 50%.
Data collection
All patients were evaluated for the presence of cardiovascular risk factors such as hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes mellitus, age, sex, diabetes mellitus (DM), body surface area (BSA), and smoking status. Hypertension was defined as systolic blood pressure ≥ 140 mm Hg and/or diastolic blood pressure ≥ 90 mm Hg, previously diagnosed hypertension, or use of any antihypertensive medications. Diabetes mellitus was defined as fasting plasma glucose (FPG) levels more than 126 mg/dl in multiple measurements, previously diagnosed diabetes mellitus, or use of antidiabetic medications such as oral antidiabetic agents or insulin.
Blood samples were obtained in the morning after overnight fasting (8 h minimum) to determine blood biochemical parameters, including white blood cells (WBC), FPG, triglyceride (TG), serum total cholesterol (TC), low-density lipoprotein (LDL), HDL, estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), and UA. UHR was defined as the ratio of UA (mg/dl) to HDL (mg/dl). LVEF was determined during hospitalization using 2D echocardiography.
The SYNTAX score was calculated via the sum of points assigned to lesions with ≥ 50% stenosis in separate vessels having ≥ 1.5 mm diameter [5]. Thereafter patients having a score ≤ 22 were defined as the low risk group, those having a score of 23–32 as the intermediate risk group and those having a score ≥ 33 as the high risk group according to current US/European guidelines [17].
For Gensini score calculation, lesions with ≤ 25% stenosis were given 1 point, 26–50% stenosis 2 points, 51–75% stenosis 4 points, 76–90% stenosis 8 points, 91–99% stenosis 16 points and total occlusion 32 points. Thereafter these points were multiplied by 5 for left main coronary artery lesions, by 2.5 for proximal left anterior descending (LAD) or circumflex artery coronary artery lesions, by 1.5 for mid LAD artery lesions, by 1 for right coronary artery, distal LAD artery, posterolateral artery, and obtuse marginal artery lesions and by 0.5 for other lesions [18, 19].
Statistical analysis
The data of the present study were analyzed using IBM SPSS Statistics v. 27.0 for Mac. Categorical variables were presented as frequency and percentage and continuous variables were presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD). Categorical variables were compared with the χ2 test. After evaluation with the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test normally distributed continuous variables were compared via Student’s t test and others with the Mann-Whitney U test. Pearson correlation analysis was used for assessment of correlation. A p-value of <0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
All data were analyzed using IBM SPSS Statistics v. 27.0 for Mac. Categorical variables were expressed as frequency and percentage; continuous variables were expressed as mean ± SD. The normal distribution of the data was evaluated using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. The variables with normal distribution were compared using Student’s t test and the Mann-Whitney U test was used when the normal distribution was not provided.
Results
A total of 894 participants were included in the study. 495 (55.4%) of the participants were male. The rates of diabetes, hypertension and smoking, which are cardiovascular risk factors, were similar in both groups. Considering the laboratory parameters, they were found to be similar in both groups, except for uric acid level and UHR. Baseline characteristics are shown in Table I. 347 patients included in the study had diabetes and 471 patients had hypertension. UHR level was higher in patients with diabetes than in those without (0.3541 ±0.10, 0.1803 ±0.10 respectively, p < 0.01). Similarly, UHR level was found to be higher in patients with hypertension than in those without (0.3083 ±0.1397, 0.1803 ±0.10 respectively, p < 0.01). Regression analysis including age, HT, DM, smoking, LDL-C level and UHR had R2 for prediction of significant CAD and among the parameters only DM and UHR were independent significant predictors.
Table I
Baseline characteristics
The mean SYNTAX score of the patient group was 23.30 ±10.86 and the mean Gensini score was 91.74 ±63.43. In the correlation analysis, it was found that UHR had positive correlations with both SYNTAX and Gensini score (p < 0.01). Patients were classified according to their SYNTAX score and their relationship with UHR was analyzed. The patients’ SYNTAX score increased in parallel to the increase in UHR (Figure 1).
Figure 1
UHR increase with SYNTAX score increase. On the horizontal axis, 1: SYNTAX score < 22, 2: Syntax score 22–32, 3: SYNTAX > 32

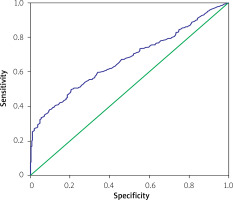
In the ROC curve analysis of UHR and CAD, the cut-off UHR value of 0.16 had a sensitivity of 61.1% and specificity of 38.7% for CAD prediction (AUC = 0.669 (0.634–0.704)) (Figure 2).
Discussion
Our study demonstrated that UHR is higher in patients with critical epicardial coronary stenosis. However, UHR showed a positive correlation with SYNTAX and Gensini scores. This result demonstrates the positive association between CAD severity and extent and high UHR levels.
UHR has been shown to be predictive of metabolic syndrome in diabetic and non-diabetic individuals [20, 21]. Studies investigating the relationship between UHR and cardiovascular risk factors such as hypertension and diabetes have shown that high UHR levels were associated with HT and DM [22–24]. In our study, similar to the literature, UHR level was found to be significantly higher in diabetic patients than in non-diabetic patients and in patients with hypertension compared to those without. Xinhe Zhou et al. reported that elevated UHR was significantly correlated with insulin resistance and could be used as an indicator of insulin resistance in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus [25].
Park et al. investigated the predictive value of UHR for CAD in non-diabetic patients. They found that high UHR values were positively associated with incident CAD in patients without diabetes. They also stated that UHR could be used as a cardiovascular risk marker in the preclinical stage [16]. In the study conducted by Li et al., patients with moderate (40–70%) coronary stenosis and who underwent fractional flow reserve (FFR) measurement for hemodynamic evaluation were included. According to the FFR result, the patients were divided into two groups – hemodynamically significant and non-significant – and their UHR levels were compared with each other. It was observed that the UHR level was significantly higher in patients with hemodynamically significant coronary stenosis [26]. In a study, the effect of UA and HDL levels on prognosis in patients with acute myocardial infarction was evaluated. The coexistence of high UA and low HDL-C was found to have a synergistic effect and provide further information for risk stratification of AMI patients [27]. In our study, we found higher UHR levels in patients with critical coronary stenosis, which was similar to studies in the literature. Additionally, we observed that UHR levels were correlated with SYNTAX and Gensini scores, which predict the prevalence and severity of CAD. Another striking aspect of our study was that the presence of diabetes, hypertension, smoking, serum total cholesterol and LDL levels, which are classical cardiovascular risk factors, was found to be similar in both the patient group and the control group, and only DM and UHR had significant predictive value for presence of CAD. This result showed that UHR is a good predictor that can be used in addition to classical risk factors in predicting the extent and severity of CAD disease. Therefore we can speculate that patients with CAD risk factors and suspicious symptoms having higher UHR levels (> 0.16 in our study) may be evaluated for presence of significant CAD more seriously.
Conclusions
This study showed that UHR is higher in patients with critical epicardial coronary stenosis. UHR is an easy-to-use parameter that can be used before invasive evaluation to predict the presence, severity, and extent of CAD. Stronger evidence-based results can be achieved with larger multi-center prospective studies on this subject.