Introduction
Pemphigus encompasses a group of acantholytic autoimmune dermatoses affecting mucocutaneous membranes [1]. Despite lack of a cure, pemphigus necessitates long-term glucocorticoid use, yet the associated side effects rank among the leading global causes of mortality. In recent years, biological agents targeting CD20 inhibitors such as rituximab have markedly enhanced recovery rates and quality of life for pemphigus patients [2]. However, the biggest barrier to effective immunotherapy is severe cutaneous drug reactions (CDRs) [3]. In 2005, two rhesus macaques which developed toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) after administration of rituximab were reported [4]. In 2009, Bae et al. [5] observed that a patient with thrombocytopenic purpura developed TEN after receiving rituximab treatment. And Fallon et al. [6] reported that in a patient with non-Hodgkin’s B-cell lymphoma, Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis (SJS/TEN) occurred after receiving allopurinol, rituximab, and bendamustine treatment. Recently, it has been reported that rituximab induced TEN in pemphigus vulgaris patients [3, 7], and after receiving etanercept, lesions can be improved. In our clinical practice, we encountered 3 cases of pemphigus patients experiencing severe CDRs following second-dose rituximab administration, specifically manifesting as SJS/TEN or drug hypersensitivity syndrome (DRESS).
Identifying susceptibility genes for rituximab-induced CDRs is imperative to optimize clinical outcomes and mitigate side effects of pemphigus treatment with rituximab. Previous studies have found statistically significant associations between and the genetic CDRs predisposition of specific alleles of human leukocyte antigen (HLA) genes. Such examples are carbamazepine (HLA-B*15:02) [8], allopurinol (HLA-B*58:01) [9], and nevirapine (HLA-C*04:01) [10]. HLA provides antigenic peptides to passing T-cells, and distinct genotypes have been implicated in regulating immune and inflammation disease development [11]. However, rituximab-induced SJS/TEN or DRESS associated with various HLA genotypes has never been reported.
Therefore, to investigate and consolidate these findings in the 3 patients, peripheral blood samples were collected and screened using second-generation sequencing. Subsequently, the results were corroborated by next-generation sequencing to delineate potential associations between specific HLA genotypes and rituximab-induced SJS/TEN in pemphigus populations.
Case reports
Case 1
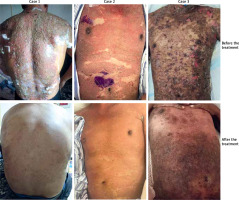
In April 2021, a 56-year-old male patient presented with chest and back erythema, blisters, and erosion for 1 month to our department and to have the biopsy performed. The results of pathological examination indicated intraepidermal suprabasal acantholysis. Fluorescent deposits of IgG and C3 autoantibodies between intercellular spaces of keratinocytes in direct immunofluorescence (DIF). Dsg1 105 U/ml. He was diagnosed with pemphigus vulgaris and treated with methylprednisolone and his first dose of rituximab. However, the rash did not improve after discharge. Two weeks later, the patient received methylprednisolone and the second dose of rituximab. Two days later, erythema appeared all over the body, as well as blisters, erosion, and exudation. Blisters and erosions occurred in the oral cavity and the genitalia. His laboratory test results (Table 1) and clinical characteristics were consistent with Steven-Johnson Syndrome (SJS). After the diagnosis of SJS, the patient was subjected to treatment with 80 mg of methylprednisolone. Complete resolution of the lesions was achieved after 2 weeks, and the treatment was terminated.
Table 1
The most important results of the patients’ laboratory tests and clinical findings at the time of severe adverse drug reactions diagnosis
Case 2
In October 2021, a 66-year-old man presented with erythema, blisters, and erosion on the chest and back, along with erythema and scabs on the face for half a year to our department and to have the biopsy performed. The results of pathological examination showed a cleft within the subcorneal layer and superficial acantholysis, positive DIF findings demonstrate C3 and IgG deposition in the upper epidermis. Dsg1 218.1U. He was diagnosed with pemphigus foliaceus and underwent treatment with glucocorticoids and cyclosporine. Although the rash gradually subsided, it recurred 1 month prior to presentation. Erythema blisters and erosion reappeared on the chest and back, along with erythema and scabs on the face. Seeking recovery from the rash, he opted for rituximab therapy. Intravenous dexamethasone of 15 mg once and rituximab of 1000 mg were administered in February 2022. Two weeks later, the erythema darkened, and the blisters and erosions on the chest and back dried up, but the affected area did not reduce in size (Figure 1). Following the second dose of rituximab administered approximately 2 weeks later, the erythema and erosion persisted on the trunk and limbs, along with erythema and scabs on the face. Subsequently, the patient developed fever, tidal erythema, and scales throughout the body. Eosinophils increased, whereas white blood cells and neutrophils decreased (Table 1). A diagnosis of drug hypersensitivity syndrome (DRESS) was made, and he received methylprednisolone and human immunoglobulin as anti-allergy therapy. Leukopenia was induced by intramuscular injection of recombinant human granulocyte-stimulating factor. Intravenous infusion of human albumin solution was administered due to hypoproteinemia, and anti-infective treatment with ganciclovir was initiated because of CMV infection. Two weeks later, the scales fell off all over the body, leaving dark erythema. One week later, the rash improved and the eosinophils returned to normal.
Case 3
In June 2021, a 32-year-old man presented with waist–abdomen erythema and blisters to outer hospital and to have the biopsy performed. The results of pathological examination showed intraepidermal bullae with a few acantholytic cells and chronic inflammation. Immunofluorescence indicated IgG(+), C3 (+), Dsg1 134U/ml, Dsg3 112U/ml. He was diagnosed with pemphigus vulgaris and received methylprednisolone and the first dose of rituximab. However, several days after the administration of rituximab, the rash did not improve, and the blisters recurred. At the end of June, he received methylprednisolone and the second dose of rituximab. Two days later, he developed toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), manifested by elevated body temperature, secondary skin infection, erythema, blisters, pustules, erosions, and epidermal exfoliation appeared throughout his body. Immunoglobulin and methylprednisolone therapy was initiated. Notably, the rash recurred 2 weeks after the start of the systemic therapy, with bullous lesions appearing in some areas, including his hands and soles of his feet. Rash was bilaterally on his arms, abdomen, and thighs, with ocular discomfort. He subsequently presented to our facility and was diagnosed with TEN based on clinical presentation and laboratory results. Treatment with immunoglobulin and prednisone led to a rapid symptom reduction and gradual normalization of inflammatory parameters. The laboratory tests showed significantly accelerated ESR and PCT (Table 1). Blood cultures grew Streptococcus hemolytic and Staphylococcus, which was treated with vancomycin. Two weeks later, the patient was discharged for personal reasons. After 3 months of follow-up, the patient continued to take methylprednisolone orally, and the rash was significantly improved.
Discussion
In clinical practice, rituximab treatment has been shown to be effective in most pemphigus patients, lowering the recurrence rate and adverse reaction rates. However, the conditions of the 3 patients included in this study worsened, and new rash appeared during the second course of rituximab treatment. The first case presented with erythema multiforme on the trunk and limbs, the second with erythema and scales all over the body, and the third with erythema, blister, erosion, and epidermal exfoliation. Although all patients had received glucocorticoids prior to rituximab, no other sensitizing antibiotics were used, new rashes still developed. Consequently, cutaneous drug reactions (CDRs) were considered to be caused by rituximab in all cases. Additionally, studies have shown no significant abnormalities in CD4+T cells and CD8+T cells in pemphigus patients treated with rituximab [12]. We observed that the CD4+T lymphocytes cells count of these 3 patients were all lower than normal. It has been noted that immunocompromised CD4+T patients are prone to Th1/Th2 imbalance and allergy [13], suggesting that CD4+T exhaustion may also contribute to the occurrence of CDRs induced by rituximab [14].
HLA-A, HLA-B and HLA-C belong to the MHC-I class, drugs bind to HLA molecules of the MHC class I (MHC I), forming drug-derived polypeptides and activating CD8+T cells [15]. Activated CD8+T cells are frequently implicated in the pathogenesis of severe CDRs, such as SJS/TEN or DRESS [16, 17]. Given the significance of HLA-related rituximab-induced susceptibility for severe CDRs, our objective was to establish the HLA haplotypes of the 3 patients with severe CDRs, and we selected 6 patients with pemphigus who had received rituximab twice without CDRs as a control group. Through the second-generation sequencing and comparison, in 2 of our patients, HLA-B*15:02:01 was detected. HLA-B*15:12 and HLA-B*15:27:01 were detected, while the control group showed that no one had simultaneously HLA-B*15. There were no differences in other HLA-related genes. Therefore, we speculated that all three genes were involved in the pathogenesis of CDRs. HLA-B*15 gene’s mutation has been reported to be involved in the pathogenesis of diseases similar to CDRs, including carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, phenytoin and cotrimoxazole-induced severe CDRs [8, 18–20]. Therefore, HLA-B*15 may constitute the high-risk gene for severe rituximab-induced CDRs. It is currently challenging to speculate whether such HLA-B*15 alleles are associated with an elevated risk of severe CDRs induced by rituximab, as the HLA-B*15 results of more patients are needed for representative validation. Clearly, comparing the HLA-B*15 of a larger cohort of similar cases is essential to draw reliable conclusions. Thus, our report should be regarded as an initial observation.
Conclusions
As has been underlined before, rituximab-induced SJS/TEN and DRESS occur in genetically predisposed individuals, and are associated with HLA-dependent inflammatory reactions. Specific HLA serves as a predictor of SJS/TEN and DRESS development. Therefore, the likelihood of SJS/TEN and DRESS occurrence due to rituximab in patients with HLA-related predisposition is considerable. The presence of HLA-B*15 in our patients likely played a significant role in the development of the severe rituximab-induced CDRs. Our findings contribute to identification of specific genes associated with CDRs caused by rituximab in pemphigus patients and to laying the groundwork for future gene kits development to prevent severe CDRs.