Introduction
Obesity is nowadays a burden for physicians from every field of medicine, as it has a highly negative influence on each organ. The consumer lifestyle has brought obesity even to regions where it was marginal. Obesity has become a modern marker for westernization of the developing countries, while national health systems are not ready to face this challenge [1]. It is proven that bariatric surgery reduces all-cause mortality and extends life expectancy when compared with results of conservative treatment [2, 3]. However, despite supremacy over conservative treatment, regular and constant postoperative observation is highly recommended [4]. Some patients in long-term observation may experience recurrence of obesity after restrictive procedures [5]. Malabsorptive procedures may cause serious vitamin and mineral deficiencies [6]. Nutritional deficiencies along with physical inactivity put the bariatric patients at risk of sarcopenia [7]. Bariatric surgery to reduce the risk of mentioned long-term complications is constantly evolving [8].
Procedures performed in bariatric centers can be divided into restrictive (sleeve gastrectomy and gastric banding) and malabsorptive (Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, one anastomosis gastric bypass) [9]. Nowadays, a lot of attention is paid to utilize neuroendocrine mechanisms that bind the alimentary tract and the nervous system. Modification of the intestinal transit changes the concentration of orexigenic and anorexigenic hormones [10, 11]. Inducing the feeling of satiety and reducing the negative effects of malabsorption are the essence of modern bariatric procedures. This mechanism is the principle of the single anastomosis sleeve ileal (SASI) bypass. It is a procedure that evolved from the Santoro method, the difference being that instead of creating a Roux-en-Y loop, an omega loop connects the gastric sleeve and the ileum [12]. SASI bypass is a procedure which links the benefits of restriction with preserved food transit through all the gastrointestinal tract (Figure 1). It benefits from the effect of fast transit of indigested food to the ileum, where anorexigenic intestinal hormones are released. These hormones bring the feeling of satiety by slowing down the peristalsis and gastric emptying. Professor Tarek Mahdy, who developed the SASI procedure, published the first article about this method in 2016 [13]. Throughout five years, effects of the SASI procedure were thoroughly investigated by bariatricians and promising conclusions on the obesity treatment have been presented [14, 15].
Aim
In this initial report, we present the first results of the SASI procedure performed in our bariatric clinic to verify the safety and efficiency of this method presented in currently available literature.
Material and methods
We analyzed retrospectively the first group of patients qualified for SASI bypass between January 2020 and February 2021. Criteria of qualification for bariatric treatment were as follows: body mass index (BMI) between 35 and 39.9 kg/m2 and obesity-related comorbidities or BMI over 40 kg/m2 only. The details of the operation were explained to all of the patients. History of bariatric surgery and inability to provide informed consent were the exclusion criteria. The preoperative management and ambulatory care pathway covered the Polish recommendations for bariatric and metabolic surgery [9]. A database describing patients’ characteristics including comorbidities was collected from the point of qualification for the follow-up ambulatory visits (Table I).
Table I
Characteristics of operated patients
Surgical technique
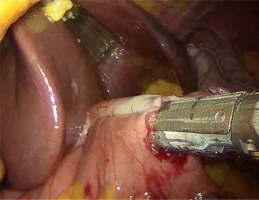
A written informed consent form was given to the patients a day before the surgery. Prior to the operation, each patient received anticoagulation and antibiotic prophylaxis according to the current bariatric guidelines. All of the operations were performed by means of laparoscopy; no conversions were noted. The patient, after inducing general anesthesia, was placed in a French setup in an anti-Trendelenburg position. A Veress needle was used to create a pneumoperitoneum of 14 mm Hg pressure. A 36 French nasogastric tube was inserted into the stomach. All of the trocars were placed in the same locations as in the sleeve gastrectomy. The first step was the devascularization of the greater curvature from the point 4 cm proximally from the pylorus to the level of the left diaphragm crus (Photo 1). Next, a linear stapler was used to create a gastric sleeve calibrated on the nasogastric tube (Photo 2). When the restriction stage of the procedure was completed, the operator moved to the ileal bypass formation. The ileocecal region was identified and proximally a 300 cm ileal loop was measured (Photo 3). When the pylorus and ileal loop were positioned properly a linear stapler was used to create a sleeve ileal side-to-side anastomosis, 6 cm proximally from the pylorus (Photo 4). The stapler defect was closed with a V-lock suture (Photo 5). Anastomosis tightness was checked with the methylene blue test. The transected stomach was removed with one of the trocars. A drain was placed next to the anastomosis (Photo 6).
Postoperative care and follow-up
At the first postoperative day the patients took the methylene blue oral test, and when no leak was observed a liquid diet was administered. Good oral diet tolerance and satisfactory well-being of the patient signaled the possibility of a discharge. All of the patients received diet recommendations, vitamin and mineral supplementation and a follow-up schedule.
The follow-up visits in the bariatric ambulatory center were planned every 3 months to observe remission of comorbidities and to diagnose any nutritional deficiencies. The remission of the diabetes was defined as plasma glucose level < 110 mg/dl and withdrawal of antidiabetic medications. No need for antihypertensive medication was considered as hypertension resolution.
Statistical analysis
Data were analyzed with the program R-3.6.3 for Windows. The Shapiro-Wilk test was used to check the normality of data distribution. Student’s t-test was applied for the correlated variables. Remission of comorbidities was tested using the McNemar test. The results with p < 0.05 were considered statistically significant. For statistical evaluation, the group was divided into 4 groups based on follow-up duration: 3-month follow-up in 5 patients; 6-month follow-up in 2 patients; 9-month follow-up in 6 patients; 12-month follow-up in 6 patients.
Results
The group evaluated in our study consisted of eighteen women and one man of mean age 43.32 ±7.83 years. Mean BMI measured at the qualification was BMI 40.3 ±3.74 kg/m2, and 9 patients exceeded 40 kg/m2. Assessed preoperatively with the American Society of Anesthesiologists scale, 13 patients were in the third class and 6 patients in the second class. The mean operative time was 182.05 ±54.27 min. The mean duration of hospital stay was 6.42 ±3.01 days. None of the patients was lost to follow-up. The results of mean excess weight loss (EWL) in subdivision into 3, 6, 9, 12-month follow-up groups were: 43%, 56%, 72.5%, 88.83% (Table II). In an analogical subdivision the results of mean total weight loss (TWL) were: 18.6%, 25.5%, 33.33, 37.67% (Table III). Mean EWL and TWL for the whole group were 68.16 ±24.92% and 30 ±9.28% respectively. Observation of patients during the follow-up visits brought excellent results in terms of comorbidity resolution. All patients treated for diabetes (6/19) were observed to have a remission. Prediabetes (8/19) was treated successfully in 4 cases. Arterial hypertension (10/19) was normalized in 8 cases (Table IV).
Table II
Results of excess weight loss (EWL) in follow-up
| Follow-up group [months] | Number of patients | Min. EWL (%) | Max. EWL (%) | Median EWL (%) | Mean EWL (%) | SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 5 | 29 | 64 | 39 | 43 | 14.16 |
| 6 | 2 | 43 | 69 | 56 | 56 | 18.39 |
| 9 | 6 | 54 | 82 | 78 | 72,5 | 11.38 |
| 12 | 6 | 53 | 123 | 89.5 | 88.83 | 25.5 |
Table III
Results of total weight loss (TWL) in follow-up
| Follow-up group [months] | Number of patients | Min. TWL (%) | Max. TWL (%) | Median TWL (%) | Mean TWL (%) | SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 5 | 24 | 24 | 18 | 18.6 | 4.16 |
| 6 | 2 | 22 | 29 | 25.5 | 25.5 | 4.95 |
| 9 | 6 | 25 | 40 | 34 | 33.33 | 5.09 |
| 12 | 6 | 28 | 44 | 38.5 | 37.67 | 6.59 |
Table IV
Results of obesity related comorbidity resolution in follow-up
| Obesity comorbidity | Preoperative | Postoperative | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prediabetes | 8/19 | 4/19 | 0.13 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 6/19 | 0/19 | 0.04 |
| Arterial hypertension | 10/19 | 2/19 | 0.02 |
Mean biochemical parameters of nutritional status in postoperative follow-up were within the range of normal. Mean concentrations of albumin and total protein were 3.75 ±0.3 and 6.75 ±0.52 g/dl respectively (Table V). Conservative treatment was sufficient to treat early complications: hematemesis (1/19) and dysphagia (1/19). One patient, in the long-term observation, complained about diarrhea, which subsided after diet modification. In 1 case, hypoalbuminemia secondary to short bowel syndrome required readmission of the patient and reoperation involving disconnection of the sleeve ileal bypass. This patient, in the postoperative ambulatory observation, had normalization of the albumin blood concentration and maintained a satisfactory weight reduction (Table VI).
Discussion
SASI bypass is a novel bariatric procedure that reaches a compromise between the effect of restriction and malnutrition. The first stage of the operation, the gastric sleeve resection, supports the weight loss in early phase after surgery. The second stage of the procedure, the sleeve ileal bypass, causes undigested aliment to reach the ileum fast, triggering hormone release from the distal ileum, bringing the feeling of satiety. By maintaining the passage of food through the duodenum and the jejunum, unwanted nutritional deficiencies are minimized. In addition, after this procedure, endoscopic inspection of the duodenum and the biliary tree is still possible. Only one anastomosis is a simplification that can significantly reduce the risk of serious complications and makes mastering this procedure much faster. For all the reasons mentioned, we expect that SASI bypass may become one of the leading bariatric operations.
In our study, a group of nineteen patients suffering from morbid obesity underwent SASI bypass and was evaluated for short-term outcomes. Out of many publications summarizing results of SASI bypass, the largest material is presented in the meta-analysis by Emile et al. [16]. In this review it is stated that SASI bypass is procedure with mean EWL reaching 90% in 12-month observation. In our study, we observed a similar satisfactory result of EWL, superior to the results of sleeve gastrectomy and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass reported in the literature [17]. What may be even more advantageous, the effect of SASI bypass is a rapid resolution of diabetes. Mahdy et al. observed, in a cohort study, that SASI bypass was more efficient in terms of diabetes than other bariatric procedures [18]. We observed a very rapid improvement in the diabetic subgroup as well. In our study group, arterial hypertension was observed to improve fast after SASI bypass. Interestingly, Emile et al. observed that a longer common limb was associated with better arterial hypertension resolution [16]. The complication rate after SASI bypass reported in the literature is similar to other bariatric procedures [18]. The essential feature of SASI bypass is maintaining the passage through all the alimentary tract to eliminate the problem of malnutrition. In our study group, nutrition status assessed in ambulatory follow-up did not require intervention in most of the cases. We noted one case of hypoalbuminemia caused by short bowel syndrome. For this reason, the patient was reoperated and had a separation of the sleeve ileal anastomosis. Analyzing this complication, which occurred in the first SASI bypass procedure in our clinic, we concluded that it was due to some operative shortcomings resulting in improper anastomosis location and obstructed passage through the common limb. This complication proved to us, however, that SASI bypass is relatively easy to deanastomose and convert to restriction only sleeve gastrectomy.
The main drawback of our analysis is the small study group, not allowing us to reach independently any conclusions to propose recommendations. We would like to state, however, that this is only an initial report carried out to confirm the positive experience of our colleagues bariatricians from other countries. We obtained similar results concerning the safety and efficiency of SASI bypass. We expect that the first publication on the SASI procedure from a Polish institution will encourage other clinics in our country to adopt this procedure. Reports on long-term follow-up are much expected, but we believe that more than the good results observed so far will encourage bariatricians to add SASI bypass to their standard procedure list.
Conclusions
SASI bypass is a procedure that brings together the advantages of restrictive and malabsorptive operations, at the same time reducing the risk of nutrient deficiencies by maintaining passage through all the alimentary tract. Based on available literature and our experience, this procedure brings very good results in terms of rapid weight loss and effective obesity comorbidities resolution in a short-term observation. Studies on long-term results of SASI bypass are highly anticipated.