Summary
Coronary artery calcification (CAC) plays a vital role in the formation of the atherosclerotic plaque. The Agatston CAC score method is a non-invasive, rapid, easily accessible tool that helps identify the weighted sum of the calcium burden in arteries using multi-detector computed tomography. The Agatston CAC score is not only associated with the occurrence of coronary artery events, but it also offers significant prognostic insights into long-term vascular diseases such as carotid and other arterial conditions. With this study for the first time, the Agatston CAC score has been identified as an independent risk factor for contrast-induced nephropathy (CIN) following percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) in patients with stable CAD. Considering that the Agatston CAC score is a simple and non-invasive method, we recommend not overlooking the score when identifying high-risk patients for CIN among patients with stable CAD before PCI, as well as initiating appropriate preventive measures promptly. We believe that conducting more extensive and prospective studies could help us understand the relationship between stable CAD and the Agatston CAC score, and determine diagnostic and therapeutic values.
Introduction
The diagnosis of contrast-induced acute kidney injury (C-AKI) was established based on a 25% increase from baseline or an increase of 0.5 mg/dl serum creatinine levels within 72 h following percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) or administration of contrast agent [1]. C-AKI is one of the most common causes of iatrogenic acute kidney injury. It has also been noted that in incidents of C-AKI, there is an increase in the length of stay in hospital, and a higher risk for end-stage renal failure (ESRD), recurrent revascularization and mortality [2]. Previous studies have identified pre-existing renal failure, diabetes mellitus (DM), advanced age, left ventricular dysfunction, the amount and type of contrast agent and use of additional nephrotoxic agents as independent risk factors for C-AKI [3]. In addition, coronary atherosclerosis is one of the common causes of mortality and morbidity [4].
Coronary artery calcification (CAC) plays a vital role in the formation of the atherosclerotic plaque [5]. The Agatston CAC score method is a non-invasive, rapid, easily accessible tool that helps identify the weighted sum of the calcium burden in arteries using multi-detector computed tomography. This weighted score is multiplied by the area in square millimeters of the calcification. The Agatston score equals the area in square millimeters × the weighted density score. In the coronary circulation, the calcium score of every calcification in each coronary artery for all the tomographic slices is summed up to give a total coronary artery calcium score [6]. The Agatston CAC score is not only associated with the occurrence of coronary artery events, but it also offers significant prognostic insights into long-term vascular diseases such as carotid and other arterial conditions [7]. However, the relationship between the Agatston CAC score and C-AKI has not been explored in previous studies.
Aim
This study examined the predictive value of the Agatston CAC score for C-AKI following PCI in patients with stable coronary artery disease (CAD).
Material and methods
This study was conducted retrospectively at a single center, upon approval from the local ethics committee. The study screened patients who underwent coronary angiography (CA) and PCI due to stable CAD between January 2023 and December 2023. All patients included in the study were clinically diagnosed with stable CAD based on the criteria recommended by the European Society of Cardiology. All patients included in the study presented with angina or angina-equivalent symptoms. In addition, coronary angiography was performed based on the results of positive noninvasive tests such as the exercise stress test, stress echocardiography, and myocardial perfusion scintigraphy. Prior to coronary angiography, the Agatston CAC score was measured noninvasively using 64-slice multi-detector computed tomography. The present study was conducted in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki.
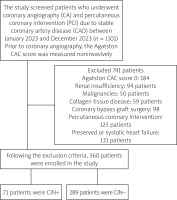
Patients were excluded from the study if they met any of the following criteria: were under the age of 18, had an Agatston score (CAC) of 0, were receiving steroid therapy, had chronic kidney or liver failure, had systemic inflammatory disorders, had either preserved or systolic heart failure, had a history of coronary bypass graft surgery, had previously undergone any form of PCI, or had abnormal electrolyte levels. Following the exclusion criteria, 360 patients were enrolled in the study. The selection of the study group is summarized in the central illustration (Figure 1).
All patients were questioned in detail for hyperlipidemia, diabetes mellitus, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), as well as their tobacco use. Additionally, all medical treatments they received were investigated in detail. Peripheral blood samples were collected following a fasting period of 12 h in order to record hematological, biochemical, and serological values. A glomerular filtration rate (GFR) of 60 ml or below for 3 months or more was considered indicative of chronic kidney disease. As for diabetes mellitus, the diagnosis was based on the use of antidiabetic medications, a level of 126 mg/dl or above in at least 2 postprandial blood glucose measurements, or an glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level greater than 6.5%. Hyperlipidemia was confirmed if low-density lipoprotein (LDL) levels were above 160 mg/dl or if the patient was taking statins. Lastly, COPD was diagnosed based on a post-bronchodilator ratio of FEV1/FEVC < 70% or FEV1 < 70%.
Evaluation of laboratory findings
The complete blood count, renal function tests, lipid parameters, serum glucose, uric acid, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), high sensitivity, and C reactive protein (CRP) levels were recorded and glomerular filtration rate and creatinine clearance (CrCl) were calculated. The diagnosis of C-AKI was established based on a 25% increase from baseline or an increase of 0.5 mg/dl serum creatinine levels within 72 h following PCI.
Echocardiographic evaluation
The echocardiographic examination of 360 patients included in the study was performed using an iE33 cardiac ultrasound system (Philips Healthcare) and a 2.5- to 5-MHz probe system. Ejection fraction was measured in accordance with the modified Simpson method.
Agatston coronary artery calcium scores
Agatston CAC score measurement was performed immediately before the coronary angiography in all patients. None of the patients had hyperthyroidism and all of them had sinus rhythm during the procedure. Imaging was performed using a 64-slice CT scanner (Aquilion 64, Toshiba Medical Systems, Tochigi, Japan). The computed tomography (CT) scan for the total CAC score was obtained by prospective gating with collimation (4 × 3.0 mm) with 3-mm reconstructed slice thickness. Tube current and tube voltage were 300 mA and 120 kV, respectively, and gantry rotation time was 0.4 s/rot. The total CAC score was calculated using dedicated software (Vitrea2 version 3.0.9.1, Vital Images, Minnesota). Calcium based on the Agatston method was defined as the presence of a lesion with an area greater than 1 mm2, and peak intensity greater than 130 Hounsfield units, which was automatically identified and marked with color by the software. All lesions were added to calculate the total CAC score by the Agatston method.
Coronary angiography
The vascular access site for PCI (femoral vs. radial) was left to the discretion of the physician. CA was performed following the Judkins technique. The CA images were evaluated by two experienced interventional cardiologists. Non-ionic low osmolar contrast medium was used as a contrast agent for CA. Anticoagulation and antiplatelet therapies were given in accordance with the current guideline recommendations for patients with CAD. After undergoing PCI, all patients were admitted to the coronary care unit. In addition, all the patients received 100 mg of aspirin, 75 mg of clopidogrel, and statins. The use of adrenergic blocking agents and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors was left to the discretion of the interventional cardiologists. Additionally, all patients were administered 1 ml/kg/h of intravenous saline solution for 12 h before the procedure and 12 h after the CM.
Syntax scoring
SS II was calculated using the online calculator (http://www.syntaxscore.com). Two experienced interventional cardiologists who were familiar with the website and blinded to the study assessed and calculated SS and SS II. In cases with conflicting results, both cardiologists reviewed the analysis collaboratively and reached a consensus.
The Mehran risk score
The Mehran risk score included eight clinical and procedural variables: presence of hypotension, congestive heart failure, chronic kidney disease, diabetes, age > 75 years, anemia, requirement of intra-aortic balloon pump, and the volume of contrast agent used. Patients were categorized into four risk groups based on MS: low (≤ 5), moderate (6–10), high (11–15), and very high (≥ 16).
Statistical analysis
The study data were evaluated using the SPSS version 21.0 statistical software. Normality of distribution of continuous variables was investigated using visual (histogram and probability charts) and analytical methods (Kolmogorov-Smirnov/Shapiro-Wilk tests). The descriptive statistics of the study were presented as the mean and standard deviation for normally distributed data and as the median, minimum, and maximum for non-normally distributed data. The χ2 test was used to show whether there was a difference between categorical variables. Student’s t-test was used to compare the continuous variables with parametric properties in independent groups, while the Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare continuous variables with non-parametric properties in independent groups. The level of statistical significance was set at a p-value less than 0.05. The variables for which the unadjusted p-value was < 0.05 in the logistic regression model were identified as potential risk markers and included in the full multivariate model. Backward elimination multivariate logistic regression analyses using a likelihood ratio test to eliminate variables were utilized. A receiver operating characteristics curve was used to determine the sensitivity and specificity of the Agatston CAC score and optimal cutoff value for predicting C-AKI.
Results
A total of 360 patients were included in the study. Patients were divided into two groups: C-AKI+ and C-AKI-. There were 289 patients (mean age: 71.1 ±11.1 years, 25.9% male) in the C-AKI- group and 71 patients (mean age: 81.8 ±12.2 years, 29.5% male) in the deceased group. There was no significant difference in terms of gender; however, the C-AKI+ group was significantly older. Additionally, there was no difference between the groups in terms of medical histories. Table I presents the baseline characteristics of the patients.
Table I
Comparison of patients’ demographics, medications and medical history
The comparison of laboratory characteristics did not show any significant differences in hemoglobin levels, white blood cell counts, or markers of renal function. The C-AKI+ group revealed a significantly higher level of uric acid (6.8 ±2.11 vs. 4.7 ±1.4 mg/dl, p = 0.001). Moreover, the comparison of angiographic characteristics showed a significantly higher Agatston CAC score (590.5 ±158.8 vs. 192.2 ±102.9, p = 0.001), SYNTAX score (19.9 ±4.1 vs. 15.9 ±8.3, p = 0.001), and Mehran score (7.12 ±2.1 vs. 4.78 ±1.2, p = 0.001) (Table II).
Table II
Comparison of patients’ laboratory and angiographic and procedural characteristics
The results of the univariate and multivariate regression analyses indicated age (OR = 1.498, 95% CI: 1.351–1.881, p = 0.001), uric acid (OR = 1.234, 95% CI: 1.121–1.454, p = 0.001), the Mehran score (OR = 1.241 95% CI: 1.001–1.358, p = 0.001), and the Agatston CAC score (OR = 1.298, 95% CI: 1.191–1.422, p = 0.001) as independent risk factors for C-AKI (Table III).
Table III
Multivariate logistic regression analysis of the risk factors for contrast-induced acute kidney injury
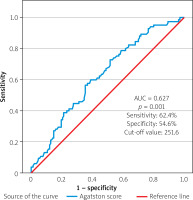
In ROC analysis, the Agatston CAC score had a sensitivity of 62.4% and a specificity of 54.6%. (cutoff value: 251.6, AUC = 0.627, p = 0.001) (Figure 2).
Discussion
This study investigated for the first time the relationship between the Agatston CAC score and C-AKI in patients with stable CAD who underwent PCI. The first finding of this study is that the Agatston CAC score is an independent risk factor for C-AKI.
Our study identified, age, uric acid, and Mehran score were also observed as independent risk factors for C-AKI. Epidemiological studies have provided evidence that age is a significant risk factor for C-AKI. The prevalence of glomerulosclerosis, interstitial fibrosis, and vascular fibrosis and tortuosity increases with age, leading to low nephron counts and impairment in renal function. Additionally, worsening renal function has been associated with inflammatory changes and decreased vasodilators, such as nitric oxide (NO), as a result of aging [8, 9]. Wang et al. in their study which investigated risk factors for C-AKI after PCI identified being over 65 years old as an independent risk factor (OR = 2.75). Similarly to previous studies, our study also identified advanced age as an independent risk factor for the development of C-AKI [10].
Elevated serum uric acid levels cause endothelial dysfunction, oxidative stress, inflammation, activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, and a decrease in NO levels [11, 12]. The study conducted by Mendi et al. identified elevated levels of serum uric acid to be an independent factor for C-AKI, demonstrating a sensitivity of 70% and specificity of 67% with the cut-off value set at 5.45 mg [13].
The Mehran score has long been used to predict the development of C-AKI after PCI. In 2004, Mehran et al. categorized 5571 patients who underwent PCI into four groups based on factors such as age, diabetes mellitus, hypotension, glomerular filtration rate, anemia, congestive heart failure, contrast volume, and intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP) values in order to determine the risk of C-AKI [14]. Abellás-Sequeiros et al. demonstrated that even after a decade, the Mehran score still remains valid [15].
The SYNTAX score is a tool to assess the severity and complexity of CAD. Numerous studies have shown that the SYNTAX score is a prognostic indicator for long-term coronary no-flow, along with cardiovascular mortality and morbidity [16]. A high SYNTAX score is associated with prolonged procedural times, reduced ejection fraction, hemodynamic instability, and an increase in contrast volume and the frequency of no-flow [17]. Oduncu et al. demonstrated that individuals with a high SYNTAX score have two-fold increased risk of developing C-AKI following PCI, along with a three-fold increased risk of end-stage renal failure [18]. In our study, although there was a statistically significant between-group difference in SYNTAX scores, no difference was observed in the regression analysis. This finding may suggest that, compared to the SYNTAX score, the Agatston CAC score is a more significant indicator.
Even though the Agatston CAC score has been shown to be an important parameter for long-term cardiovascular mortality and morbidity, there is currently no study that elucidates the etiopathogenesis between C-AKI and the Agatston CAC [19]. The only study in the literature that addressed the relationship between CAC and C-AKI is that of Osugi et al., which examined 140 patients with chronic kidney disease who underwent CA, irrespective of the cause. However, this study did not utilize the Agatston CAC scoring, which is considered to be the gold standard for evaluating coronary artery calcification [20]. The development of C-AKI in the presence of a high Agatston score is thought to be due to a variety of reasons.
The Agatston CAC score has been closely linked to endothelial dysfunction, systemic inflammation, and arterial stiffness in several studies. Furthermore, the Agatston CAC score and endothelial dysfunction, systemic inflammation and arterial stiffness have been demonstrated to play a fundamental role in the pathophysiology of renal failure [21, 22]. Wu et al.’s study conducted on mice illustrated that increased systemic inflammation is an independent risk factor for peritubular capillary dysfunction and renal damage. In addition, a positive correlation was observed between inflammation and renal damage [23]. In their prospective study, Guo et al. found arterial stiffness to be an independent risk factor for the progression of ESRD in the long term [24]. Moreover, in a retrospective study by Yun et al., which was conducted on 8130 patients with CKD, it was observed that individuals with an Agatston CAC of > 100 had a 1.42 times higher risk of progressing to ESRD [25]. Although our study did not detect any between-group differences in renal function, this could be attributed to subclinical renal dysfunction.
Renal cholesterol embolism or atheroembolism occurs when cholesterol crystals, platelets, fibrin, and calcified atheroma debris cause mechanical obstruction and inflammation of the small renal arteries after a PCI or invasive vascular procedures. Some patients can be asymptomatic, while others may present with mild to moderate or even life-threatening stages of kidney failure [26, 27]. Although no study in the literature directly links the Agatston CAC score to renal embolism, Takahashi et al.’s study revealed a higher frequency of renal embolism in the presence of chronic total occlusion and calcification [28]. The Agatston calcium score was also observed as an independent risk factor for distal coronary embolization (DCE) and no-reflow by Modolo et al. [29]. We speculate that this could potentially contribute to the development of C-AKI.
This study has several limitations. The most significant limitation is that it relied on data from a single center, with a limited sample size. Moreover, renal biopsy, which is a gold standard for diagnosis of renal embolism, was not performed. Lastly, patients did not receive long-term follow-up upon discharge.
Conclusions
With this study for the first time, the Agatston CAC score has been identified as an independent risk factor for C-AKI following PCI in patients with stable CAD. Considering that the Agatston CAC score is a simple and non-invasive method, we recommend not overlooking the score when identifying high-risk patients for C-AKI among patients with stable CAD before PCI, as well as initiating appropriate preventive measures promptly. We believe that conducting more extensive and prospective studies could help us understand the relationship between stable CAD and the Agatston CAC score, and determine diagnostic and therapeutic values.