Purpose
Single-channel vaginal cylinder (SCVC) is commonly used in adjuvant radiation treatments for gynecological malignancies to reduce local recurrence [1]. Interstitial brachytherapy (ISBT) with implanted needles is recommended when cylinder placement is technically impossible, or expected to result in sub-optimal dose distributions. In this case, achieving adequate dose coverage of high-risk target volumes while sparing surrounding radiation to sensitive normal organs can be more challenging for single-channel cylinder techniques due to its simple geometry and thus limited capabilities of dose volume optimization. Needle implants, however, could potentially provide superior dose coverage and better normal tissue sparing, because the source dwell positions can be made more proximal to the targets. Advanced inverse optimization algorithms readily available in the modern treatment planning systems also bring the advantageous of needle implants, with more distributed source dwell positions to reach an optimal dose distribution and high clinical workflow efficiency.
Various needle placement techniques for ISBT have been developed based on perineal templates, such as MUPIT (Nucletron, Elekta Company, Sweden) and Syed-Neblett template (Best Medical International, Inc., Springfield, USA) [2, 3]. Treatment protocol for patients in this study prescribed multiple outpatient treatment fractions separated. Each fraction is expected to last for a few hours from needle insertion to removal, with only a handful of needles implanted. On the other hand, for patients whose post-operative pathology shows positive vaginal stump margins or parametrial involvement, 0.5 cm submucosal treatment cannot meet clinical needs, while image-guided free-hand implantation can increase high-risk clinical target volume (HR-CTV) dose coverage of the vaginal stump. It can greatly simplify the ISBT process compared with template-based interstitial procedures. Additionally, it is expected to provide favorable target coverage and less doses to organs at risk (OARs) compared with SCVC.
The aim of this study was to analyze and compare dose differences using a CT-guided SCVC and free-hand interstitial needles (FIN) in patients after total hysterectomy.
Material and methods
Patients
This was a retrospective study, and all patients were selected randomly. Twenty-two patients pathologically diagnosed with cervical (n = 14), endometrial (n = 5), and vaginal (n = 3) cancers from July to December, 2018 were included in this study. The 14 cervical cancer cases showed post-operative conditions, including high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions and vaginal masses on the vaginal cutting edge. Their characteristics are summarized in Table 1. Post-operative brachytherapy indications for patients with cervical cancer in this study were as follows: 1. Post-operative pathology suggestive of positive vaginal margin and insufficient safe distance; 2. Post-operative pathology suggestive of positive parametrium; 3. Infiltration of deep muscular layer close to whole layer; 4. Patients with accidental detection of cervical cancer. All post-operative patients with endometrial cancer included in this study had thickening of the vaginal stump, and intra-vaginal cylinder could not meet HR-CTV dose distribution of the thickened part of vaginal stump. Patients with vaginal cancer had paravaginal invasion, and 0.5 cm could not adequately cover the depth of vaginal stump. Patients included in this study were unexpectedly found to have cervical cancer. Pathological type was adenocarcinoma, with insufficient parametrial resection and inadequate length of vaginal resection. Therefore, post-operative interstitial brachytherapy was supplemented.
Table 1
Patient characteristics
After surgery, all patients received EBRT of 4500-5040 cGy in 25-28 fractions, followed by high-dose-rate (HDR) vaginal brachytherapy (VBT) of a total dose of 1400-2100 cGy in 3 fractions, 700 cGy per fraction under local anesthesia, and with administration of antibiotics. Subsequently, all patients received interstitial brachytherapy 1-2 times a week. The depth given by prescription needed to be greater than 0.5 cm. Patients who could not tolerate brachytherapy procedure and those who did not fully complete the treatment were excluded from the study. All patients were additionally treated using paclitaxel with platinum-based chemotherapy, except for patients with stage IA of cervix carcinoma and endometrium carcinoma. This project and protocols were approved by the Ethics Committee of Fujian Cancer Hospital (approval number: K2021-072-01). All patients signed an informed consent form.
Applicator placement and CT simulation
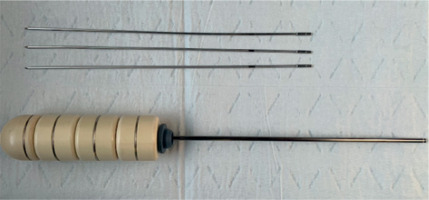
Before BT procedure, all patients’ emptied bladders were filled with 150 ml normal saline. Patients received local anesthesia with lidocaine under aseptic conditions in an afterloader operation room. SCVC with 2.5 cm diameters (Elekta Company, Sweden) were successively inserted into the vagina for dosimetric comparison purposes. All patients were first scanned in a CT room, and the applicator was removed in vivo. Afterwards, FIN was performed. For free-hand brachytherapy, the number of needles and their locations were determined by attending radiation oncologist, based on clinical examination and post-treatment MRI. A 16 cm long and 1.3 mm in diameter 3 metallic needles (Elekta Company, Sweden) were used for free-hand insertion by an oncologist (Figure 1). A semi-circular rubber piece with a diameter of 1 cm and a thickness of 0.1 cm was applied to secure the implantation needle at a position of 1 cm away from the tip of the needle to ensure the depth of insertion. The final depth required adjustments according to a CT scan image. After implantation was completed, a small amount of cotton ball was packed into the vaginal opening to fix the position of implantation needle. The choice of three needles was made due to flat and elongated shape of the healing vagina after surgery, so that dose distribution would ensure an adequate dose at both ends of the vaginal stump. Excluding patients who could not tolerate this process, there were 55 treatment sessions in total among the groups of 2.5 cm diameter cylinder applicators and free-hand needles.
Fig. 1
Free-hand interstitial needles (FIN) and singlechannel vaginal cylinder (SCVC) used in this study
After applicator insertion, patients were scanned using a CT scanner (Brilliance Big Bore, Philips, The Netherlands), with 2 mm slice thickness from 5 cm above the L3 vertebral body to 5 cm below the ischial tuberosity. CT datasets were transferred to Oncentra Brachytherapy system for treatment planning (version 4.3, Elekta Company, Sweden). HR-CTV (the vaginal stump tissue to the lower edge of pubic symphysis) and OARs (the bladder, rectum, and sigmoid colon) were delineated and verified by the attending radiation oncologist following the GEC-ESTRO (ACROP)-ABS-CBG recommendations [4] and magnetic resonance images. In order to reproduce the maximum CTV in 3 implants, this study used the same type of packing employed in these 3 implants to separate vaginal walls. In this case, the target area in the single-channel group was subtracted from the volume of applicator (Figure 2). All treatment plans were optimized using the following constraints: 1. HR-CTV D90 ought to receive 700 cGy per fraction; 2. D2cc to the bladder and rectum should be less than 560 cGy (80%) and 490 cGy (70%) [5], respectively. Plans for each group were optimized with Oncentra Brachy system using a simulated annealing algorithm. HR-CTV was set as the reference target area; its minimum surface dose and OARs’ maximum surface doses were set as the constraints. All the optimization parameters are shown in Table 2.
Fig. 2
The typical dose distribution comparison of in axial ,sagittal and coronal views of a typical treatment with single-channel vaginal cylinder (A, B, C) and free-hand interstitial needles (D, E, F)
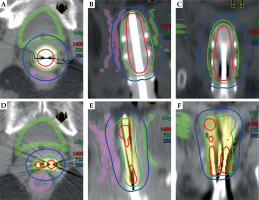
Table 2
Parameters used for inverse planning simulated annealing (IPSA) optimization in Oncentra treatment planning system
Comparison
High-risk CTV D90, V200%, V150%, V100%, homogeneity index (HI = (V100% – V150%)/V100%), the rectum and bladder’s D0.1cc, D1cc, and D2cc were compared [6] in addition to treatment time and other parameter indicators if applicable. The typical dose distribution comparison of treatment planning is shown in Figure 2.
Results
High-risk clinical target volume
As shown in Table 3, all the plans met dose requirements for the clinical target area. D90 and V100% of HR-CTV showed no significant difference between the SCVC and FIN groups (p > 0.05). The FIN group had higher V150% and V200% (p < 0.05). In addition, it had lower HI (p < 0.05).
Table 3
Dosimetric parameters between single-channel vaginal cylinder (SCVC) group and free-hand interstitial needles (FIN) group
Organs at risk
As shown in Table 4, all the plans met clinical dose requirements for OARs. Doses to the rectum D0.1cc/D1cc/D2cc/Dmean and bladder D0.1cc/D1cc were lower in the FIN group than in the SCVC group. The average values of D2cc of the bladder were similar in the SCVC and FIN groups (p = 0.16).
Table 4
Comparison of organs at risk (OARs) parameters between single-channel vaginal cylinder (SCVC) group and free-hand interstitial needles (FIN) group
Discussion
Single-channel and multi-channel applicators are generally used for brachytherapy treatment of gynecological malignancies, such as early vaginal cancer with invasion depth not exceeding 0.5 cm and after external irradiation [7, 8]. They can reduce the exposure dose to normal tissues to a certain extent while ensuring coverage of the target area. Single-channel applicators are characterized by minimal operation and non-invasiveness; however, their ability to optimize the dose is limited. Multi-channel applicators provide a better solution by placing multi-channel cylindrical applicators in the vagina. Kim et al. [7] showed that the use of a multi-channel applicator reduced the dose to the rectum compared with a single-channel applicator, but had no effect on the bladder dose. Notably, both single-channel and multi-channel applicators have an air gap between the applicator and mucous membrane after insertion into the vagina [9], resulting in a decreased vaginal mucosal dose, which may in turn increase the rate of local recurrence. Richardson et al. [10] reported that the use of a single-channel applicator was associated with an average gap of 0.34 cm3, resulting in a decrease in vaginal mucosal dose of about 27%.
The current study compared the dosimetric differences between SCVC and FIN. All treatment plans met the clinical treatment requirements. Compared with the SCVC group, the FIN group resulted in similar dose coverage of target volumes, with lower doses to all OARs. This demonstrate dosimetric advantages of FIN. Mendez et al. [11] reported that an OAR dose was always lower with ISBT compared with a multi-channel vaginal cylinder application, and the needle insertion technique was particularly effective in reducing the dose to the bladder and rectum. The insertion technique is generally guided by imaging, allowing the needle track to be placed directly at the lesion site, thus ensuring good conformability and reducing dose to the bladder and rectum.
Interstitial brachytherapy has been widely used in recent years, usually in a transperineal template and fixed needle tracks. In the current study, direct trans-vaginal free-hand implantation was applied, which is flexible and more maneuverable, allowing direct needle insertion into the diseased area. Some previous studies evaluated plans quality using metrics, such as dose non-uniformity index (DNR, DNR = V150%/V100%) to determine high-dose areas of HR-CTV. Bahadur et al. [12] compared single-channel and multi-channel applicator plans, and confirmed that the former presented higher HI (HI = 1-DNR) than the latter. This is similar to the results of the current study. It was lower than 0.6-0.7 according to the American Brachytherapy Society vaginal interstitial brachytherapy guidelines [13]. It is generally believed that the number of needles is positively related to conformity and inversely proportional to an uneven dose distribution. Considering patient’s tolerance and scope of the disease, 3 needles were implanted uniformly across the target area, and the number of needles was much smaller compared with typical interstitial brachytherapy. In addition, because there are no standard guidelines for the acceptable high-dose area, the V150% of HR-CTV was not included by dose constraints during the inverse optimization in treatment planning. Therefore, it could result in HI lower than the ABS published values.
In the present study, commonly used vaginal cylinder size (2.5 cm) was used in the SCVC group. Dosimetry was very comparable, but not reported in detail here since it was outside the scope of this paper. However, since our patient group had an average body mass index (BMI) of less than 24 and a history of whole pelvic RT, 2.5 cm was favored. This was similar to a study by Rakhra et al. [14] who found that lower body weight and BMI as well as a EBRT history prior to VBT were associated with better accommodation of smaller cylinder sizes.
The current study has some limitations. The free-hand needle implantation technique can be relatively more invasive compared with cylinder applicators, with more associated risks of severe pain and acute complications during anesthesia. It is a time-consuming, labor-intensive, and more complex technology, demanding more clinical expertise and support. To this end, our institution has formulated planning specifications and established a new clinical workflow. As a result, the total treatment workflow time was even less than procedures with single-channel applicators. However, the overall process, including needle implantation, CT scanning, treatment planning, and delivery required a great deal of dedicated manpower and material resources. Therefore, improving efficiency while ensuring treatment quality remains a top priority at our clinic. Damato et al. [15] reported that a re-designed treatment plan components in a flowchart reduced planning time by 29% and simplified quality assurance process. In recent years, 3D template printing technology has become increasingly available for ISBT. These personalized treatment implant templates greatly improve the speed of CT-guided implantation, and promote the development of move advanced implantation technologies [16, 17].
Conclusions
Free-hand interstitial needles is an effective solution for patients with advanced gynecological tumors who need VBT boost. Compared with SCVC, this technique ensures adequate coverage of the target area and reduces the dose to OARs. However, further studies are warranted to confirm clinical significance of this technique.



