Purpose
In contrast to the AAPM TG-43 [1-3] dosimetry protocol that is currently considered the international brachytherapy dosimetry standard, the commercially available model-based dose calculation algorithms (MBDCA) [4-6] for brachytherapy account for the effect of heterogeneities, contoured catheter material and shape as well as the limited scatter conditions in bounded patient anatomy for dose calculation. Their characteristics, the rationale of transitioning to MBDCA, and their potential for brachytherapy dosimetry have been presented by several authors [7-10]. Previous retrospective dosimetry comparison studies for clinical plans have focused on the dosimetric differences within high-dose-rate (HDR) mainly for the breast [10-14], gynecological [12, 15-18], and to a lesser extent, for head and neck [19] interstitial brachytherapy cases. The purpose of this work was to compare the dosimetry of TG-43 protocol with the grid-based Boltzmann solver (GBBS) algorithm, not only for clinical breast interstitial brachytherapy plans, but also to expand the comparison for clinical head and neck and lung iridium-192 (192Ir) interstitial implants. To our knowledge, this work presented the first results of interstitial lung brachytherapy dosimetric comparisons for the AcurosTM BV algorithm. Furthermore, various clinical scenarios were included for each anatomical site to allow for generalization of the results. Cases with both plastic and metallic needles, definitive and palliative schemes, and a range of prescriptions were included. This retrospective comparison was performed between the TG-43 and AcurosTM BV algorithms [5] found in the BrachyVisionTM treatment planning system (Varian Medical Systems Inc., CA, USA). Differences of plan quality indices were computed for multi-catheter HDR brachytherapy implants in the breast, head and neck, and lung cases, where the proximity of treated clinical target volumes to bounded and/or heterogeneous anatomies raises dosimetric accuracy concerns, and the significance of dosimetric deviations was analyzed.
Material and methods
Patient cohort
Fifty-nine patients who received CT-guided interstitial multi-catheter HDR brachytherapy in our institution between 2018 and 2022 were retrospectively selected. Twenty-two patients received treatment for tumors in the breast region, twenty-two patients received treatment for tumors in the head and neck (H&N) region, while fifteen patients received treatment for the lung tumors.
Implant technique
Breast cases were implanted under sedation, and guide needles were inserted using CT-guided free-hand implantation technique. Guide needles were replaced by flexible plastic catheters (6F OncoSmart, Elekta AB), which were secured in place with radio-opaque buttons. The number of catheters ranged from 5 to 19 (median, 11; mean, 12).
Head and neck cases were implanted with CT guidance under general anesthesia. The number of catheters ranged from 1 to 12 (median, 8; mean, 7.2), while flexible plastic catheters were employed in 16 cases and stainless-steel needles (Trocar needles, Elekta AB) in 6 patients.
Lung cases were implanted with CT guidance under sedation. One (n = 13) or two (n = 2) needles were inserted for each implant, while plastic needles (ProGuide sharp, Elekta AB) were employed in 9 cases and stainless-steel needles in 6 patients. When plastic needles were used, a CT marker was inserted immediately before the final planning CT scan for better visualization of catheter paths and distal position on CT images. For treatment planning purposes, the CT marker was contoured and set to Hounsfield unit (HU) number equal to 350 (i.e., the average HU number observed within plastic catheters without CT marker), in order to represent the treatment delivery reality, where CT markers inside interstitial needles were not present.
Treatment planning
Treatment plans for all cases were optimized and calculated on CT scans obtained from General Electric Optima CT580 RT CT scanner. Most breast cases represented accelerated partial breast irradiation (APBI) with curative intends. These patients were prescribed either 32 Gy in 8 fractions or 34 Gy in 10 fractions [20-22]. In palliative breast setting, prescriptions ranged from 8 to 30 Gy in 1 to 6 fractions. Head and neck cases were treatments of palliative setting (10 lymph node metastatic cases, 3 buccal cancer cases, 2 parotid cancer cases, 2 nasal cavity cancer cases, 1 oropharyngeal, 1 base of tongue, 1 mandible, 1 maxilla, and 1 malignant peripheral nerve sheath neck tumor case), with prescriptions ranging from 24 to 30 Gy in 3 to 10 fractions [23]. Lung cases were palliative and/or re-irradiation treatments, with prescriptions ranging from 8 to 25 Gy per implant [24].
In APBI cases, planning target volume (PTV) represented a minimum of 2 cm margin around the tumor area as defined by surgical clips [20-22]. For palliative cases, gross tumor volume (GTV) also represented PTV, with no additional expansion.
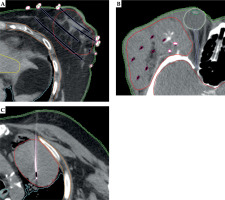
All relevant organs at risk (OARs) in the vicinity of PTVs were contoured to assist treatment planning and plan evaluation. Figure 1 shows representative example cases from each anatomical site, including the respective contours generated for each case. A sub-set of those contours, for which dosimetric differences between the two algorithms due to the presence of tissue heterogeneities and/or bounded patient anatomy would be expected, were included in comparative analysis. These OARs were the skin, ipsilateral lung, and chest wall. The skin contour was defined as a 2 mm thick rind inside the external patient contour.
Fig. 1
Typical implant and contours drawn for each treatment of the breast (A), head and neck (B), and lung cancer cases (C)
Treatment plans for each case were initially generated using the TG-43 algorithm, starting with inverse optimization and finalizing the plan with graphical optimization. The optimization process aimed at achieving plan objectives and constraints for each anatomical site, as proposed in respective recommendations and clinical trials [20-24]. Following finalization of the treatment plan, review, and approval by a radiation oncologist, each was retrospectively re-calculated without re-optimization using the AcurosTM BV algorithm with exactly the same plans parameters (source strength, catheter reconstruction points and position, dwell positions inside each catheter, and dwell times).
For the AcurosTM BV dose calculation, HU values derived from the CT scan were converted into material mass density based on HU to mass density calibration curve of the CT scanner. Iridium-192 GammaMed HDR plus source was utilized, and dose calculation grid resolution of 2.5 mm for both algorithms was selected. For AcurosTM BV, dose to medium option was used.
DVH parameter analysis
Several dose volume histogram (DVH) parameters were selected for analysis, based on treatment plan objectives and constraints found in studies investigating differences in dose calculations algorithms as well as international recommendations and publications [11-24] for each treatment site. For the PTV, the dose to 90% of the volume (D90%), and the volume receiving 95%, 100%, and 150% of the prescribed dose (V95%, V100%, V150%) were applied. For the ipsilateral lung, the percentage volume receiving at least 5 Gy (V5Gy). For the skin the minimum dose received by the hottest section of the contour with volume of 0.1, 0.2, and 1 cubic centimeter (D0.1cm3, D0.2cm3, and D1cm3) were calculated, while for the chest wall, D0.1cm3 and D1cm3 were considered for both the TG-43 dosimetry formalism and for AcurosTM BV.
All DVH data were generated in BrachyVisionTM, exported as text files and analyzed in Matlab® (MathWorks, Massachusetts, USA), where parameters for each patient and each plan were extracted. Data for each parameter were then exported into a spreadsheet. Non-parametric Wilcoxon paired test was conducted on each dataset to expose statistical significance differences using R (www.r-project.org). Statistical significance was considered with p < 0.01.
Results
Planning target volume
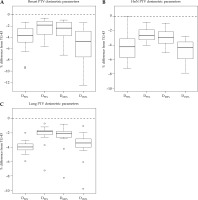
Dose volume histogram (DVH) parameter analysis results for the PTV revealed statistically significant differences (p < 0.001) between the dose calculated using the AcurosTM BV compared with the TG-43 algorithm. Specifically, as summarized in Table 1, AcurosTM BV calculated lower doses for all DVH parameters analyzed (D90%, V95%, V100%, and V150%). For the breast, the mean percentage differences from TG-43 ((AcurosTM BV – TG-43)/TG-43) ranged from –2.2% to –5.4%, for the head and neck cases, they ranged from –2.5% to –4.7%, while for the lung cases, the values ranged from –2.2% to –4.4%, with all of the mean percentage differences showing statistical significance (p < 0.001). Figure 2 shows a box and whisker plot of the PTV parameters analyzed, where is evident that TG-43 clearly overestimated the dose coverage of the PTV for each anatomical site, since it did not account for the missing scatter photon dose component in the vicinity of the PTV to the lung and/or PTV to patient body boundaries. The highest D90% mean percentage difference was evident in the lung PTV, where the PTVs were anatomically mostly surrounded by air-inflated lung tissue. For the breast cases, the maximum percentage dose difference of AcurosTM BV from TG-43 for D90% was equal to –10.7%, for V95%, it was –5.5%, for V100%, –6.8%, and for V150%, it was –5.9%, while for the head and neck cases, the maximum percentage dose difference were equal to –7.5%, –3.7%, –4.5%, and –4.7%, respectively. For the lung cases, the maximum dose percentage differences were equal to –11.3% for D90%, –6.8% for V95%, –7.6% for V100%, and –5.3% for V150%. The higher dose overestimation by the TG-43 formalism for D90% and V100% was more pronounced for interstitial lung cases, where PTVs were almost completely surrounded by air-inflated lung tissue, and not in anatomical regions close to a homogeneous structure (i.e., the liver).
Table 1
Analysis of dose to planning target volume (PTV) showing median and mean percentage difference of dose calculated with AcurosTM BV from that calculated using TG-43 algorithms ((AcurosTM BV – TG-43)/TG-43), with 1st and 3rd quartiles (Q1-Q3), standard error, and p-value calculated using Wilcoxon paired test
Fig. 2
Box and whisker plots showing the percentage difference of dose volume histogram (DVH) parameters when calculated with AcurosTM BV from the TG-43 algorithm ((AcurosTM BV – TG-43)/TG-43) for the planning target volume (PTV). Plots show results A) for the breast, B) for the head and neck (HnN), and C) for the lung cases. For each boxplot, the thick bold line represents the median value (2nd quartile), the top line of the box is the 3rd quartile, while the bottom line represents the 1st quartile. The whiskers represent the near minimum and maximum values, and the circles are the outliers
Organs at risk
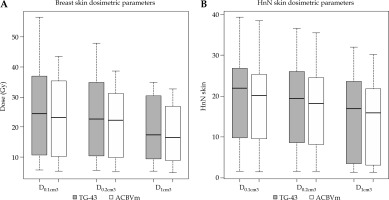
The results of DVH parameter analysis for organs at risk also revealed important differences in certain stages of the dose calculated by the two algorithms. Table 2 summarizes the results of the absolute dose difference for the skin, chest wall, and ipsilateral lung, which were common in most of the cases, revealing statistically significant differences. AcurosTM BV calculated lower dose for all skin DVH parameters analyzed (D0.1cm3, D0.2cm3, and D1cm3). For the breast implants, the mean absolute differences were –1.4, –1.8, and –2.0 Gy (AcurosTM BV – TG-43), respectively, while for the head and neck region, the mean absolute differences were –1.0 for all DVH statistics, showing statistical significance (p < 0.01). The ipsilateral lung V5Gy was also calculated lower by AcurosTM BV, with the mean difference of –1% for the breast cases (p < 0.01) and –2% for the lung region (p < 0.001). For the chest wall, the absolute difference of median dose values for D0.1cm3 and D1cm3 was 0.6 and 0.5 Gy (ranging from 0.1 to 2.2 Gy) for the breast implants, and 0.6 and 0.7 Gy (ranging from 0.1 to 0.8 Gy) for the interstitial lung implants, respectively, with TG-43 calculating higher dose values than AcurosTM BV, demonstrating statistical significance (p < 0.001). The maximum absolute dose overestimation of the TG-43 formalism in comparison with AcurosTM BV was equal to 2.2 and 2.1 Gy for D0.1cm3 and D1cm3, and 0.6 and 0.8 Gy for D0.1cm3 and D1cm3 for the lung implant, respectively. Figure 3 shows a box and whisker plot of the skin dose parameters analyzed, where it is evident that TG-43 clearly overestimated the dose received by the skin for both the breast and head and neck cases due to the inability of TG-43 to account for bounded patient geometry. For the breast, the maximum absolute dose overestimation by TG-43 for the skin D0.2cm3 was equal to 10.9 Gy, but this was because the PTV was extended inside the skin contour due to skin infiltration by the tumor, and because of the catheter vicinity (< 1 cm), which resulted in the presence of high-dose gradients.
Table 2
Analysis of dose to selected organs at risk showing median and mean difference of dose calculated with AcurosTM BV from that calculated using TG-43 algorithms, with 1st and 3rd quartiles (Q1-Q3), standard error, and p-value calculated using Wilcoxon paired test
Fig. 3
Box and whisker plots showing the absolute differences of dose volume histogram (DVH) parameters when calculated with AcurosTM BV from the TG-43 algorithm for the skin in treatments of the breast (A), and head and neck (HnN) region (B). For each boxplot, the thick bold line represents the median value (2nd quartile), the top line of the box is the 3rd quartile, while the bottom line represents the 1st quartile. The whiskers represent the near minimum and maximum values, and the circles are the outliers
Discussion
Since the AcurosTM BV algorithm is known for its ability to account for heterogeneities and bounded patient anatomy by providing dosimetric accuracy comparable with Monte Carlo (MC) dose calculations [10], it was employed in the current study to retrospectively calculate 22 breast, 22 head and neck, and 15 lung cases, and to compare the dosimetric results with the TG-43 dose formalism, as it has been presented previously by several groups and summarized in a recent review article [25]. A notable difference of the current study is the analysis of a wide and heterogeneous group of cases, with varying anatomical localization of the tumor, total prescribed dose, fractionation, and type of implant material employed (i.e., plastic or metal needles). This heterogeneity was chosen to demonstrate the expected range of differences across many possible clinical scenarios.
For the breast PTV, all dosimetric results showed a statistically significant dose overestimation by the TG-43 formalism in comparison with AcurosTM BV, which agrees with previous findings of 4% reported by Sinnatamby et al. [13]. This is also evident for all head and neck cases in our study, and in accordance with findings of Siebert et al. [19] who reported V100% and D90% median dose overestimations by TG-43 with 3%. TG-43 overestimated V150% more than it did for V100%. For example, in breast implants, V150% percentage difference between the two algorithms was 5.4%, and for V100%, it was 2.9%, i.e., 86% higher. A similar pattern was seen for head and neck implants, where V150% percentage difference between the algorithms was 4.7%, and for V100%, it was 2.9%, i.e., 62% higher. The TG-43 formalism calculated median V150%/V100% ratio, and was higher by 3.7% for the breast and by 2.7% for the head and neck implants, in comparison with AcurosTM BV. Therefore, AcurosTM BV calculated plans generally resulted in more homogeneous dose distributions in our study. This comes in line with an increase of dose homogeneity index of 8% in AcurosTM BV when compared with TG-43, as reported previously by Sinnatamby et al. [13] for the breast. It should be noted that, as the user focuses on the dosimetric analysis with higher percentage dose values (> 200%), dose volume calculations should be considered with caution; because of steep dose gradient, uncertainties of more than 10% may arise [26].
For the interstitial lung cases, all dose coverage indices were statistically higher for the TG-43 protocol than that calculated by AcurosTM BV as well as V150%. The dose coverage reduction calculated with AcurosTM BV was contrary to previous findings reported by O’Connel et al. [27] using the Elekta MBDCA algorithm, where a dose increase of 7% for D90% and 3% for V100% was reported. To our knowledge, there is no study that investigated AcurosTM BV dose difference compared with TG-43 for lung implants. The higher discrepancies for D90% and V100% were found for cases, in which the PTVs were surrounded by air-inflated lung tissue.
The skin mean dose indices differences in the current work were significantly higher for TG-43 than that calculated with AcurosTM BV. The maximum skin dose differences were observed in the vicinity of the catheters, when the PTVs included the skin, in the case where the tumor has infiltrated the skin, and the PTV was adjacent or overlapping the skin contour. The skin D0.1cm3 and D1cm3 overestimation by TG-43 in the present study was lower than the one reported by Hofbauer et al. [12] who reported values equal to 5.7% and 6.7%, respectively. This may be attributed to the position of the implant in relation to the skin and to the method for skin delineation used by Hofbauer et al. [12]. Generally, for small structure volumes following recommendations by Kirisits et al. [26], large differences should be handled with care, since uncertainties in DVH dose calculation are higher for smaller volumes than for larger ones.
In the breast implant, the chest wall median dose indices were also statistically significantly higher for TG-43 compared with AcurosTM BV, as reported previously by Hofbauer et al. study [12]. Although the median TG-43 D0.1cm3 and D1cm3 for all breast cases were 0.6 and 0.5 Gy higher than AcurosTM BV respective values, for the case of deeply located breast implants in the vicinity of the chest wall and ipsilateral lung, the TG-43 dose discrepancy from AcurosTM BV became more profound. This finding has been reported by Zourari et al. [10], and also observed in the current study, where a 2.2 and 2.1 Gy for D0.1cm3 and D1cm3 TG-43 overestimations as compared with AcurosTM BV for a deep-seated breast implant were reported. This is attributed to the inability of TG-43 to account for the lack of backscatter due to the presence of ipsilateral lung in a region relatively close to the border of CTV. For the interstitial lung implants, the maximum absolute chest wall dose overestimations of 0.6 and 0.8 Gy by TG-43 compared with AcurosTM BV was less pronounced in comparison with the breast implants. This may be attributed to the fact that in the case where the solid mass lung tumor lies in the close vicinity of the chest wall, this organ at risk is encompassed on one side by the solid tumor, and on the other side by the adipose or breast tissue; thus, leading to a situation of higher scatter conditions compared with a situation of the breast implants, where on one side of the chest wall, the presence of air-inflated lung leads to a lower backscatter conditions, causing TG-43 to deviate from AcurosTM BV more profoundly than in the case of the chest wall lying in the vicinity of the lung tumor implant.
The lung V5Gy was statistically significantly higher when calculated with TG-43 compared with AcurosTM BV by 1% for both the breast and lung cases. Since the 5 Gy isodose line for our breast implants was lower than 20% of the prescribed isodose, this overestimation was due to the inability of TG-43 to account for the lack of scatter photon dose component due to the presence of air-inflated lung in an area further away from the implanted catheters. In this area, the scattered photon dose component plays the predominant role, which is in line with findings of Pantelis et al. [28] for isodoses of less than 60% of the prescribed dose.
Conclusions
The undisputed benefit of AcurosTM BV in dosimetric calculation accuracy lies in its ability to account for the tissue as well as the brachytherapy catheter material (i.e., stainless steel or titanium needles) heterogeneities as well as the bounded anatomical geometry of the patient contour around the PTV and OARs, which may exhibit totally different tissue characteristics (bone and/or air) from the ones considered by the TG-43 formalism. In our work, AcurosTM BV calculates significantly lower doses to PTVs for the breast, head and neck, and lung implants as well as for the surrounding OARs. In specific cases, this might lead to a dose important coverage reduction not carefully accounted for, if only the TG-43 formalism is considered for dose calculation and dose reporting. As stated in a study by Papagiannis et al. [8], the benefit of AcurosTM BV as a MBDCA lies in the amount of reduction in the response to clinical trial populations through the individualization of patient dosimetry. In order to move to a fully model-based optimization in clinical practice, clinical trials for confirmation and/or re-evaluation of the current dosimetric objectives and constraints are needed, since these established from clinical trials and TG-43-based algorithms were solely applied.



