Introduction
Biomarkers are believed to be measurable indicators of pathogenic processes in the body or predictors of a response to therapeutic interventions. They may help in screening, diagnosis, characterisation, and monitoring of a disease [1]. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) was demonstrated to correspond with increased cytokine signalling in hidradenitis suppurativa [2, 3], a response to gold in allergic contact dermatitis [4], and a healing process of chronic venous leg ulcers [5].
NGAL belongs to antimicrobial peptides participating in the recruitment of T cells and neutrophils into the skin [6]. It was primarily identified in granules of neutrophils, but the epidermis was shown to be a prominent source of the substance [7]. Possible involvement of NGAL in the psoriasis pathogenesis was proposed by enhancing T-helper 1 (Th1)/T-helper 17 (Th17)-mediated inflammation [8] and parakeratosis [9].
Decreased expression of NGAL in psoriatic skin was previously observed after biologics (risankizumab, ustekinumab) [10] and narrow-band UVB phototherapy (NB-UVB) [11]. Reduction in the serum level of NGAL was recently found to correspond with a good response to cyclosporine therapy in patients with psoriasis [12].
Aim
The aim of the study was to investigate whether NGAL may serve as a biomarker of disease activity in psoriasis vulgaris.
Material and methods
Patients with psoriasis vulgaris were enrolled at the Dermatology Department between October 2021 and November 2022, having first given written informed consent. The study had earlier been approved by the Local Ethics Committee (PCN/CBN/0022/KB1/46/I/21). All subjects were evaluated towards concomitant chronic inflammatory skin diseases and previous treatment of psoriasis other than topical at the enrolment to the study stage. No systemic treatment of psoriasis (acitretin, methotrexate, cyclosporine, biologics), no phototherapy (NB-UVB or psoralen plus UVA therapy), no systemic steroids, and no immunosuppressive therapies for other reasons within the last 3 months were mandatory prerequisites to participate in the study. Soon before the enrolment, only topical therapies were allowed, and patients suffering from other variants of psoriasis (pustular and erythrodermic ones, psoriatic arthritis), concomitant inflammatory or chronic skin disease, chronic kidney disease, and subjects who experienced infections within the preceding 2 weeks were excluded.
Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) and body surface area (BSA) constituted the tools used to estimate the disease severity. Each of the patients was evaluated towards involvement of the scalp, genital region, nails, and hands. They were asked about the itch, and its occurrence was included in the patient’s characteristics when the itch was reported both at the medical interview and during the fulfilment of DLQI questionnaire. Intensity of the itch within the last week was assessed using the Peak Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale (PP-NRS).
A blood sample was taken from each patient’s antecubital vein to a clot activator tube after 12–14 h of fasting. It was centrifuged at 1996 RCF for 15 min to obtain a serum sample and then stored at –80°C until assayed. A commercially available ELISA test obtained from Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. (#EHLCN2, Waltham, USA) was used to measure the level of NGAL in serum. Its sensitivity was 4 pg/ml with 4.1–1000 pg/ml detection range. The level of C-reactive protein (CRP) in serum was measured using the Alinity C Immunoassay System (Abbott, Illinois, USA) using an immunoturbidimetric method (kit 07P56, Abbott). Statistical analysis of laboratory measurements with calculation of their correlations with clinical characteristics was performed using PQStat (v.1.6.8.061, PQ-Stat Software). A p-value below 0.05 was found to be statistically significant.
Measurements in patients were referred to those obtained from age-matched healthy controls who attended to the Outpatient Clinic for the evaluation of pigmental nevus but not suffering from any disorders. Their detailed characteristics are included to Supplementary Tables S1 and S2 in the supplementary file. Nicotine smokers and subjects with intense suntan gained within the preceding month were not allowed to participate in the study. All subjects who suffered from cutaneous, respiratory, or genitourinary tract infections as well as those receiving antibiotics, analgesic drugs, or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs within the last 2 weeks were excluded.
Results
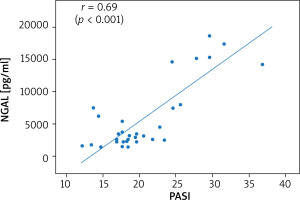
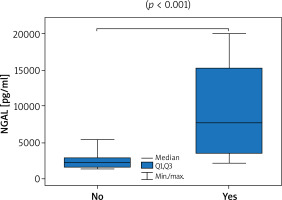
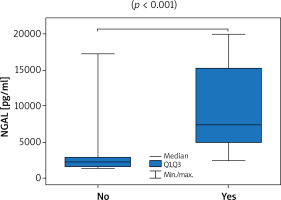
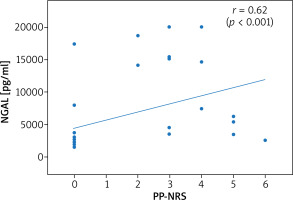
Thirty-six patients with psoriasis vulgaris and 33 healthy controls were enrolled to the study. All patients were characterised in Table 1. Serum levels of NGAL did not prove to be sex-dependent (p = 0.24). A significantly higher level of NGAL in serum was found in patients with psoriasis when compared to healthy controls (3090 pg/ml vs. 2573 pg/ml; p = 0.01; U Mann-Whitney test). The level of NGAL in serum showed a moderate correlation with PASI (Figure 1) but none with BSA, in both women and men (Table 2). A significantly greater serum level of NGAL was determined in the case of genital involvement (Figure 2) in both sexes. Itch was associated with significantly higher concentration of NGAL in patients’ serum (Figure 3), and its intensity measured with PP-NRS corelated moderately with the level of circulating NGAL (Figure 4). No correlations were found between the concentration of NGAL and the level of CRP in serum, disease duration, BMI, and patients’ age.
Table 1
Clinical characteristics of the patients
| Parameter | Women | Men | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number | 16 | 20 | |
| Age median (range) [years] | 45 (27–58) | 38 (31–59) | 0.22* |
| Disease duration median (range) [years] | 7 (1.5–17) | 6 (1–16) | 0.85* |
| BMI mean (range) [kg/m2] | 28.0 ±5.3 | 27.8 ±4.5 | 0.89*** |
| Elevated CRP | 5 (28%) | 3 (17%) | 0.42** |
| PASI median (range) | 19.6 (13.4–38.2) | 18.4 (12.1–36.8) | 0.99* |
| BSA median (range) | 37 (21–90%) | 36 (21–74) | 0.73* |
| Involvement of: | |||
| Nails | 4 (25%) | 10 (50%) | 0.18** |
| Scalp | 16 (100%) | 18 (90%) | 0.49** |
| Genital | 10 (62.5%) | 8 (40%) | 0.31** |
| Hands | 3 (19%) | 11 (55%) | 0.04** |
| Itch | 7 (44%) | 8 (40%) | 1.0** |
| PP-NRS median (range) | 0 (0–5) | 0 (0–6) | 1.0* |
| Previous treatment other than topical: | |||
| Cyclosporine | 1 (6%) | 1 (5%) | 1.0** |
| Methotrexate | 3 (18%) | 4 (20%) | |
| Phototherapy | 6 (38%) | 7 (35%) | |
| None | 6 (38%) | 8 (40%) | |
| NGAL [pg/ml] | 4819 | 2984 | 0.24* |
Table 2
Correlations between serum level of NGAL and clinical characteristics
| Parameter | All | Women | Men | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs (p-value) | Age | –0.03 (p = 0.86) | 0.29 (p = 0.27) | –0.29 (p = 0.2) |
| Disease duration | 0 (p = 0.98) | 0.12 (p = 0.64) | –0.19 (p = 0.42) | |
| BMI | –0.03 (p = 0.85) | 0.17 (p = 0.52) | –0.15 (p = 0.52) | |
| PASI | 0.69 (p < 0.001) | 0.77 (p < 0.001) | 0.64 (p = 0.002) | |
| BSA | 0.27 (p = 0.11) | 0.22 (p = 0.42) | 0.25 (p = 0.3) | |
| Itch PP-NRS | 0.62 (p < 0.001) | 0.6 (p = 0.01) | 0.56 (p = 0.009) | |
| Concentration of NGAL [pg/ml] (p-value)* | Itch | 7479 vs. 2275 (p < 0.001) | 11035 vs. 2185 (p < 0.001) | 5427 vs. 2395 (p = 0.008) |
| CRP elevated | 5322 vs. 2785 (p = 0.15) | 6207 vs. 3431 (p = 0.74) | 4438 vs. 2658 (p = 1.0) | |
| Nails involvement | 5733 vs. 2576 (p = 0.11) | 15201 vs. 2964 (p = 1.0) | 3300 vs. 2526 (p = 0.25) | |
| Scalp involvement | 3090 vs. 3935 (p = 1.0) | n/a | n/a | |
| Genital involvement | 7734 vs. 2259 (p < 0.001) | 7479 vs. 2243 (p = 0.013) | 7990 vs. 2275 (p = 0.001) | |
| Hands involvement | 3300 vs. 2578 (p = 0.39) | 7474 vs. 3431 (p = 1.0) | 3124 vs. 2395 (p = 0.2) | |
Discussion
The search for biomarkers remains a constant objective of ongoing research studies on the aetiopathogenesis of psoriasis, and NGAL has been identified as a potential candidate. This is another study that demonstrates significantly higher levels of circulating NGAL compared to healthy controls, as similarly shown by previous authors [13–19]. Although the level of circulating NGAL was previously found to be higher in patients with psoriatic arthritis [20], it was not elevated in the case of isolated joint disease without skin involvement [21].
Keratinocytes were postulated to be the main source of NGAL in the skin [13], and the serum level of NGAL was shown to be lower than its tissue level in patients with psoriasis [22]. Expression of NGAL in normal and non-lesional psoriatic skin is probably restricted only to follicular epithelium, but its upregulation in the epidermis may occur in a wide spectrum of skin disorders associated with hyperkeratosis and abnormal differentiation of keratinocytes [23, 24]. Injection of NGAL was shown to exacerbate the erythema and scaling in a murine model of imiquimod-induced psoriasiform skin, which suggests its contribution to the development of psoriasis [8].
Increased keratinocyte load does not explain the higher level of circulating NGAL, because only moderate correlations were observed between circulating NGAL and PASI in the current study. It corresponds only to the observations of Sokolova et al. [21] but remains in contrast to most previous authors who did not find correlations between the severity of psoriasis and circulating NGAL [16, 18, 19, 22, 25]. Clinical improvement of skin lesions after topical treatment with 5% salicylic ointment and 0.3% anthralin was not associated with a reduction in the level of circulating NGAL in the study of Baran et al. [19]. Despite successful treatment response, neither anti-TNF inhibitors [16] nor NB-UVB phototherapy [15, 16] caused a reduction of circulating NGAL. A significantly lower serum level of NGAL was, however, observed in patients with psoriasis who responded to cyclosporine therapy [12]. The treatment of psoriasis with biologics (risankizumab, ustekinumab) [10], including both TNF and IL-17 inhibitors [21], as well as NB-UVB [11], were previously found to be associated with a decline in tissue expression of NGAL.
The novel finding of this study involves noticeable dependence of the level of circulating NGAL on the involvement of the genital region and the itch. Psoriasis affecting the genital region was associated with significantly greater concentration of NGAL in serum, but no association was seen in other special locations like hands, nails, and scalp. The dependence of circulating NGAL level on the involvement of special locations in psoriasis has not been analysed in previous studies, but it may help to explain the refractory of the genital region to standard anti-psoriatic treatment [26]. It was difficult to evaluate the association with the scalp involvement because the majority of patients suffered from the lesions in that region. Undoubtedly, subsequent studies should measure the level of circulating NGAL in patients with isolated involvement of special locations with psoriasis but sparing other body areas because genital involvement was associated with significantly higher PASI (p = 0.003; Supplementary Table S3).
The itch corresponded herein to higher levels of circulating NGAL, and the intensity of the itch assessed using PP-NRS correlated moderately with the serum level of NGAL. Observations relating to itch remain in compliance with the findings of Aizawa et al. regarding patients with psoriasis, but without similar correlations seen in subjects with atopic dermatitis. Interestingly, a significant decrease of circulating NGAL was observed only in patients with psoriasis receiving biological treatment who experienced itch reduction [18]. NGAL constitutes a potential itch mediator produced by astrocytes in the spinal cord [27], whereas its elevated serum level was proposed to potentiate itch in patients with chronic kidney disease [28].
It is difficult to propose NGAL as a biomarker of disease activity in psoriasis. An elevated level of circulating NGAL only indicates its participation in the pathogenesis of psoriasis and can be responsible for the development of the itch. The serum level of NGAL does not allow for the evaluation of disease severity because it shows none to moderate correlation with PASI. Determination of the circulating NGAL level may help to identify patients with greater risk for the involvement of the genital region, but these observations should be revaluated in studies recruiting only patients with isolated involvement of special locations.