Introduction
Neonatal sepsis (NS) is a life-threatening infection occurring within the first 28 days of birth [1]. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), NS claims 1 million lives annually, with 42% of these deaths occurring in the first week of life [2]. Given its swift progression and severe symptoms, every hour of delay in diagnosing NS reduces the NS survival rate [3]. Presently, the diagnosis of NS is challenging due to the lack of specific clinical presentation. Blood cultures, the current gold standard for identifying NS, are prone to false positives and often cannot deliver accurate results within 72 h. This delay can lead to missed diagnoses and consequent delayed treatment [4]. Hence, a rapid and highly specific diagnostic biomarker for NS could significantly improve treatment timing and reduce mortality rates.
Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) is a type of linear RNA molecule. Dysregulation of lncRNAs is linked with disease initiation and progression [5, 6], which includes NS [7]. Additionally, lncRNAs deserve attention as biomarkers due to their stable expression [8]. Interestingly, the lncRNA human histocompatibility leukocyte antigen complex P5 (HCP5) is located on human chromosome 6q21.33, which plays a role in regulating ischemia-reperfusion injury [9]. NS is a disease associated with inflammation. HCP5 modulates the high glucose-induced excessive inflammation in human glomerular mesangial cells [10]. HCP5 influences the airway mucosal inflammation in nasal epithelial cells [11]. It is also linked to systemic vascular inflammation in infants and children caused by Kawasaki disease [12] and associated with the autoimmune disease systemic lupus erythematosus [13] and psoriasis [14]. More notably, Liu et al. identified 20 differentially expressed lncRNAs in NS, including HCP5 [15]. However, the possible function of HCP5 in NS and its clinical value have not been reported.
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are highly conserved non-coding RNA molecules, typically ranging in length from 18 to 24 nucleotides [16]. MiR-138-5p, located on chromosome 3q21.32, significantly contributes to acute lung injury [17] and is involved in sepsis-induced myocardial injury [18]. However, few studies have reported the functions of miR-138-5p in NS. Sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) is a highly conserved NAD-dependent histone deacetylase. SIRT1 is implicated in sepsis-related acute kidney injury [19] and downregulated in a mouse model of sepsis [20]. Previous studies reported that HCP5 was involved in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma via targeting miR-138-5p, and SIRT1 is a known target of miR-138-5p [21, 22]. Therefore, we hypothesized that HCP5 might be involved in the inflammation in NS through the miR-138-5p/SIRT1 axis. The present study attempted to prove this hypothesis in anticipation of understanding the diagnostic value and potential mechanisms of HCP5 in NS.
Material and methods
Participants and serum sample collection
Ethical approval for this study was obtained from the Maternity & Child Care Center of the Xinyu Ethics Committee. Written informed consent was obtained from the parents before sample collection. Eighty-six patients with NS from January 2017 to December 2020 in the Maternity & Child Care Center of Xinyu were enrolled. Of these, 45 were males with a mean age of 10.69 ±4.84 days. The inclusion criteria were aligned with the international definition of pediatric NS. They included inflammation and infection accompanied by any two of the following signs: 1) temperature < 36°C or > 38.5°C; 2) bradycardia or tachycardia (heart rate < 100 beats/min or > 180 beats/min); 3) white blood cell count < 5.0 < 109/l or > 19.5 < 109/l; 4) respiratory distress with respiratory rate > 40 breaths/min. Pathogen detection was based on the criteria developed at the 2003 Kunming Conference on the definition of Neonatal Sepsis. Additionally, 80 neonates without sepsis but diagnosed with respiratory tract infection or pneumonia were enrolled as controls. All patients in both groups were admitted within 48 h of onset, had complete clinical data, and had not received drug or physical therapy prior to admission. The exclusion criteria were congenital infections, suspected inborn metabolic abnormalities, chromosomal abnormalities, congenital defects, hematologic disorders, and combined jaundice. A 2 ml sample of venous blood was collected and centrifuged at 15,000 rpm for 15 min, and the serum in the supernatant was stored at –80°C. White blood cell count (WBC), serum procalcitonin (PCT), and C-reactive protein (CRP) were assessed within 12 h of hospital admission and measured with the SYSMEX-800i blood analyzer.
Cell culture and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induction
Macrophage cells (RAW264.7) were purchased from BeNa Culture Collection and cultured in RPMI 1640 medium containing 10% FBS and maintained in an incubator at 37°C with 5% CO2 and suitable humidity. According to previous reports [23], an in vitro sepsis cell model was constructed using different concentrations of LPS (0.5, 1, and 2 µg/ml) for 12 h.
Cell transfection
HCP5 overexpression plasmid (pcDNA3.1-HCP5) and its empty vector (pcDNA3.1) were purchased from GenePharma (Shanghai, China). miR-138-5p mimic or inhibitor and mimic NC or inhibitor NC were provided by RibiBio (Guangzhou, China). When the cells grew to the logarithmic phase, pcDNA3.1-HCP5 was individually transfected into cells under the transfection reagent Lipofectamine 2000 to enhance the expression of HCP5 for detecting the potential role of HCP5. Subsequently, to test whether miR-138-5p could restore the role of HCP5, pcDNA3.1-HCP5 was co-transfected into cells with miR-138-5p mimic.
Reverse transcription-quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
Total RNA was extracted from either the subject’s serum or cell lines using the miRNeasy serum/plasma kit. cDNA was produced by adding the PrimeScript RT-reagent Kit and the mir-X miRNA First-Strand Synthesis Kit to reverse transcribe 500 ng of RNA. The SYBR-Green I Master Mix or miR-X miRNA qPCR SYBP kit, primer, and cDNA were mixed, and the PCR amplification reaction was performed on an Applied Biosystems 7900 Real-Time PCR System. U6 or GAPDH was normalized as an internal control gene to normalize the relative expression of miR-138-5p or HCP5 and SIRT1, respectively. 2-ΔΔCt methods were calculated for the levels of three replicates.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
ELISA was used to measure the concentration of inflammatory cytokines interleukin (IL)-8 and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α in the patient’s serum and cell supernatant. Serum and cell supernatants were collected for antibody incubation and color development according to the commercial kit instructions for IL-8 (550999, BD Biosciences, USA) and TNF-α (550610, BD Biosciences, USA). Readings were taken on an enzyme marker at 450 nm.
Dual-luciferase reporter assay
Online profiling software RNA22 v2 (https://cm.jefferson.edu/rna22/Interactive/ ) and TargetScan 7.2 (http://www.targetscan.org/ , accessed on 1 October 2020) revealed that miR-138-5p binds to HCP5 or SIRT1. The sequences of 3’ UTR of wild type (WT) and mutant (MUT) HCP5 or SIRT1 mRNA containing the putative miR-138-5p binding sites were chemically synthesized from GeneChem and cloned into downstream of the luciferase vectors to generate the vectors HCP5-WT, SIRT1-WT, HCP5-MUT or SIRT1-MUT. RAW264.7 was seeded into 48-well plates and the above plasmids were co-transfected with miR-138-5p mimic or inhibitor. After 48 h, cells were lysed, and luciferase activity was detected by a dual-luciferase reporter assay kit (cat: E1910, Promega, USA), and the renilla luciferase activity was used as an internal reference.
Statistical analysis
Data were represented as mean ± SD of three biological replications, and statistics were calculated using SPSS 23.0 and GraphPad 7.0. Student’s t-test and one-way ANOVA were used to evaluate differences between groups. ROC curves were utilized to determine the diagnostic significance, while Pearson correlation coefficient analysis was conducted to investigate the potential association. A p value of less than 0.05 was considered significant.
Results
Demographic and clinicopathological data
Demographic and clinical parameters were compared. There were no statistically significant differences between the two groups regarding gender, age, and weight (p > 0.05, Table 1). The parameters respiratory rate, WBC, PCT, CRP, IL-8, and TNF-α were significantly higher in NS patients than in controls (p < 0.05).
Table 1
Demographic characteristics and biochemical parameters of the subjects
[i] Control group, neonatal without sepsis but diagnosed with respiratory tract infection or pneumonia. NS – neonatal sepsis, WBC – white blood cells, CRP – C-reactive protein, PCT – procalcitonin, IL-8 – interleukin 8, TNF-α – tumor necrosis factor α. Data are expressed as n or mean ± standard deviation
Reduced HCP5 has potential as a diagnostic marker for NS
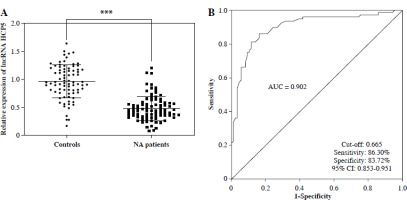
Serum levels of HCP5 in NS patients and controls were assessed by RT-qPCR. Serum HCP5 was significantly lower in NS patients compared to controls (p < 0.05, Fig. 1A). To understand the potential value of this significant reduction of HCP5 in NS patients, we plotted the ROC and calculated the area under the curve (AUC). As illustrated in Figure 1B, the AUC of HCP5 was 0.902, with sensitivity and specificity rates of 86.30% and 83.72%, respectively, using a cut-off value of 0.665. This suggests that HCP5 can differentiate patients with respiratory infection or pneumonia from NS cases.
Fig. 1
Reduced HCP5 has potential as a bio-diagnostic marker for neonatal sepsis (NS). A) Serum HCP5 was reduced in NS patients compared to controls as confirmed by the RT-qPCR results. B) ROC was plotted based on serum HCP5 levels in NS patients and controls to evaluate the diagnostic significance of HCP5. AUC – area under the curve of ROC; ***p < 0.001 vs. controls
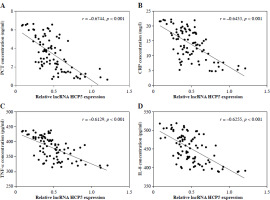
Serum HCP5 was negatively correlated with PCT, CRP, and inflammatory factors
Procalcitonin and CRP were identified as good indicators for early diagnosis of NS, the severity of sepsis, and correlation with mortality. Pearson correlation coefficient analysis verified a negative association between serum HCP5 and PCT (r = –0.6774, p < 0.001, Fig. 2A) and CRP (r = –0.6453, p < 0.001, Fig. 2B) in NS patients. Additionally, the serum HCP5 in NS patients was also negatively associated with secretion of the pro-inflammatory factors TNF-α (r = –0.6129, p < 0.001, Fig. 2C) and IL-8 (r = –0.6255, p < 0.001, Fig. 2D). However, HCP5 was not significantly correlated with them in healthy individuals (Supplementary Figure). The research recommends that reduced HCP5 is associated with the severity of NS and may participate in its progression by affecting secretion of inflammatory cytokines.
Fig. 2
Serum HCP5 was negatively correlated with procalcitonin (PCT), C-reactive protein (CRP), and inflammatory factors in the patients with neonatal sepsis (NS). Pearson correlation coefficient was adopted to assess the association between HCP5 and PCT (A), CRP (B), TNF-α (C), and IL-8 (D) in NS patients
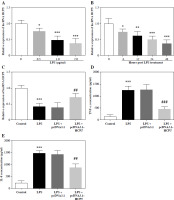
Overexpression of HCP5 attenuated LPS-induced inflammatory factor secretion in macrophages
As the LPS increased and induction time was delayed, the HCP5 level gradually decreased (p < 0.05, Fig. 3A, B). Based on these results, we used 1 µg/ml LPS induction for 12 h in subsequent studies. Transfection with pcDNA3.1-HCP5 effectively reversed the decrease in HCP5 levels caused by LPS (p < 0.05, Fig. 3C). An ELISA revealed that LPS induction increased the secretion of TNF-α and IL-8, whereas this increase was mitigated by pcDNA3.1-HCP5 (p < 0.05, Fig. 3D, E).
Fig. 3
Overexpression of HCP5 significantly attenuated LPS-induced inflammatory factor secretion. HCP5 expression levels were reduced in an LPS dose-dependent (A) and time-dependent (B) manner. C) Expression levels of HCP5 after transfection of pcDNA3.1-HCP5 in LPS-induced RAW264.7. ELISA detected the effect of HCP5 overexpression on the secretion of inflammatory factors TNF-α (D) and IL-8 (E). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 vs. 0 μg/ml or 0 h or control; ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 vs. LPS + pcDNA3.1
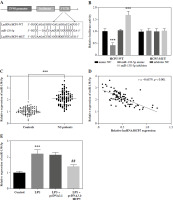
miR-138-5p is a target of lncRNA HCP5
The function of the lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA network in diseases is becoming more apparent [24]. Using the bioinformatics tool RNA22, we analyzed the po- tential target miRNA of HCP5 in NS, confirming the binding sites between HCP5 and miR-138-5p (Fig. 4A). miR-138-5p mimic decreased the luciferase activity of HCP5-WT, while miR-138-5p inhibitor increased it (p < 0.05). However, neither had any effect on cells transfected with HCP5-MUT (p > 0.05, Fig. 4B). Furthermore, miR-138-5p was more prevalent in NS patients (p < 0.05, Fig. 4C) and was negatively correlated with HCP5 levels (r = –0.6879, p < 0.05, Fig. 4D). In the LPS-induced cell model, LPS increased miR-138-5p levels, but this increase was suppressed by pcDNA3.1-HCP5 (p < 0.05, Fig. 4E).
Fig. 4
miR-138-5p was a target miRNA of HCP5. A) Bioinformatics tools confirmed the binding site between HCP5 and miR-138-5p. B) Luciferase reporter analysis was employed to confirm the relationship between miR-138-5p and HCP5. C) Serum miR-138-5p levels in neonatal sepsis (NS) patients and controls (neonatal without sepsis but diagnosed with respiratory tract infection or pneumonia). D) Pearson correlation coefficient was employed to assess the correlation between miR-138-5p and HCP5. E) miR- 138-5p levels after transfection of HCP5 overexpression plasmid in LPS-inducible RAW264.7. ***p < 0.001 vs. controls or mimic NC; ##p < 0.01 vs. LPS + pcDNA3.1
Elevated miR-138-5p attenuated the remission of inflammation by HCP5
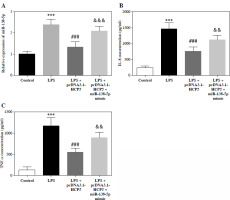
To examine whether HCP5 alleviates inflammation in NS in association with miR-138-5p, we introduced miR-138-5p mimic into LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells overexpressing HCP5. As illustrated in Figure 5A, the HCP5-induced reduction of miR-138-5p levels was significantly reversed by the miR-138-5p mimic (p < 0.05). What is more, pcDNA3.1-HCP5 alleviated LPS-induced over- secretion of IL-8 and TNF-α, and this alleviation was attenuated by elevated miR-138-5p (p < 0.05, Fig. 5B, C).
Fig. 5
Elevated miR-138-5p impairs mitigation of the inflammatory response by HCP5. A) miR-138-5p levels after transfection with miR-138-5p mimic in LPS-induced and HCP5 overexpressing RAW264.7. B) ELISA was conducted to analyze the effect of elevated miR-138-5p on the secretion of inflammatory factors IL-8 (B) and TNF-α (C). ***p < 0.001 vs. control; ###p < 0.001 vs. LPS; &&p < 0.01, &&&p < 0.001 vs. LPS + pcDNA3.1-HCP5
SIRT1 is a direct downstream target of miR-138-5p
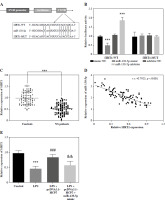
The TargetScan database was employed to further examine the mechanisms of the HCP5/miR-138-5p axis in NS. SIRT1 was identified as a potential target of miR-138-5p, complete with a proposed binding site (Fig. 6A). The luciferase activity of SIRT1-WT was significantly suppressed or enhanced by the miR-138-5p mimic or inhibitor, but the luciferase activity of SIRT1-MUT was unaffected (p < 0.05, Fig. 6B). In NS patients, serum SIRT1 was lower (p < 0.05, Fig. 6C) and negatively associated with miR-138-5p levels (r = –0.7925, p < 0.05, Fig. 6D). In the in vitro model, LPS reduced SITR1 levels. While overexpression of HCP5 significantly counteracted this reduction, the effect was lessened by increased miR-138-5p (p < 0.05, Fig. 6E).
Fig. 6
SIRT1 is a direct downstream target of miR-138-5p. A) SIRT1 was predicted as a downstream target of miR- 138-5p by the online tool TargetScan. B) Dual-luciferase reporter was employed to analyze the relationship between miR-138-5p and SIRT1. C) Serum levels of SIRT1 in neonatal sepsis (NS) patients and controls (neonatal without sepsis but diagnosed with respiratory tract infection or pneumonia). D) Pearson correlation coefficient was used to analyze the correlation between miR-138-5p and SIRT1 in NS patients. E) Regulation of SIRT1 levels after LPS-induced overexpression of HCP5 or miR-138-5p in RAW264.7. ***p < 0.001 vs. controls or mimic NC; ###p < 0.001 vs. LPS; &&p < 0.01 vs. LPS + pcDNA3.1-HCP5
Discussion
Diagnosis of NS remains a considerable concern for clinicians and basic researchers due to the lack of specific clinical presentation and the high cost of ICU stay, rapid rate of progression, organ failure rate, and mortality of NS [25]. Furthermore, uncontrolled inflammation and refractory immune dysfunction are key factors in the progression of NS [26]. This report suggests that HCP5 could potentially serve as a bio-diagnostic marker for NS and may help mitigate its progression by targeting miR-138-5p and SIRT1 to suppress inflammation. These findings underscore the potential diagnostic and therapeutic role of HCP5 in NS.
HCP5 in inflammation-related diseases has been extensively reported. HCP5 is downregulated in nasal epithelial cells of patients with allergic rhinitis and regulates their inflammatory response [11]. It also possibly contributes to the progression of ankylosing spondylitis by inducing epigenetic dysregulation [27]. Liu et al. identified HCP5 as one of the five potential bio-diagnostic markers for NS, linked to the immune response [15]. Given this information, we hypothesized that HCP5 might play a role in NS progression. In this study, we included NS patients and neonates diagnosed with respiratory tract infection or pneumonia as controls, excluding sepsis. NS patients displayed a higher respiratory rate and slower heartbeat, consistent with previous NS studies, indicating that our NS patients are representative. To verify our hypothesis, we analyzed HCP5 expression and discovered that serum HCP5 in NS patients was significantly lower than in controls, suggesting that HCP5 may be involved in the progression of NS.
White blood cell count, CRP, and PCT are traditionally recognized as blood markers of NS [28]. Additionally, CRP and PCT are considered significant indicators of NS severity [29]. This study found that WBC, CRP, and PCT levels were higher in NS patients than in controls. Furthermore, PCT and CRP have negatively correlated with patients’ serum HCP5 levels, confirming that HCP5 levels are correlated with NS severity and potential diagnostic value. The ROC revealed that HCP5 levels significantly distinguished NS patients from controls, demonstrating potential as a diagnostic biomarker. Previous studies have associated IL-8 and TNF-α levels with NS risk [30]. However, their variability prevents their use as routine diagnostic tools. NS patients in our study had overproduction of inflammatory factors IL-8 and TNF-α, consistent with previous studies [31]; however, their levels were negatively correlated with HCP5, suggesting that HCP5 may participate in NS progression by regulating inflammation. To further explore the regulatory role of HCP5 in NS, we established an in vitro NS model according to previous studies [32]. In LPS-induced RAW264.7, HCP5 was reduced in a dose-dependent and time-dependent manner. LPS-induced overproduction of inflammatory factors was significantly attenuated by HCP5 overexpression. Thus, we confirmed that HCP5 may be involved in NS progression by regulating inflammation.
In our study, we confirmed that miR-138-5p is a target miRNA for HCP5 and is elevated in NS patients and negatively correlated with the levels of HCP5. miR-138-5p regulates neuroinflammation [33], monocrotaline-induced inflammation in pulmonary hypertension [34], and the progression of osteoarthritis [35]. It is also involved in sepsis-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome [36]. Interestingly, the targeting relationship between HCP5 and miR-138-5p was confirmed [37], which is consistent with our results. We found that the overproduction of inflammatory factors induced by LPS was reduced by elevated HCP5. However, this reduction was reversed by miR-138-5p overexpression, suggesting that HCP5 may contribute to NS progression by inhibiting miR-138-5p, which regulates inflammation.
Finally, we found that SIRT1 is a downstream target of miR-138-5p, and the relationship between miR-138-5p and SIRT1 was confirmed in arthritis [38]. SIRT1 activation has anti-inflammatory effects by blocking nuclear factor-kappaB, thereby inhibiting the production of TNF-α and IL-8 [39]. Resveratrol was also found to significantly inhibit the TNF-α induced release of IL-8 from endometrial ectopic stromal cells by activating SIRT1, thereby suppressing the inflammatory response [40]. In line with this research, we identified a significant decrease in SIRT1 in NS patients. LPS caused a decrease in SIRT1 in RAW264.7 and its expression was promoted by elevated HCP5. However, the overexpression of miR-138-5p suppressed its level. As such, we suspect that the HCP5/miR-138-5p axis influences the inflammatory response of NS by affecting the level of SIRT1, which in turn contributes to its progression. Although this study reported for the first time the clinical value and potential mechanisms of HCP5 in NS, there are some limitations to consider. Firstly, the small sample size of the study may have some bias. Second, the role of HCP5/miR-138-5p/SIRT1 axis in the NS requires animal models for validation. PCT and IL-6 as diagnostic biomarkers can be studied by an automated analysis platform in a large clinical center, but they are also aberrantly expressed in patients with acute infections such as urticaria [41] or COVID-19 [42]. The detection method of lncRNA as a biomarker may limit its clinical application, and needs to be further simplified and improved, but our study offers the possibility of lncRNA as a diagnostic biomarker. Finally, despite agreement with most previous studies, there are still reports suggesting that LPS-induced RAW264.7 may not be a reliable in vitro cellular model of sepsis. Additionally, a new animal-free human whole-blood sepsis model has been identified for studying changes in innate immunity [43], which will be addressed in our further research.
In conclusion, HCP5 is down-regulated in NS and has potential as a bio-diagnostic marker. Moreover, HCP5 suppressed miR-138-5p/SIRT1 axis to improve the inflammation to regulate NS progression. Our study highlights the potential of HCP5 in the diagnosis and treatment of NS.


