Ultrasound (US)-guided interscalene (IS) block is a commonly performed procedure for anaesthesia and analgesia for shoulder and humerus surgery. Though it provides excellent analgesia, it is associated with adverse effects such as hemidiaphragmatic paralysis, dyspnoea and hoarseness [1, 2]. It can also result in dorsal scapular or long thoracic nerve injury. Recently, Burkett et al. [3] described superior trunk (ST) block wherein the local anaesthetic was deposited around the ST (formed by fusion of C5 and C6 nerve roots). They stated that it reduces the risk of hemidiaphragmatic paresis and provides adequate analgesia in shoulder arthroscopies. Other studies have also confirmed its utility in arthroscopic surgery [4]. Recently, two studies have used ST block as an anaesthetic technique in open humerus surgery. It provided adequate analgesia with no adverse effects [5, 6]. We hypothesized that administering an ST block to a patient undergoing humerus surgery would preserve hemidiaphragmatic function while providing comparable perioperative analgesia as compared to an IS block. The study aimed to compare ST block with IS block in terms of incidence of hemidiaphragmatic paresis, perioperative opioid requirement, and other adverse effects.
Methods
After Institutional Ethics committee (AIIMS/Pat/IEC/2020/454) approval, this trial was registered in the Clinical Trial Registry of India (CTRI/2021/05/033841). The study was carried out according to the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki, 2013, and good clinical practice. Written informed consent to participate in the study and use the patient data for research and educational purposes was obtained from all subjects. We screened 70 ASA (American Society of Anaesthesiologist) I–II patients in the age group 25 to 60 years undergoing unila-teral internal fixation (plating) for proximal or mid shaft humerus fracture. The patients were explained about the study protocol and written informed consent was taken. Patients with a history of allergy to local anaesthetics, body mass index (BMI) > 30 kg m–2, with known pulmonary disease, infection at puncture site, patients with neuromuscular disorders, pregnant patients, chronic pain disorders or on antidepressant medications, unable to understand the functioning of a patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) pump or numerical rating scale (NRS) were excluded from the study.
The sample size of the study was calculated based on a study by Kim et al. [7]. The incidence of hemidiaphragmatic paresis was 97% in patients receiving IS block. Anticipating a reduction of at least 30% in the incidence, with an a error of 5% and power of 80%, the sample size was calculated to be 26 in each group. Taking a drop-out rate of 20%, we enrolled a total of 62 patients over a period of 9 months, as shown in the CONSORT flow diagram (Figure 1).
Computer-generated random numbers were used to allocate the patients randomly to one of the two groups. The random allocation sequence was concealed in opaque, sealed envelopes until the day of intervention, when the envelope was opened and the intervention done accordingly.
All the blocks were performed in the preoperative holding area. After transferring the patients to the preoperative holding area, standard ASA monitors were attached. An 18G cannula was secured in the contralateral hand and a balanced salt solution was started. Baseline diaphragmatic movement was documented with the patient in a sitting position [8]. These measurements were done by anaesthesiologists with at least 5 years of experience in point-of-care ultrasound. They were unaware of the group allocation. A low frequency (2 to 5 MHz) curvilinear transducer was placed under the lowest rib at the anterior or midaxillary line to visualise the liver or spleen, which was used as the acoustic window. The diaphragm was seen as a hyperechoic structure moving with respiration. The patients were asked to inspire and expire maximally. An average of three readings of unilateral diaphragmatic excursion was documented according to the site of the planned block.
Patients in group I received US-guided ST block as described by Burkett et al. [3] while those in group II received US-guided IS block. ST was identified using a high frequency linear probe (5 to 13 MHz) by tracing C5 and C6 nerve roots distally until they joined. After skin infiltration with 1 mL of 2% lignocaine, a 5 cm, 22 G Sonoplex needle (Pajunk, Germany) was introduced in a lateral-to-medial direction to target the trunk. IS block was administered using an in-plane technique wherein the needle targeted the cervical roots in between the scalene muscles. The tip of the needle was placed in between C5 and C6 nerve roots. Both groups received 15 mL of 0.5% bupivacaine. Care was taken to avoid long thoracic and dorsal scapular nerves. Twenty minutes after giving the block, the patients were assessed for sensory blockade (numbness in the arm) and weakness in shoulder abduction. In the absence of these, the block was considered a failure, and the patient was not considered to be part of the study.
Thirty minutes after the block, unilateral diaphragmatic excursion was measured again by the same anaesthesiologist who took the initial reading. An average of three readings was taken. Following this, the patients were transferred to the operating room. A decrease of 75 to 100% in the diaphragmatic excursion or visualization of para-doxical movement was classified as complete paresis. A 25 to 75% decrease was considered as partial while less than a 25% decrease was classified as absent paresis [9].
All the patients received general anaesthesia in a standardised manner (2 mg kg–1 propofol, 0.5 mg kg–1 atracurium, 2 mg kg–1 fentanyl). An appropriate-sized endotracheal tube was inserted. Maintenance of anaesthesia was done by isoflurane in air. All the patients received 0.5 mg/kg–1 fentanyl hourly as part of the protocol. Apart from this, additional doses of fentanyl were repeated at the discretion of the senior anaesthesiologist (increase in the heart rate or mean arterial pressure 20% above baseline). At the end of the surgery, the patient’s trachea was extubated and the patient was transferred to the post-operative ward. A PCA pump loaded with fentanyl was attached to all the patients with the following settings – bolus: 20 mg, lock-out interval 10 minutes. All the patients received IV paracetamol 1 g three times a day as part of our institutional protocol. Pain scores – NRS was documented at timely intervals: 0, 2, 4, 8, 12, and 24 hours. Twenty-four-hour fentanyl consumption was also documented. All these assessments were made by the resident on duty, unaware of the interventions made.
The primary outcome was the incidence of hemi-diaphragmatic paresis. Secondary outcomes included a decrease in diaphragmatic excursion, total opioid consumption in 24 hours, NRS scores at various intervals, and any adverse effects (respiratory depression as defined by peripheral oxygen saturation: SPO2 less than 90% or respiratory rate less than 8).
The data were entered in Microsoft Excel and analysed in IBM SPSS Statistics software version 23. Normality of the data was tested using the Shapiro-Wilk test. Categorical variables were presented as percentage and continuous variables as mean ± standard deviation (SD) or median and interquartile range (IQR) depending on normality of data and a boxplot was used to display the percentage of reduction of diaphragmatic excursion. Pain scores on the NRS, diaphragmatic excursion of patients, and patient satisfaction were presented as median (IQR) and tested by the Mann-Whitney U test, and the independent t-test was applied to compare between ST and IS nerve blocks for normally distributed data.
Results
Both groups were similar in the demographic and surgical characteristics (Table 1). The baseline diaphragmatic excursion was similar in both groups. The incidence of complete/incomplete paresis was significantly higher in the IS group. Thirty-eight percent of the patients (11) had complete paresis in the IS group, compared to none in the ST group. Partial paresis was observed in 62% of patients in the IS block group and 19% in the ST block group (P < 0.001) (Table 2).
TABLE 1
Baseline characteristics of patients (N = 61)
TABLE 2
Hemi-diaphragmatic paresis in patients (N = 61)*
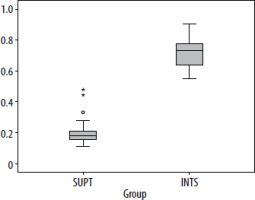
The decrease in diaphragmatic excursion was significantly larger in the IS group than the ST group (P < 0.001) (Figure 2, Table 3). Despite this, none of the patients in either group complained of dyspnoea or had a decrease in peripheral saturation after receiving the block in the postoperative period.
TABLE 3
Characteristics of diaphragmatic function
The baseline pain scores between both groups were not significantly different. The trend of pain scores at various time intervals was also similar (Table 4). The worst pain scores were not significantly different between groups (4 [4, 5] vs. 4 [4, 7]; P = 0.115). Intraoperative top-ups were given in 4 patients in the ST group as compared to 2 in the IS group (apart from hourly top-ups). The amount of opioid consumption in 24 hours postoperatively was similar in both groups. None of the patients complained of nausea/vomiting or pruritis. Patient satisfaction was also similar in both groups: median (IQR) 7.50 (7–8) vs. 8.0 (7.5–8).
TABLE 4
Comparison between pain scores: NRS (N = 61)*
Discussion
This study revealed that IS block was associated with high incidence of diaphragmatic paresis (complete and incomplete) compared with ST block. ST block provides analgesia comparable to the IS block for proximal humerus surgery with preservation of diaphragmatic function. Hence it could be a viable alternative in patients with compromised respiratory functions scheduled for such procedures.
Phrenic nerve palsy is a common phenomenon after IS block. This usually occurs due to the direct spread of local anaesthetic to the nerve, its origin (roots) or its branches (accessory phrenic nerve) [9]. The incidence is nearly 100% when the volume used is high (more than 20 mL). Various modifications in the block technique, drug volume, and concentration have been suggested to reduce this complication [10, 11]. A few authors have even suggested using axillary, suprascapular nerve block for these operations [12]. The incidence of hemidiaphragma-tic paralysis remain high despite these modifications. Healthy individuals might tolerate unilate-ral phrenic nerve palsy well, while patients with compromised lung functions – chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, obese, or patients having one functional lung – might suffer from hypoxia or dyspnoea. None of our patients suffered desaturation/oxygen requirement after the block or after general anaesthesia. This could be due to inclusion of only ASA I/II patients in this study. The distance between the phre-nic nerve and C5 nerve root is barely 2 mm at the cricoid level, where the traditional IS block is given. For every cm the phrenic nerve courses medially downwards into the root of the neck, the distance between the two structures increases by 3 mm [13]. Blocking at the level of the ST (C5, C6 fusion) spares the phrenic nerve as it has already moved away. The primary supply of the shoulder joint includes the suprascapular nerve, axillary nerve and the la-teral pectoral nerve. All these branches originate distally to the fusion of C5 and C6. Hence blocking the ST does not compromise shoulder analgesia. Our study confirmed this as patients in both groups had comparable analgesia and opioid consumption. The ST can also be blocked at the supraclavicular fossa. However, this location spares the suprascapular nerve, as it has already moved away from the trunk at this level. Since the suprascapular nerve is a major supplier of the shoulder region, blocking the ST in the supraclavicular fossa might lead to greater analgesic requirement. There have been a few randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing IS block and ST block in arthroscopic surgery. Kang et al. [8] randomised 80 patients undergoing arthroscopic shoulder surgery to two groups: (1) the C5–C6 nerve roots (IS block group) or (2) the ST (ST block group). Both these groups received a volume of 15 mL. They concluded that ST block provided non-inferior analgesia with lower incidence of hemidiaphragmatic paresis [8]. Around 70% of the patients in the IS group had complete hemidiaphragmatic paresis compared to 5% in the ST group. In our study the incidence of complete paresis was around 38% in the IS block group. None of the patients in the ST group had complete paresis. The decrease in diaphragmatic excursion was larger in the IS group (72%) than the ST group (21%) and the difference between the groups was highly significant.
In another RCT, performed by Kim et al. [7], 126 patients scheduled to undergo shoulder arthroscopy received an ST block or an IS block. The ST group had a significantly lower incidence of hemidiaphragmatic paralysis compared with the IS group (3 of 62 [4.8%] vs. 45 of 63 [71.4%]; P < 0.001). This incidence was similar to that of our study as the amount of drug used was similar in both the studies.
Vijaykumar et al. [5] described three high-risk cases of patients who underwent open shoulder surgery under regional anaesthesia techniques: superior and middle trunk block. Mistry et al. [6] also described the successful surgical management of shaft humerus surgery after administering ST block. They used a much lower dose of 5 mL of local anaesthetic with no paresis of the diaphragm. We used a larger dose of 15 mL of local anaesthetic as described in earlier studies. This might have led to partial paresis of the hemidiaphragm, as observed in a few cases in the ST group.
Limitations
There are a few other limitations of this study. Firstly, the sample size of the study was small. Multi-centric studies with larger sample size might be required to validate our results. The rate of injection of the drug was not standardised, though all the blocks were conducted by two anaesthesiologists experienced in this block technique. We used a dose of 15 mL of local anaesthetic based on previous studies, which might be considered high. Further studies can be planned investigating the efficacy and safety of low-volume ST block. Studies assessing the postoperative diaphragmatic function could also be designed.